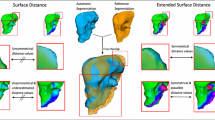
This chapter describes a new approach that integrates the T-Surfaces model and isosurface generation methods in a general framework for segmentation and surface reconstruction in 3D medical images. Besides, the T-Surfaces model is applied for offset generation in the context of geometry extraction.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
10 References
Kass M, Witkin A, Terzopoulos D. 1988. Snakes: active contour models. Int J Comput Vision 1(4):321-331.
McInerney T, Terzopoulos D. 1996. Deformable models in medical image analysis: a survey. Med Image Anal 1(2): 91-108.
Cohen LD, Cohen I. 1993. Finite-element methods for active contour models and balloons for 2D and 3D images. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Machine Intell 15(11): 1131-1147.
ter Haar Romery BM, Niessen WJ, Viergever MA. 1998. Geodesic deformable models for medical image analysis. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 17(4):634-641.
Sapiro G. 1997. Color snakes. Comput Vision Image Understand 68(2):247-253.
Black A, Yuille A, eds. 1993. Active vision. Cambridge: MIT Press.
Caselles V, Kimmel R, Sapiro G. 1997. Geodesic active contours. Int J Comput Vision 22(1):61-79.
Malladi R, Sethian JA, Vemuri BC. 1995. Shape modeling with front propagation: a level set approach. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Machine Intell 17(2):158-175.
McInerney TJ. 1997. Topologically adaptable deformable models for medical image analysis. PhD dissertation. University of Toronto.
McInerney T, Terzopoulos D. 1999. Topology adaptive deformable surfaces for medical image volume segmentation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 18(10):840-850.
McInerney T, Terzopoulos D. 1995. Topologically adaptable snakes. In Proceedings of the fifth international conference on computer vision (ICCV’95), Cambridge, MA, USA, pp. 840-845.
Sutton P, Hansen C. 2000. Accelerated isosurface extraction in time-varying fields. IEEE Trans Visualiz Comput Graphics 6(2):98-107.
Allgower EL, Georg K. 1990. Numerical continuation methods: an introduction. Berlin:Springer-Verlag.
Lorensen WE, Cline HE. 1987. Marching cubes: a high-resolution 3D surface construction algorithm. Comput Graphics 21(4):163-169.
Strauss E, Jimenez W, Giraldi G, Silva R, Oliveira A. 2002. A surface extraction approach based on multi-resolution methods and T-surfaces framework. Technical report, National Laboratory for Scientific Computing, ftp://ftp.lncc.br/pub/report/rep02/rep1002.ps.Z.
Giraldi G, Strauss E, Apolinario A, Oliveira AF. 2001. An initialization method for deformable models. In Fifth world multiconference on systemics, cybernetics and informatics (SCI).
Strauss E, Jimenez W, Giraldi GA, Silva R, Oliveira AF. 2002. A semiautomatic surface reconstruction framework based on T-surfaces and isosurface extraction methods. In Proceedings of the international symposium on computer graphics, image processing and vision (SIBGRAPI’2001), Florian ópolis, Brazil, October 15-18.
Giraldi GA, Strauss E, Oliveira AF. 2003. Dual-T-snakes model for medical imaging segmentation. Pattern Recognit Lett 24(7):993-1003.
Xu C, Pham D, Rettmann M, Yu D, Prince J. 1999. Reconstruction of the human cerebral cortex from magnetic resonance images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 18(6):467-480.
Giraldi GA, Strauss E, Oliveira AF. 2000. An initialization method for active contour models. In Proceedings of the 2000 international conference on imaging science, systems, and technology (CISST’2000).
Pohle R, Behlau T, Toennies KD. 2003. Segmentation of 3D medical image data sets with a combination of region based initial segmentation and active surfaces. In Progress in biomedical optics and imaging. Proc SPIE Med Imaging 5203:1225-1231.
Cohen LD. 1991. On active contour models and balloons. Comput Vision Graphics Image Process:Image Understand 53(2):211-218.
Falc ão AX, da Cunha BS, Lotufo RA. 2001. Design of connected operators using the image foresting transform. Proc SPIE Med Imaging 4322:468-479.
Jolion JM, Montanvert A. 1992. The adaptive pyramid: a framework for 2D image analysis. Comput Vision Graphics Image Process: Image Understand 55(3):339-348.
Xu C, Prince J. 1998. Snakes, shapes, and gradient vector flow. IEEE Trans Image Process 7(3):359-369.
Giraldi GA, Oliveira AF. 1999. Convexity analysis of snake models based on hamiltonian formulation. Technical report, Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro, Departamento Engenharia de Sistemas e Computaç ão, http://www.arxiv.org/abs/cs.CV/0504031.
Chiang Y-J, Silva C, Schroeder W. 1998. Interactive out-of-core isosurface extraction. In IEEE Visualization ’98, pp. 167-174.
Carneiro BP, Silva CT, Kaufman AE. 1996. Tetra-cubes: An algorithm to generate 3D isosurfaces based upon tetrahedra. In Proceedings of the international symposium on computer graphics, image processing and vision (SIBGRAPI’96).
Berger MJ, Oliger J. 1984. Adaptive mesh refinement for hyperbolic partial differential equations. J Comput Phys 54:484-512.
Sethian JA. 1996. Level set methods: evolving interfaces in geometry, fluid mechanics, computer vision and materials sciences. Cambridge: Cambridge UP.
Cohen J, Varshney A, Manocha D, Turk G, Weber H, Agarwal P, Brooks F, Wright W. 1996. Simplification envelopes. Comput graphics 30:119-128.
Perona P, Malik J. 1990. Scale-space and edge detection using anisotropic diffusion. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Machine Intell 12(7):629-639.
Sarti A, Ortiz C, Lockett S, Malladi R. 1998. A unified geometric model for 3D confocal image analysis in cytology. In Proceedings of the international symposium on computer graphics, image processing and vision (SIBGRAPI’98), pp. 69-76.
Giraldi GA, Strauss E, Oliveira AF. 2001. Dual and topologically adaptable snakes and initializa- tion of deformable models. In Proceedings of the International conference on imaging science, systems, and technology (CISST’2001).
Taubin G. 2001. Linear anisotropic mesh filtering. Technical report RC-22213, IBM T.J. Watson Research Center.
Sethian JA. 1994. Curvature flow and entropy conditions applied to grid generation. J Comput Phys 115:440-454.
Xu C, Prince JL. 2000. Global optimality of gradient vector flow. In Proceedings of the conference on information sciences and systems, Princeton University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2007 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Suri, J.S. et al. (2007). T-Surfaces Framework For Offset Generation And Semiautomatic 3d Segmentation. In: Deformable Models. Topics in Biomedical Engineering. International Book Series. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-68343-0_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-68343-0_1
Publisher Name: Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-0-387-31204-0
Online ISBN: 978-0-387-68343-0
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)