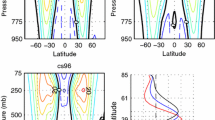
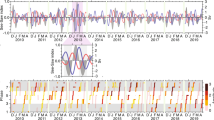
Abstract
The launch of the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) satellite mission in March 2002 has made timely the study of geophysical processes that redistribute the Earth’s mass. This study uses the Hadley Centre coupled ocean- atmosphere model HadCM3 to examine the ocean’s role in mass redistribution on inter-annual to decadal timescales. The leading empirical mode of inter-annual bottom pressure variability is a striking, basin-wide, oscillation between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. Our analysis suggests that this mode is primarily a wind driven phenomenon. We find some evidence for such a mode in a re-analysis of the global ocean, although the indirect nature of this evidence means no certain conclusions can yet be drawn. Thus, we consider the gravitational effects of this mode and the potential of current geodetic missions to detect it. A surprising result is that oceanic mass redistribution can lead to decadal trends in the zonal harmonic J 2, with a slope of approximately one-third that observed in geodetic measurements of J 2, all of which is normally attributed to post glacial rebound.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carton, J., G. Chepurin, X. Cao, and B. Giese (2000), A Simple Ocean Data Assimilation analysis of the global upper ocean 1950–95. Part I: Methodology, J. Phys. Oceanogr., 30, 294–309.
Chao, B., A. Au, J. Boy, and C. Cox (2003), Time-variable gravity signal of an anomalous redistribution of water mass in the extratropic Pacific during 1998–2002, Geo-chemistry Geophysics Geosystems, 4(11), 1096, doi: 10.1029/2003GC000589.
Chen, J., C. Wilson, X. Hu, and B. Tapley (2003), Large-scale mass redistribution in the oceans, 1993–2001, Geophys, Res. Lett., 30(20), 2024, doi:10.1029/2003GL018048.
Collins, M., S. Tett, and C. Cooper (2001), The internal climate variability of HadCM3, a version of the Hadley Centre coupled model without flax adjustments, Clim. Dyn., 17, 61–81.
Condi, F., and C. Wunsch (2004), Measuring gravity field variability, the geoid, ocean bottom pressure fluctuations, and their dynamical implications, JGR, 109, C02013, doi:10.1029/2002JC001727.
Cox, C., and B. Chao (2002), Detection of a large-scale mass redistribution in the terrestrial system since 1998, Science, 297, 832–833.
Dickey, J., S. Marcus, O. de Viron, and I. Fukumori (2002), Recent Earth oblateness variations: unravelling climate and postglacial rebound effects, Science, 298, 1975–1977.
Emery, W., and R. Thomson (2001), Data analysis methods in physical oceanography, 638 pp., Elsevier.
Frankignoul, C., P. Muller, and E. Zorita (1997), A simple model of the decadal response of the ocean to stochastic wind forcing, J. Phys. Oceanogr., 27, 1533–1546.
Gegout, P., and A. Cazenave (1993), Temporal variations of the Earth gravity field for 1985–1989 derived from LAGEOS, Geophys. J. Int., 114(2), 347–359.
Gill, A., and P. Niiler (1973), The theory of seasonal variability in the ocean, Deep-Sea Research, 20, 141–177.
Gordon, C., C. Cooper, C. Senior, H. Banks, J. Gregory, T. Johns, J. Mitchell, and R. Wood (2000), The simulation of SST, sea ice extents and ocean heat transports in a version of the Hadley Centre coupled model without flix adjustments, Clim. Dyn., 16, 147–168.
Greatbatch, R. (1994), A note on the representation of steric sea-level in models that conserve volume rather than mass, J. Geophys. Res., 99, 12,767–12,771.
Leuliette, E., R. Nerem, and G. Russell (2002), Detecing time variations in gravity associated with climate change, J. Geophys. Res., 107(B6), 2112, doi:10.1029/2001JB000404.
Levitus, S. (1994), World Ocean Atlas, Volume 4: Temperature, NOAA/NESDIS E/OC21, US Department of Commerce, Washington DC.
Ponte, R. (1999), A preliminary model study of the large-scale seasonal cycle in the bottom pressure over the global ocean, J. Geophys. Res., 104(Cl), 1289–1300.
Qiu, B. (2002), Large-scale variability in the midlatitude subtropical and subpolar North Pacific Ocean: Observations and causes, J. Phys. Oceanogr., 32, 353–375.
Sturges, W., B. Hong, and A. Clarke (1998), Decadal wind forcing of the North Atlantic subtropical gyre, J. Phys. Oceanogr., 28, 659–668.
Wahr, J., M. Molenaar, and F. Bryan (1998), Time variability of the Earth’s gravity field: Hydrological and oceanic effects and their possible detection using GRACE, J. Geophys. Res., 103, 30,205–30,229.
Wunsch, C., and D. Stammer (1997), Atmospheric loading and the oceanic “inverted barometer” effect, Rev. Geophys., 35, 79–107.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2005 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Bingham, R., Haines, K. (2005). Decadal Ocean Bottom Pressure Variability and its Associated Gravitational Effects in a Coupled Ocean- Atmosphere Model. In: Jekeli, C., Bastos, L., Fernandes, J. (eds) Gravity, Geoid and Space Missions. International Association of Geodesy Symposia, vol 129. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-26932-0_52
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-26932-0_52
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-26930-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-26932-8
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)