Abstract
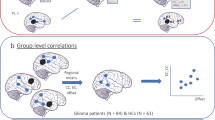
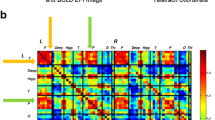
Structural as well as functional connectivity of the cerebral network may be affected by the presence of a brain tumor. Magnetoencephalography (MEG) is one of the methods to study functional connectivity. Within predefined, classical frequency bands, various resting-state network characteristics can be studied. These characteristics enable us to describe a network in terms of synchronization, clustering coefficient, and so-called small worldness. These phenomena appear to be correlated with cognitive functioning and with the occurrence of epileptic seizures in low-grade glioma patients. A better understanding of the relation between the presence of a glioma and the disruption of the neural network will in the future contribute to the planning of surgery and will make it possible to study neural plasticity.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aertsen AM, Gerstein GL, Habib MK, Palm G. Dynamics of neuronal firing correlation: modulation of “effective connectivity”. J Neurophysiol. 1989;61:900–17.
Bullmore E, Sporns O. Complex brain networks: graph theoretical analysis of structural and functional systems. Nature. 2009;10:186–98.
Pallud J, Varlet P, Devaux B, Geha S, Badoual M, Deroulers C, Page P, Dezamis E, Daumas-Duport C, Roux FX. Diffuse low-grade oligodendrogliomas extend beyond MRI-defined abnormalities. Neurology. 2010;74:1724–31.
Yordanova YN, Moritz-Gasser S, Duffau H. Awake surgery for WHO Grade II gliomas within “noneloquent” areas in the left dominant hemisphere: toward a “supratotal” resection. J Neurosurg. 2011;115:232–9.
Martino J, Honma SM, Findlay AM, Guggisberg AG, Owen JP, Kirsch HE, Berger MS, Nagarajan SS. Resting functional connectivity in patients with brain tumors in eloquent areas. Ann Neurol. 2011;69:521–32.
Sporns O. From simple graphs to the connectome: networks in neuroimaging. Neuroimage. 2012;62(2):881–6.
Tijms BM, Seriès P, Wilshaw DJ, Lawrie SM. Similarity-based extraction of individual networks from gray mather MRI scans. Cereb Cortex. 2012;22(7):1530–41.
Hillebrand A, Barnes GR, Bosboom JL, Berendse HW, Stam CJ. Frequency-dependent functional connectivity within resting-state networks: an atlas-based MEG beamformer solution. Neuroimage. 2011;59(4):3909–21.
Hillebrand A, Barnes GR. Practical constraints on estimation of source extent with MEG beamformers. Neuroimage. 2011;54(4):2732–40.
Schreiber A, Hubbe U, Ziyeh S, Hennig J. The influence of glioma and nonglial space-occupying lesion on blood-oxygen-level-dependent contrast enhancement. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000;21:1055–63.
Stippich C, Freitag P, Kassubek J, Sörös P, Kamada K, Kober H, Scheffler K, Hopfengärtner R, Bilecen D, Radü EW, Vieth JB. Motor, somatosensory and auditory cortex localization by fMRI and MEG. Neuroreport. 1998;9:1953–7.
Stam CJ, van Dijk BW. Synchronization likelihood: an unbiased measure of generalized synchronization in multivariate data sets. Physica D. 2002;163:236–41.
Stam CJ, van Cappellen van Walsum AM, Micheloyannis S. Variability of EEG synchronization during a working memory task in healthy subjects. Int J Psychophysiol. 2002;46:53–66.
Bartolomei F, Bosma I, Klein M, Baayen JC, Reijneveld JC, Postma TJ, Heimans JJ, van Dijk BW, de Munck JC, de Jongh A, Cover KS, Stam CJ. How do brain tumors alter functional connectivity? A magnetoencephalography study. Ann Neurol. 2006;59:128–38.
Klein M, Heimans JJ, Aaronson NK, van der Ploeg HM, Grit J, Muller M, Postma TJ, Mooij JJ, Boerman RH, Beute GN, Ossenkoppele GJ, van Imhoff GW, Dekker AW, Jolles J, Slotman BJ, Struikmans H, Taphoorn MJ. Effect of radiotherapy and other treatment-related factors on mid-term to long-term cognitive sequelae in low-grade gliomas: a comparative study. Lancet. 2002;360:1361–8.
Klein M, Engelberts NH, van der Ploeg HM, Kasteleijn-Nolst Trenité DG, Aaronson NK, Taphoorn MJ, Baaijen JH, Vandertop WP, Muller M, Postma TJ, Heimans JJ. Epilepsy in low-grade gliomas: the impact on cognitive function and quality of life. Ann Neurol. 2003;54:514–20.
Bartolomei F, Bosma I, Klein M, Baayen JC, Reijneveld JC, Postma TJ, Heimans JJ, van Dijk BW, de Munck JC, de Jongh A, Cover KS, Stam JC. Disturbed functional connectivity in brain tumour patients: evaluation by graph analysis of synchronization matrices. Clin Neurophys. 2006;117:2039–49.
Stam CJ, Jones BF, Nolte G, Breakspear M, Scheltens P. Small-world networks and functional connectivity in Alzheimer’s disease. Cereb Cortex. 2007;17(1):92–9.
Stam CJ, Reijneveld JC. Graph theoretical analysis of complex networks in the brain. Nonlinear Biomed Phys. 2007;1:3.
Halgren E, Boujon C, Clarke J, Wang C, Chauvel P. Rapid distributed fronto-parieto-occipital processing stages during working memory in humans. Cereb Cortex. 2002;12:710–28.
Watts DJ, Strogatz SH. Collective dynamics of ‘small-world’ networks. Nature. 1998;393:440–2.
Sporns O, Chialvo DR, Kaiser M, Hilgetag CC. Organization, development and function of complex brain networks. Trends Cogn Sci. 2004;8:418–25.
Heimans JJ, Reijneveld JC. Factors affecting the cerebral network in brain tumor patients. J. Neurooncol 2012;108:231–7.
Humphries MD, Gurney K. Network ‘small-world-ness’: a quantitative method for determining canonical network equivalence. PLoS One. 2008;3(4):e0002051.
Douw L, Schoonheim MM, Landi D, van der Meer ML, Geurts JJG, Reijneveld JC, Klein M, Stam CJ. Cognition is related to resting-state small-world network topology: an magnetoencephalographic study. Neuroscience. 2011;175:169–77.
Van den Heuvel MP, Stam CJ, Kahn RS, Hulshoff Pol HE. Efficiency of functional brain networks and intellectual performance. J Neurosci. 2009;29(23):7619–24.
Douw L, Baayen JC, Bosma I, Klein M, Vandertop WP, Heimans JJ, Stam CJ, de Munck JC, Reijneveld JC. Treatment-related changes in functional connectivity in brain tumor patients: a magnetoencephalography study. Exp Neurol. 2008;212(2):285–90.
Stam CJ, Jones BF, Manshanden I, van Cappellen van Walsum AM, Montez T, Verbunt JP, de Munck JC, van Dijk BW, Berendse HW, Scheltens P. Magnetoencephalographic evaluation of resting-state functional connectivity in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimage. 2006;32(3):1335–44.
Stam CJ, Nolte G, Daffartshofer A. Phase lag index: assessment of functional connectivity from multi channel EEG and MEG with diminished bias from common sources. Hum Brain Map. 2007;28(11):1178–93.
Bosma I, Douw L, Bartolomei F, Heimans JJ, van Dijk BW, Postma TJ, Stam CJ, Reijneveld JC, Klein M. Synchronized brain activity and neurocognitive function in patients with low-grade glioma: a magnetoencephalography study. Neuro Oncol. 2008;10:734–44.
Bosma I, Reijneveld JC, Klein M, Douw L, van Dijk BW, Heimans JJ, Stam CJ. Disturbed functional brain networks and neurocognitive function in low-grade glioma patients: a graph theoretical analysis of resting-state MEG. Nonlinear Biomed Phys. 2009;3:9.
Ganslandt O, Fahlbusch R, Nimsky C, Kober H, Möller M, Steinmeier R, Romstöck J, Vieth J. Functional neuronavigation with magnetoencephalography: outcome in 50 patients with lesions around the motor cortex. J Neurosurg. 1999;91:73–9.
Schiffbauer H, Berger MS, Ferrari P, Freudenstein D, Rowley HA, Roberts TPL. Preoperative magnetic source imaging for brain tumor surgery: a quantitative comparison with intraoperative sensory and motor mapping. J Neurosurg. 2002;97:1333–42.
Guggisberg AG, Honma SM, Findlay AM, Dalal SS, Kirsch HE, Berger MS, Nagarajan SS. Mapping functional connectivity in patients with brain lesions. Ann Neurol. 2008;63:193–203.
Duffau H, Thiebaut de Schotten M, Mandonnet E. White matter functional connectivity as an additional landmark for dominant temporal lobectomy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2008;79:492–5.
Duffau H. Surgery of low-grade gliomas: towards a ‘functional neurooncology’. Curr Opin Oncol. 2009;21:543–9.
Englot DJ, Berger MS, Barbaro NM, Chang EF. Predictors of seizure freedom after resection of supratentorial low-grade gliomas. J Neurosurg. 2011;115:240–4.
Kalitzin S, Velis D, Suffczynski P, Para J, da Silva FL. Electrical brain-stimulation paradigm for estimating the seizure onset site and the time to ictal transition in temporal lobe epilepsy. Clin Neurophysiol. 2005;116:718–28.
Ponten SC, Bartolomei F, Stam CJ. Small-world networks and epilepsy: graph theoretical analysis of intracerebrally recorded mesial temporal lobe seizures. Clin Neurophysiol. 2007;118:918–27.
Morgan RJ, Soltesz I. Nonrandom connectivity of the epileptic dentate gyrus predicts a major role for neuronal hubs in seizures. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:6179–84.
Wendling F, Hernandez A, Bellanger JJ, Chauvel P, Bartolomei GF. Interictal to ictal transition in human temporal lobe epilepsy: insights from a computational model of intracerebral EEG. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2005;22:343–56.
Chavez M, Hwang DU, Amann A, Boccaletti S. Synchronizing weighted complex networks. Chaos. 2006;16:015106.
Vlooswijk MCG, Vaessen MJ, Jansen JFA, de Krom MCFTM, Majoie HJM, Hofman PAM, Aldenkamp AP, Backes WH. Loss of network efficiency associated with cognitive decline in chronic epilepsy. Neurology. 2011;77:938–44.
Meador KJ. Networks, cognition, and epilepsy. Neurology. 2011;77:930–1.
Douw L, van Dellen E, de Groot M, Heimans JJ, Klein M, Stam CJ, Reijneveld JC. Epilepsy is related to theta band brain connectivity and network topology in brain tumor patients. BMC Neurosci. 2010;11:103.
Vulliemoz S, Lemieux L, Daunizeau J, Michel CM, Duncan JS. The combination of EEG source imaging and EEG-correlated functional MRI to map epileptic networks. Epilepsia. 2010;51:491–505.
Duffau H. Lessons from brain mapping in surgery for low-grade glioma: insights into associations between tumour and brain plasticity. Lancet Neurol. 2005;4:476–86.
Duffau H, Capelle L, Denvil D, Sichez N, Gatignol P, Lopes M, Mitchell MC, Sichez JP, Van Effenterre R. Functional recovery after surgical resection of low-grade gliomas in eloquent brain: hypothesis of brain compensation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2003;74:901–7.
Stam CJ, Hillebrand A, Wang H, van Mieghem P. Emergence of modular structure in a large-scale brain network with interaction between dynamics and connectivity. Front Comput Neurosci. 2010;24(4): p 133.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer-Verlag London
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Heimans, J.J., Reijneveld, J.C., Stam, C.J. (2013). Magnetoencephalography, Functional Connectivity, and Neural Network Topology in Diffuse Low-Grade Gliomas. In: Duffau, H. (eds) Diffuse Low-Grade Gliomas in Adults. Springer, London. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4471-2213-5_21
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4471-2213-5_21
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, London
Print ISBN: 978-1-4471-2212-8
Online ISBN: 978-1-4471-2213-5
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)