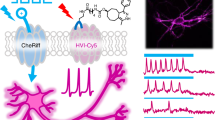
Abstract
Fluorescence-based biosensors for membrane voltage allow dynamic optical recording of neuronal activity. Interestingly, the development of genetically encoded voltage indicators constitutes a good alternative to classical voltage-sensitive dyes, since they allow overcoming some of the inherent problems (e.g., optical noise, etc.) associated to organic compounds. Here, we show the use of a genetically encoded voltage-sensitive fluorescent protein (VSFP), namely the VSFP2.32. This biosensor contains a mCerulean and Citrine tandem, which can engage in a constitutive fluorescent resonance energy transfer (FRET) process. We first expressed VSFP2.32 in hippocampal cultured neurons. And, subsequently, we monitored membrane voltage alterations in single neurons by recording (in a real-time mode) VSFP2.32 conformation-mediated FRET changes.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mutoh H, Knöpfel T (2013) Probing neuronal activities with genetically encoded optical indicators: from a historical to a forward-looking perspective. Pflügers Arch 465:361–371. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-012-1202-z
Lin MZ, Schnitzer MJ (2016) Genetically encoded indicators of neuronal activity. Nat Neurosci 19:1142–1153. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4359
Shen Y, Nasu Y, Shkolnikov I et al (2020) Engineering genetically encoded fluorescent indicators for imaging of neuronal activity: progress and prospects. Neurosci Res 152:3–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neures.2020.01.011
Borisov SM, Wolfbeis OS (2008) Optical biosensors. Chem Rev 108:423–461. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr068105t
Grinvald A, Hildesheim R (2004) VSDI: a new era in functional imaging of cortical dynamics. Nat Rev Neurosci 5:874–885. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn1536
Knöpfel T, Díez-García J, Akemann W (2006) Optical probing of neuronal circuit dynamics: genetically encoded versus classical fluorescent sensors. Trends Neurosci 29:160–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2006.01.004
Day RN, Davidson MW (2009) The fluorescent protein palette: tools for cellular imaging. Chem Soc Rev 38:2887–2921. https://doi.org/10.1039/b901966a
Knöpfel T (2012) Genetically encoded optical indicators for the analysis of neuronal circuits. Nat Rev Neurosci 13:687–700. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3293
Mutoh H, Akemann W, Knöpfel T (2012) Genetically engineered fluorescent voltage reporters. ACS Chem Neurosci 3:585–592. https://doi.org/10.1021/cn300041b
Murata Y, Iwasaki H, Sasaki M et al (2005) Phosphoinositide phosphatase activity coupled to an intrinsic voltage sensor. Nature 435:1239–1243. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03650
Perron A, Akemann W, Mutoh H, Knöpfel T (2012) Genetically encoded probes for optical imaging of brain electrical activity. Prog Brain Res 196:63–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-59426-6.00004-5
Lundby A, Mutoh H, Dimitrov D et al (2008) Engineering of a genetically encodable fluorescent voltage sensor exploiting fast Ci-VSP voltage-sensing movements. PLoS One 3:e2514. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0002514
Akemann W, Mutoh H, Perron A et al (2010) Imaging brain electric signals with genetically targeted voltage-sensitive fluorescent proteins. Nat Methods 7:643–649. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1479
Clark JD, Gebhart GF, Gonder JC et al (1997) Special report: the 1996 guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. ILAR J 38:41–48
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades–Agencia Estatal de Investigación-FEDER-UE (SAF2017-87349-R MICIU/AEI/FEDER/UE) and Generalitat de Catalunya (2017SGR1604).We thank Centres de Recerca de Catalunya (CERCA) Programme/Generalitat de Catalunya for IDIBELL institutional support. We thank Esther Castaño and Benjamín Torrejón from the CCiT-Bellvitge Campus of the University of Barcelona.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Fernández-Dueñas, V., Morató, X., Knöpfel, T., Ciruela, F. (2021). Dynamic Recording of Membrane Potential from Hippocampal Neurons by Using a Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer-Based Voltage Biosensor. In: Lujan, R., Ciruela, F. (eds) Receptor and Ion Channel Detection in the Brain. Neuromethods, vol 169. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1522-5_31
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1522-5_31
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-1521-8
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-1522-5
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols