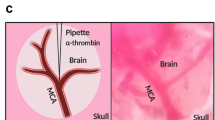
Abstract
Acute ischemic stroke, in which a clot of blood manages to obstruct an artery supplying blood to a part of the brain and leads to brain damage, ranks as the third leading cause of death and is the leading cause of serious long-term disability in the United States. At present, the administration of the clot-dissolving drug, tissue-plasminogen activator, remains the only FDA-approved reperfusion therapy for acute ischemic stroke. Unfortunately, relatively few people (4–14%, depending on the study) access medical care in time or are eligible enough for treatment to benefit [8,10,24]. There is a need to develop additional therapies. The occlusion that causes a stroke is a dynamic one that is prone to spontaneous re-canalization and varying degrees of spontaneous reperfusion. The incorporation of this tendency into a translational stroke model will maximize clinical relevance.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akai F, Maeda M, Hashimoto S, Taneda M, Takagi H. A new animal model of cerebral infarction: magnetic embolization with carbonyl iron particles. Neurosci Lett. 1995;194:139–41.
Alexandrov AV, Grotta JC. Arterial reocclusion in stroke patients treated with intravenous tissue plasminogen activator. Neurology. 2002;59(6):862–7.
Amin-Hanjani S, Stagliano NE, Yamada M, Huang PL, Liao JK, Moskowitz MA. Mevastatin, an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, reduces stroke damage and upregulates endothelial nitric oxide synthase in mice. Stroke. 2001;32(4):980–6.
Asahi M, Huang Z, Thomas S, Yoshimura S, Sumii T, Mori T, Qiu J, Amin-Hanjani S, Huang PL, Liao JK, Lo EH, Moskowitz MA. Protective effects of statins involving both eNOS and tPA in focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2005;25(6):722–9.
Baracchini C, Manara R, Ermani M, Meneghetti G. The quest for early predictors of stroke evolution: can TCD be a guiding light? Stroke. 2000;31(12):2942–7.
Barreto AD, Albright KC, Hallevi H, Grotta JC, Noser EA, Khaja AM, Shaltoni HM, Gonzales NR, Illoh K, Martin-Schild S, Campbell 3rd MS, Weir RU, Savitz SI. Thrombus burden is associated with clinical outcome after intra-arterial therapy for acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2008;39(12):3231–5.
Bederson JB, Pitts LH, Tsuji M, Nishimura MC, Davis RL, Bartkowski H. Rat middle cerebral artery occlusion: evaluation of the model and development of a neurologic examination. Stroke. 1986;17(3):472–6.
California Acute Stroke Pilot Registry (CASPR) Investigators. Prioritizing interventions to improve rates of thrombolysis for ischemic stroke. Neurology. 2005;64(4):654–9.
Caplan LR. Brain embolism, revisited. Neurology. 1993;43(7):1281–7.
Caplan LR. The treatment of acute stroke; still struggling. JAMA. 2004. 292:1183–1185.
Castillo J, Leira R, Garcia MM, Serena J, Blanco M, Davalos A. Blood pressure decrease during the acute phase of ischemic stroke is associated with brain injury and poor stroke outcome. Stroke. 2004;35(2):520–6.
Cimino M, Gelosa P, Gianella A, Nobili E, Tremoli E, Sironi L. Statins: multiple mechanisms of action in the ischemic brain. Neuroscientist. 2007;13(3):208–13.
Di Napoli P, Taccardi AA, Oliver M, De Caterina R. Statins and stroke: evidence for cholesterol-independent effects. Eur Heart J. 2002;23(24):1908–21.
Dietrich WD, Prado R, Halley M, Watson BD. Microvascular and neuronal consequences of common carotid artery thrombosis and platelet embolization in rats. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1993;52:351–60.
Durukan A, Strbian D, Tatlisumak T. Rodent models of ischemic stroke: a useful tool for stroke drug development. Curr Pharm Des. 2008;14(4):359–70.
Essig M, Nguyen G, Prie D, Escoubet B, Sraer J-D, Friedlander G. 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitors increase fibrinolytic activity in rat aortic endothelial cells. Circ Res. 1998;83:683–9.
Fisher M, Feuerstein G, Howells DW, Hurn PD, Kent TA, Savitz SI, Lo EH, STAIR Group. Update of the stroke therapy academic industry roundtable preclinical recommendations. Stroke. 2009;40(6):2244–50.
Futrell N, Millikan C, Watson BD, Dietrich WD, Ginsberg MD. Embolic stroke from a carotid arterial source in the rat: pathology and clinical implications. Neurology. 1989;39:1050–6.
Gadda D, Vannucchi L, Niccolai F, Neri AT, Carmignani L, Pacini P. Multidetector computed tomography of the head in acute stroke: predictive value of different patterns of the dense artery sign revealed by maximum intensity projection reformations for location and extent of the infarcted area. Eur Radiol. 2005;15(12):2387–95.
Guarini S. A highly reproducible model of arterial thrombosis in rats. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 1996;35(2):101–5.
Guluma KZ, Lapchak PA. Comparison of the post-embolization effects of tissue-plasminogen activator and simvastatin on neurological outcome in a clinically relevant rat model of acute ischemic stroke. Brain Res. 2010;1354:206–16.
Kammersgaard LP, Jørgensen HS, Rungby JA, Reith J, Nakayama H, Weber UJ, Houth J, Olsen TS. Admission body temperature predicts long-term mortality after acute stroke: the copenhagen stroke study. Stroke. 2002;33(7):1759–62.
Kassem-Moussa H, Graffagnino C. Nonocclusion and spontaneous recanalization rates in acute ischemic stroke: a review of cerebral angiography studies. Arch Neurol. 2002;59(12):1870–3.
Katzan IL, Hammer MD, Hixson ED, Furlan AJ, Abou-Chebl A, Nadzam DM. Cleveland Clinic Health System Stroke Quality Improvement Team. Utilization of intravenous tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. Arch Neurol. 2004;61(3):346–50.
Kawamata T, Dietrich WD, Schallert T, Gotts JE, Cocke RR, Benowitz LI, Finklestein SP. Intracisternal basic fibroblast growth factor enhances functional recovery and up-regulates the expression of a molecular marker of neuronal sprouting following focal cerebral infarction. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 1997;94:8179–84.
Kestenbaum B. Reevaluating erythropoiesis-stimulating agents. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(18):1742 (author reply 1743–4).
Kharitonova T, Thorén M, Ahmed N, Wardlaw JM, von Kummer R, Thomassen L, Wahlgren N, SITS investigators. Disappearing hyperdense middle cerebral artery sign in ischaemic stroke patients treated with intravenous thrombolysis: clinical course and prognostic significance. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2009;80(3):273–8.
Kimura K, Minematsu K, Yasaka M, Wada K, Yamaguchi T. The duration of symptoms in transient ischemic attack. Neurology. 1999;52:976–80.
Kilic E, Hermann DM, Hossman K-A. A reproducible model of thromboembolic stroke in mice. Neuroreport. 1998;9:2967–70.
Koudstaal PJ, van Gijn J, Lodder J, Frenken WG, Vermeulen M, Franke CL, Hijdra A, Bulens C. Transient ischemic attacks with and without a relevant infarct on computed tomographic scans cannot be distinguished clinically. Dutch Transient Ischemic Attack Study Group. Arch Neurol. 1991;48:916–20.
Laufs U, Gertz K, Huang P, Nickenig G, Böhm M, Dirnagl U, Endres M. Atorvastatin upregulates type III nitric oxide synthase in thrombocytes, decreases platelet activation, and protects from cerebral ischemia in normocholesterolemic mice. Stroke. 2000;31(10):2442–9.
Leonardi-Bee J, Bath PM, Phillips SJ, Sandercock PA, IST Collaborative Group. Blood pressure and clinical outcomes in the international stroke trial. Stroke. 2002;33(5):1315–20.
Liebeskind DS, Sanossian N, Yong WH, Starkman S, Tsang MP, Moya AL, Zheng DD, Abolian AM, Kim D, Ali LK, Shah SH, Towfighi A, Ovbiagele B, Kidwell CS, Tateshima S, Jahan R, Duckwiler GR, Viñuela F, Salamon N, Villablanca JP, Vinters HV, Marder VJ, Saver JL. CT and MRI Early Vessel Signs Reflect Clot Composition in Acute Stroke. Stroke. 2011;42(5):1237–43.
Lo EH. Experimental models, neurovascular mechanisms and translational issues in stroke research. Br J Pharmacol. 2008;153 Suppl 1:S396–405.
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, Cummins R. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 1989;20(1):84–91.
Mandava P, Kent TA. Reversal of dense signs predicts recovery in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2005;36(11):2490–2.
Marder VJ, Chute DJ, Starkman S, Abolian AM, Kidwell C, Liebeskind D, Ovbiagele B, Vinuela F, Duckwiler G, Jahan R, Vespa PM, Selco S, Rajajee V, Kim D, Sanossian N, Saver JL. Analysis of thrombi retrieved from cerebral arteries of patients with acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2006;37(8):2086–93.
Markgraf CG, Kraydieh S, Prado R, Watson BD, Dietrich WD, Ginsberg MD. Comparative histopathologic consequences of photothrombotic occlusion of the distal middle cerebral artery in Sprague-Dawley and Wistar rats. Stroke. 1993;24:286–93.
Matsuno H, Uematsu T, Umemura K, Takiguchi Y, Asai Y, Muranaka Y, Nakashima M. A simple and reproducible cerebral thrombosis model in rats induced by a photochemical reaction and the effect of a plasminogen-plasminogen activator chimera in this model. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 1993;29:165–73.
Menzies SA, Hoff JT, Betz AL. Middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats: a neurological and pathological evaluation of a reproducible model. Neurosurgery. 1992;31(1):100–6; discussion 106–7.
Mizuno K, Satomura K, Miyamoto A, Arakawa K, Shibuya T, Arai T, Kurita A, Nakamura H, Ambrose JA. Angioscopic evaluation of coronary-artery thrombi in acute coronary syndromes. N Engl J Med. 1992;326(5):287–91.
Mizuno K, Arakawa K, Isojima K, Shibuya T, Satomura K, Kurita A, Nakamura H, Arai T, Kikuchi M. Angioscopy, coronary thrombi and acute coronary syndromes. Biomed Pharmacother. 1993;47(5):187–91.
Molina CA, Montaner J, Abilleira S, Ibarra B, Romero F, Arenillas JF, Alvarez-Sabín J. Timing of spontaneous recanalization and risk of hemorrhagic transformation in acute cardioembolic stroke. Stroke. 2001;32(5):1079–84.
Nedelmann M, Wilhelm-Schwenkmezger T, Alessandri B, Heimann A, Schneider F, Eicke BM, Dieterich M, Kempski O. Cerebral embolic ischemia in rats: correlation of stroke severity and functional deficit as important outcome parameter. Brain Res. 2007;1130(1):188–96.
Niessen F, Hilger T, Hoehn M, Hossmann KA. Differences in clot preparation determine outcome of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator treatment in experimental thromboembolic stroke. Stroke. 2003;34(8):2019–24.
NINDS rt-PA Study Group. Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 1995;333:1581–7.
O’Collins VE, Macleod MR, Donnan GA, Horky LL, van der Worp BH, Howells DW. 1,026 experimental treatments in acute stroke. Ann Neurol. 2006;59(3):467–77.
Okumura K, Ohya Y, Maehara A, Wakugami K, Iseki K, Takishita S. Effects of blood pressure levels on case fatality after acute stroke. J Hypertens. 2005;23:1217–23.
Overgaard K, Sereghy T, Boysen G, Pedersen H, Høyer S, Diemer NH. A rat model of reproducible cerebral infarction using thrombotic blood clot emboli. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1992;12(3):484–90.
Puetz V, Dzialowski I, Hill MD, Subramaniam S, Sylaja PN, Krol A, O’Reilly C, Hudon ME, Hu WY, Coutts SB, Barber PA, Watson T, Roy J, Demchuk AM, Calgary CTA Study Group. Intracranial thrombus extent predicts clinical outcome, final infarct size and hemorrhagic transformation in ischemic stroke: the clot burden score. Int J Stroke. 2008;3(4):230–6.
Reith J, Jørgensen HS, Pedersen PM, Nakayama H, Raaschou HO, Jeppesen LL, Olsen TS. Body temperature in acute stroke: relation to stroke severity, infarct size, mortality, and outcome. Lancet. 1996;347(8999):422–5.
Rha JH, Saver JL. The impact of recanalization on ischemic stroke outcome: a meta-analysis. Stroke. 2007;38(3):967–73.
Sironi L, Cimino M, Guerrini U, Calvio AM, Lodetti B, Asdente M, Balduini W, Paoletti R, Tremoli E. Treatment with statins after induction of focal ischemia in rats reduces the extent of brain damage. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2003;23(2):322–7.
Stolz E, Cioli F, Allendoerfer J, Gerriets T, Del Sette M, Kaps M. Can early neurosonology predict outcome in acute stroke? A metaanalysis of prognostic clinical effect sizes related to the vascular status. Stroke. 2008;39(12):3255–61.
Tamura A, Graham DI, McCulloch J, Teasdale GM. Focal cerebral ischaemia in the rat: description of technique and early neuropathological consequences following middle cerebral artery occlusion. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1981;1:53–60.
Toni D, Fiorelli M, Zanette EM, Sacchetti ML, Salerno A, Argentino C, Solaro M, Fieschi C. Early spontaneous improvement and deterioration of ischemic stroke patients. A serial study with transcranial Doppler ultrasonography. Stroke. 1998;29(6):1144–8.
Vlaar PJ, Svilaas T, Vogelzang M, Diercks GF, de Smet BJ, van den Heuvel AF, Anthonio RL, Jessurun GA, Tan E, Suurmeijer AJ, Zijlstra F. A comparison of 2 thrombus aspiration devices with histopathological analysis of retrieved material in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2008;1(3):258–64.
Vemmos KN, Tsivgoulis G, Spengos K, Zakopoulos N, Synetos A, Manios E, Konstantopoulou P, Mavrikakais M. U-shaped relationship between mortality and admission blood pressure in patients with acute stroke. J Intern Med. 2004;255:257–65.
Wang CX, Todd KG, Yang Y, Gordon T, Shuaib A. Patency of cerebral microvessels after focal embolic stroke in the rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2001;21:413–21.
Wunderlich MT, Goertler M, Postert T, Schmitt E, Seidel G, Gahn G, Samii C, Stolz E, Duplex Sonography in Acute Stroke (DIAS) Study Group. Competence network stroke. Recanalization after intravenous thrombolysis: does a recanalization time window exist? Neurology. 2007;68(17):1364–8.
Yang Y, Tao Yang T, Li Q, Wang CX, Shuaib A. A new reproducible focal cerebral ischemia model by introduction of polyvinylsiloxane into the middle cerebral artery: a comparison study. J Neurosci Meth. 2002;118:199–206.
Yong M, Diener HC, Kaste M, Mau J. Characteristics of blood pressure profiles as predictors of long-term outcome after acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2005;36(12):2619–25.
Zaidat OO, Suarez JI, Sunshine JL, Tarr RW, Alexander MJ, Smith TP, Enterline DS, Selman WR, Landis DM. Thrombolytic therapy of acute ischemic stroke: correlation of angiographic recanalization with clinical outcome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005;26(4):880–4.
Zausinger S, Hungerhuber E, Baethmann A, Reulen H, Schmid-Elsaesser R. Neurological impairment in rats after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion: a comparative study under various treatment paradigms. Brain Res. 2000;863(1–2):94–105.
Zhang RL, Chopp M, Zhang ZG, Jiang Q, Ewing JR. A rat model of focal embolic cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 1997;766:83–92.
Zhang Z, Zhang RL, Jiang Q, Raman SBK, Cantwell L, Chopp M. A new rat model of thrombotic focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1997;17:123–35.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Guluma, K. (2012). Clinical Relevance in a Translational Rodent Model of Acute Ischemic Stroke: Incorporating the Biological Variability of Spontaneous Recanalization. In: Lapchak, P., Zhang, J. (eds) Translational Stroke Research. Springer Series in Translational Stroke Research. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-9530-8_26
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-9530-8_26
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4419-9529-2
Online ISBN: 978-1-4419-9530-8
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)