Abstract
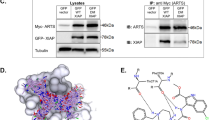
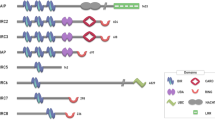
X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) is a member of the family of inhibitor of apoptosis proteins and part of the programmed cell death (apoptosis) pathway. Also known as BIRC4 (baculovirus IAP repeat-containing 4), XIAP resides in the cytoplasm. It acts as an inhibitor of caspases by directly binding to and inhibiting caspases 3, 7, and 9 and thus may inhibit both the intrinsic and extrinsic apoptosis pathways. Protein and RNA levels of XIAP can be measured but there are currently no FDA-approved tests for the measurement of XIAP in either tumor tissue or blood. XIAP is overexpressed in numerous malignancies. XIAP is currently being investigated as a predictive and prognostic tool in cancer and as a marker of resistance to cancer therapies. Restoration of apoptosis is an important priority for cancer drug development, thus targeting of XIAP is of critical significance. Second mitochondrial-derived activator of caspases (SMAC)-mimetics such as LCL-161 and antisense oligonucleotides such as AEG35156 inhibit XIAP and are being investigated in therapeutic clinical trials.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dorsey FC, Steeves MA, Cleveland JL. Apoptosis, autophagy, and necrosis. In: Mendesohn J, Howley PM, Israel MA, Gray JW, Thompson CB, editors. The molecular basis of cancer. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier; 2008. p. 207–10.
Emanuel PO, Phelps RG, Mudgil A, et al. Immunohistochemical detection of XIAP in melanoma. J Cutan Pathol. 2008;35(3):292–7.
Green DR. Means to an end: apoptosis and other cell death mechanisms. New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 2011. p. 5–28.
Kang HG, Lee SJ, Chae MH, Lee WK, Cha SK, Kim CH, Kam S, Park RW, Kim IS, Kim DS, Kim YC, Jung TH, Park JY. Identification of polymorphisms in the XIAP gene and analysis of association with lung cancer risk in a Korean population. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2008;180(1):6–13.
Kashkar H. X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis: a chemoresistance factor or a hollow promise. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16(18):4496–502.
LaCasse EC. Pulling the plug on a cancer cell by eliminating XIAP with AEG35156. Cancer Lett. 2013; 332(2):215–24. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2012.06.015. Epub 2012 Jul 7.
Li J, Li ZN, Bao QL, Ge LP, Li XQ, Chen P. Evaluation of pleural fluid survivin and XIAP for the diagnosis of malignant pleural effusion. Tumour Biol. 2012;33(5):1803–10.
Lodish H, Berk A, Kaiser CA, Krieger M, Bretscher A, Ploegh H, Amon A, Scott MP. Chapter 21: Molecular cell biology. 7th edn. In: Stem cells, asymmetry, and cell death. p. 1006–16. W. H Freeman and Company, New York/Houndsmills, Basingstoke.
Mizutani Y, Nakanishi H, Li YN, Matsubara H, Yamamoto K, Sato N, et al. Overexpression of XIAP expression in renal cell carcinoma predicts a worse prognosis. Int J Oncol. 2007;30(4):919–25.
Tamm I, Richter S, Oltersdorf D, et al. High expression levels of x-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein and survivin correlate with poor overall survival in childhood de novo acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10(11):3737–44.
Wiki.medipedia.com/x_linkied_Inhibitor_of_apoptosis_(XIAP). Accessed 3 Mar 2013.
Wu M, Kafanas A, Gan L, Kohtz DS, Zhang L, Genden E, et al. Feasibility of immunocytochemical detection of tumor markers (XIAP, phosphohistone H1 and p63) in FNA cellblock samples from head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Diagn Cytopathol. 2008;36(11):797–800.
www.clinicaltrials.gov. Accessed 4 Mar 2013.
Xiang G, Wen X, Wang H, Chen K, Liu H. Expression of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein in human colorectal cancer and its correlation with prognosis. J Surg Oncol. 2009;100:708–12.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer Science+Business Media, New York (outside the USA)
About this entry
Cite this entry
Noonan, A. (2017). X-Linked IAP. In: Marshall, J. (eds) Cancer Therapeutic Targets. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-0717-2_68
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-0717-2_68
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4419-0716-5
Online ISBN: 978-1-4419-0717-2
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesReference Module Biomedical and Life Sciences