Abstract
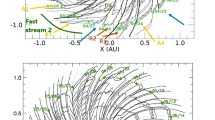
Atmospheric photoelectrons have been observed well above the ionosphere of Mars by the ASPERA-3 ELS instrument on Mars Express. To systematically interpret these observations, field lines from two global MHD simulations were analyzed for Connectivity to the dayside ionosphere (allowing photoelectron escape). It is found that there is a hollow cylinder behind the planet from 1–2 R M away from the Mars-Sun line that has a high probability of containing magnetic field lines with Connectivity to the dayside ionosphere. These results are in complete agreement with the ELS statistics. It is concluded that the high-altitude photoelectrons are the result of direct magnetic Connectivity to the dayside at the moment of the measurement, and no extra trapping or bouncing mechanisms are needed to explain the data.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acuña, M. H., et al.: 1998, Science 279, 1676.
Arkani-Hamed, J.: 2001, J. Geophys. Res. 106, 23,197.
Arkani-Hamed, J.: 2002, J. Geophys. Res. 107(E10), 5083, doi: 10.1029/2001JE001835.
Barabash, S., et al.: 2004, in Wilson, A. (ed.), Mars Express: The Scientific Payload, European Space Agency Publications Division, European Space Research and Technology Centre, Noordwijk, The Netherlands, SP-1240, p. 121.
Chicarro, A., Martin, P., and Trautner, R.: 2004, in Wilson, A. (ed.), Mars Express: The Scientific Payload, European Space Agency Publications Division, European Space Research and Technology Centre, Noordwijk, The Netherlands, SP-1240, p. 3.
Connerney, J. E. P, Acuña, M. H., Wasilewski, P. J., Kleteschka, G., Ness, N. F., Rème, H., et al.: 2001, Geophys. Res. Lett. 28, 4015.
Crider, D. H., et al.: 2002, Geophys. Res. Lett. 29(8), 1170, doi: 10.1029/2001GL013860.
Frahm, R. A., et al.: 2006, Icarus, in press.
Frahm. R., et al.: Space Sci. Rev., this issue, doi: 10.1007/s11214-006-9119-5.
Hanson, W. B., Sanatani, S., and Zuccaro, D. R.: 1977, J. Geophys. Res. 82, 4351.
Khazanov, G. V., and Liemohn, M. W.: 1995, J. Geophys. Res. 100, 9669.
Khazanov, G. V., Liemohn, M. W., Kozyra, J. U., and Moore, T. E.: 1998, J. Geophys. Res. 103, 23, 485.
Khazanov, G. V., Liemohn, M. W., Kozyra, J. U., and Gallagher, D. L.: 2000, J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Physics 62, 947.
Lejeune, J., and Wörmser, F.: 1992, J. Geophys. Res. 97, 159.
Liemohn, M. W., et al.: 2006, Icarus 182, 383.
Luhmann, J. G., and Brace, L. H.: 1991, Rev. Geophys. 29, 121.
Ma, Y., Nagy, A. F., Hansen, K. C., DeZeeuw, D. L., and Gombosi, T. L: 2002, J. Geophys. Res. 107(A10), 1282, doi: 10.1029/2002JA009293.
Ma, Y., Nagy, A. F., Sokolov, I. V., and Hansen, K. C.: 2004, J. Geophys. Res. 109, A07211, doi: 10.1029/2003JA010367.
Mitchell, D. L., et al.: 2001, J. Geophys. Res. 106(E10), 23,419.
Nagy, A. F., and Banks, P. M.: 1970, J. Geophys. Res. 75, 6260.
Powell, K. G., Roe, P. L., Linde, T. J., Gombosi, T. I., and De Zeeuw, D. L.: 1999, J. Comp. Phys. 153, 284.
Schunk, R. M., and Nagy, A. F.: 2000, Ionospheres, Cambridge University Press, New York.
Swartz, W. E., Bailey, G. J., and Moffett, R. J.: 1975, Planet. Space Sci. 23, 589.
Vennerstrom, S., Olsen, N., Purucker, M., Acuha, M. H., and Cain, J. C.: 2003, Geophys. Res. Lett. 30(7), 1369, doi: 10.1029/2003GL016883.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2007 Springer
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Liemohn, M.W. et al. (2007). Mars Global MHD Predictions of Magnetic Connectivity between the Dayside ionosphere and the Magnetospheric Flanks. In: Russell, C.T. (eds) The Mars Plasma Environment. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-70943-7_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-70943-7_4
Received:
Accepted:
Publisher Name: Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-0-387-70941-3
Online ISBN: 978-0-387-70943-7
eBook Packages: Physics and AstronomyPhysics and Astronomy (R0)