Abstract
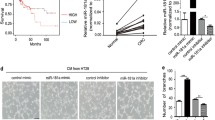
The study aims to investigate the effect of microRNA-497 (miR-497) expression and bufalin treatment in regulating colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis. The expression of miR-497 in colorectal cancer cells with prior treatment with bufalin was determined using real-time quantitative PCR. The nude mouse abdominal aortic ring assay and the human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC) migration assays were used to measure the angiogenic effect of bufalin. The effect of both bufalin treatment and miR-497 overexpression on colorectal cancer metastasis was measured using an animal tumor model together with in vivo imaging. These results suggested: (1) In the HCT116 cells and HUVECs, proliferation was inhibited in a time-dependent and/or concentration-dependent manner following the administration of bufalin; (2) Bufalin inhibited cell migration in a concentration-dependent manner by cell motility assays; (3) In the aortic ring assay, administration bufalin to the aortic ring significantly promoted micro-angiogenesis of nude mouse abdominal aorta in a concentration-dependent and time-dependent manner; (4) miR-497 was upregulated in human colorectal cancer HCT116 cells treated with different concentrations of bufalin in a concentration-dependent manner; and (5) Combined application of bufalin and miR-497 significantly reduced metastatic lesions and reduced weight loss compared with bufalin alone and control groups in vivo. This study revealed that bufalin inhibited angiogenesis and regulated miR-497 expression and that bufalin and miR-497 acted in synergy to inhibit colorectal cancer metastasis, resulting in improved quality of life in a nude mouse model.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shike M, Winawer SJ, Greenwald PH, et al. Primary prevention of colorectal cancer. The WHO Collaborating Centre for the Prevention of Colorectal Cancer. 1990;68:377–85.
Figueredo A, Coombes ME, Mukherjee S. Adjuvant therapy for completely resected stage II colon cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008;16, CD005390.
Hunter KW, Crawford NP, Alsarraj J. Mechanisms of metastasis. Breast Cancer Res. 2008;10:S2.
Tookman L, Roylance R. New drugs for breast cancer. Br Med Bull. 2010;96:111–29.
Hassan MS, Ansari J, Spooner D, et al. Chemotherapy for breast cancer (review). Oncol Rep. 2010;24:1121–31.
Sibley CR, Seow Y, Wood MJ. Novel RNA-based strategies for therapeutic gene silencing. Mol Ther. 2010;18:466–76.
Ireson CR, Kelland LR. Discovery and development of anticancer aptamers. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006;5:2957–62.
Guo P, Coban O, Snead NM, et al. Engineering RNA for targeted siRNA delivery and medical application. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010;62:650–66.
Kim SJ, Oh JS, Shin JY, et al. Development of microRNA-145 for therapeutic application in breast cancer. J Control Release. 2011;155:427–34.
Sun L, Chen T, Wang X, et al. Bufalin induces reactive oxygen species dependent bax translocation and apoptosis in ASTC-a-1 cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011;2011:249090.
Gao Y, Li HX, Xu LT, et al. Bufalin enhances the anti-proliferative effect of sorafenib on human hepatocellular carcinoma cells through downregulation of ERK. Mol Biol Rep. 2012;39:1683–9.
Yu CH, Kan SF, Pu HF, et al. Apoptotic signaling in bufalin- and cinobufagin-treated androgen-dependent and -independent human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2008;99:2467–76.
Yin JQ, Shen JN, Su WW, et al. Bufalin induces apoptosis in human osteosarcoma U-2OS and U-2OS methotrexate300-resistant cell lines. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2007;28:712–20.
Tsai SC, Yang JS, Peng SF, et al. Bufalin increases sensitivity to AKT/mTOR-induced autophagic cell death in SK-HEP-1 human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol. 2012;41:1431–42.
Hong SH, Kim GY, Chang YC, et al. Bufalin prevents the migration and invasion of T24 bladder carcinoma cells through the inactivation of matrix metalloproteinases and modulation of tight junctions. Int J Oncol. 2013;42:277–86.
Wang J, Wilcken DE, Wang XL. Cigarette smoke activates caspase-3 to induce apoptosis of human umbilical venous endothelial cells. Mol Genet Metab. 2001;72:82–8.
Senthil D, Raveendran M, Shen YH, et al. Genotype-dependent expression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) and its regulatory proteins in cultured endothelial cells. DNA Cell Biol. 2005;24:218–24.
Bookout AL, Mangelsdorf DJ. Quantitative real-time PCR protocol for analysis of nuclear receptor signaling pathways. Nucl Recept Signal. 2003;1:e012.
Pang X, Yi T, Yi Z, et al. Morelloflavone, a biflavonoid, inhibits tumor angiogenesis by targeting rho GTPases and extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathways. Cancer Res. 2009;69:518–25.
Sui H, Zhou S, Wang Y, et al. COX-2 contributes to P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance via phosphorylation of c-Jun at Ser63/73 in colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2011;32:667–75.
Guo ST, Jiang CC, Wang GP, et al. MicroRNA-497 targets insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor and has a tumour suppressive role in human colorectal cancer. Oncogene. 2013;32:1910–20.
Folkman J, Klagsbrun M. Vascular physiology. A family of angiogenic peptides. Nature. 1987;329:671–2.
Takahashi Y, Kitadai Y, Bucana CD, et al. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor, KDR, correlates with vascularity, metastasis, and proliferation of human colon cancer. Cancer Res. 1995;55:3964–8.
Volm M, Rittgen W, Drings P. Prognostic value of ERBB-1, VEGF, cyclin A, FOS, JUN and MYC in patients with squamous cell lung carcinomas. Br J Cancer. 1998;77:663–9.
Hurst DR, Edmonds MD, Welch DR. Metastamir: the field of metastasis-regulatory microRNA is spreading. Cancer Res. 2009;69:7495–8.
He L, Hannon GJ. MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5:522–31.
Vasudevan S, Tong Y, Steitz JA. Switching from repression to activation: microRNAs can up-regulate translation. Science. 2007;318:1931–4.
Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:857–66.
Nicoloso MS, Spizzo R, Shimizu M, et al. MicroRNAs—the micro steering wheel of tumour metastases. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9:293–302.
Lehmann U, Streichert T, Otto B, et al. Identification of differentially expressed microRNAs in human male breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 2010;10:109.
Lajer CB, Garnæs E, Friis-Hansen L, et al. The role of miRNAs in human papilloma virus (HPV)-associated cancers: bridging between HPV-related head and neck cancer and cervical cancer. Br J Cancer. 2012;106:1526–34.
Yin PH, Liu X, Qiu YY, et al. Anti-tumor activity and apoptosis—regulation mechanisms of bufalin in various cancers: new hope for cancer patients. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012;13:5339–43.
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by Shanghai Committee of Science and Technology, China (no. 114119b3100) and Putuo District Committee of Science and Technology, Shanghai China (no.201102). This research work was also supported by Construct Program of the Key Discipline of State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine of People’s Republic of China.
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Yan-yan Qiu and Qiang Hu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, Yy., Hu, Q., Tang, Qf. et al. MicroRNA-497 and bufalin act synergistically to inhibit colorectal cancer metastasis. Tumor Biol. 35, 2599–2606 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-1342-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-1342-6