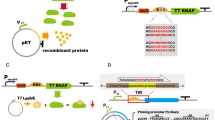
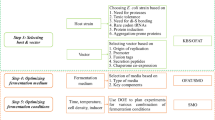
Abstract
Escherichia coli remains a traditional and widely used host organism for recombinant protein production. Its well-studied genome, availability of vectors and strains, cheap and relatively straight-forward cultivation methods paired with reported high protein yields are reasons why E. coli is often the first-choice host expression system for recombinant protein production. The chapter enclosed here details protocols and design strategies in strain selection and methods on how to parallelize expression conditions to optimize for soluble target protein expression in E. coli. The methods described have been validated in a protein production research facility.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fernandez FJ, Vega MC (2016) Choose a suitable expression host: a survey of available protein production platforms. Adv Exp Med Biol 896:15–24
Sezonov G, Joseleau-Petit D, D'Ari R (2007) Escherichia coli physiology in Luria-Bertani broth. J Bacteriol 189(23):8746–8749
Soini J, Ukkonen K, Neubauer P (2008) High cell density media for Escherichia coli are generally designed for aerobic cultivations—consequences for large-scale bioprocesses and shake flask cultures. Microb Cell Factories 7:26
Choi JH, Keum KC, Lee SY (2006) Production of recombinant proteins by high cell density culture of Escherichia coli. Chem Eng Sci 61(3):876–885
Yang Z, Zhang L, Zhang Y, Zhang T, Feng Y, Lu X, Lan W, Wang J, Wu H, Cao C, Wang X (2011) Highly efficient production of soluble proteins from insoluble inclusion bodies by a two-step-denaturing and refolding method. PLoS One 6(7):e22981
Singh A, Upadhyay V, Upadhyay AK, Singh SM, Panda AK (2015) Protein recovery from inclusion bodies of Escherichia coli using mild solubilization process. Microb Cell Factories 14:41
Singh SM, Panda AK (2005) Solubilization and refolding of bacterial inclusion body proteins. J Biosci Bioeng 99(4):303–310
Honda J, Andou H, Mannen T, Sugimoto S (2000) Direct refolding of recombinant human growth differentiation factor 5 for large-scale production process. J Biosci Bioeng 89(6):582–589
Sakono M, Goto M, Furusaki S (2000) Refolding of cytochrome c using reversed micelles. J Biosci Bioeng 89(5):458–462
Paraskevopoulou V, Falcone FH (2018) Polyionic tags as enhancers of protein solubility in recombinant protein expression. Microorganisms 6(2):47
Costa S, Almeida A, Castro A, Domingues L (2014) Fusion tags for protein solubility, purification and immunogenicity in Escherichia coli: the novel Fh8 system. Front Microbiol 5:63
Zhou P, Wagner G (2010) Overcoming the solubility limit with solubility-enhancement tags: successful applications in biomolecular NMR studies. J Biomol NMR 46(1):23–31
Quax TE, Claassens NJ, Soll D, van der Oost J (2015) Codon bias as a means to fine-tune gene expression. Mol Cell 59(2):149–161
Gustafsson C, Govindarajan S, Minshull J (2004) Codon bias and heterologous protein expression. Trends Biotechnol 22(7):346–353
Studier FW, Moffatt BA (1986) Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol 189(1):113–130
Miroux B, Walker JE (1996) Over-production of proteins in Escherichia coli: mutant hosts that allow synthesis of some membrane proteins and globular proteins at high levels. J Mol Biol 260(3):289–298
Zhang X, Studier FW (1997) Mechanism of inhibition of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase by T7 lysozyme. J Mol Biol 269(1):10–27
Grunberg-Manago M (1999) Messenger RNA stability and its role in control of gene expression in bacteria and phages. Annu Rev Genet 33:193–227
Kido M, Yamanaka K, Mitani T, Niki H, Ogura T, Hiraga S (1996) RNase E polypeptides lacking a carboxyl-terminal half suppress a mukB mutation in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 178(13):3917–3925
Lopez PJ, Marchand I, Joyce SA, Dreyfus M (1999) The C-terminal half of RNase E, which organizes the Escherichia coli degradosome, participates in mRNA degradation but not rRNA processing in vivo. Mol Microbiol 33(1):188–199
Baca AM, Hol WG (2000) Overcoming codon bias: a method for high-level overexpression of plasmodium and other AT-rich parasite genes in Escherichia coli. Int J Parasitol 30(2):113–118
Sorensen HP, Sperling-Petersen HU, Mortensen KK (2003) Production of recombinant thermostable proteins expressed in Escherichia coli: completion of protein synthesis is the bottleneck. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 786(1–2):207–214
Ferrer M, Chernikova TN, Yakimov MM, Golyshin PN, Timmis KN (2003) Chaperonins govern growth of Escherichia coli at low temperatures. Nat Biotechnol 21(11):1266–1267
Bessette PH, Aslund F, Beckwith J, Georgiou G (1999) Efficient folding of proteins with multiple disulfide bonds in the Escherichia coli cytoplasm. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96(24):13703–13708
Prinz WA, Aslund F, Holmgren A, Beckwith J (1997) The role of the thioredoxin and glutaredoxin pathways in reducing protein disulfide bonds in the Escherichia coli cytoplasm. J Biol Chem 272(25):15661–15667
Lobstein J, Emrich CA, Jeans C, Faulkner M, Riggs P, Berkmen M (2012) SHuffle, a novel Escherichia coli protein expression strain capable of correctly folding disulfide bonded proteins in its cytoplasm. Microb Cell Factories 11:56
Wagner S, Klepsch MM, Schlegel S, Appel A, Draheim R, Tarry M, Hogbom M, van Wijk KJ, Slotboom DJ, Persson JO, de Gier JW (2008) Tuning Escherichia coli for membrane protein overexpression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(38):14371–14376
Schlegel S, Lofblom J, Lee C, Hjelm A, Klepsch M, Strous M, Drew D, Slotboom DJ, de Gier JW (2012) Optimizing membrane protein overexpression in the Escherichia coli strain Lemo21(DE3). J Mol Biol 423(4):648–659
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Tang, S.R., Somasundaram, B., Lua, L.H.L. (2022). Protein Expression Optimization Strategies in E. coli: A Tailored Approach in Strain Selection and Parallelizing Expression Conditions. In: Garcia Fruitós, E., Arís Giralt, A. (eds) Insoluble Proteins. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2406. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1859-2_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1859-2_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-1858-5
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-1859-2
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols