Abstract
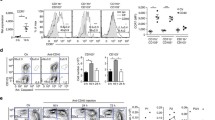
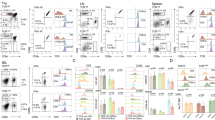
TCRγδ+ T cells play a critical role in protecting the intestinal mucosa against pathogenic infection. In the absence of infection, TCRγδ+ T cell activation must be continuously regulated by T regulatory cells (Treg) to prevent the development of colitis. However, the activation of intestinal TCRγδ+ T cells under normal conditions has not been clearly resolved. In order to determine TCRγδ+ T cell activation in vivo, we designed an NF-κB based reporter system. Using the recombinant lentiviral method, we delivered the NF-κB reporter to isolated TCRγδ+ T cells, which were then adoptively transferred into normal mice. Our data indicate that the NF-κB activation level in TCRγδ+ T cells is higher in the intestinal intraepithelial layer than in the lamina propria region. In addition, the surface expression level of lymphocyte activation marker CD69 in TCRγδ+ T cells is also higher in the intestinal intraepithelial layer and this activation was reduced by Sulfatrim treatment which removes of commensal bacteria. Collectively, our data indicate that the TCRγδ+ T cell population attached to the intestinal lumen is constitutively activated even by normal commensal bacteria.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TCR:
-
t cell receptor
- APC:
-
antigen presenting cell
- Treg:
-
regulatory T cell
- IEL:
-
intraepithelial lymphocyte
- LPL:
-
lamina propria lymphocyte
- LTR:
-
long terminal repeat
References
Allison, J.P. and Havran, W.L. 1991. The immunobiology of T cells with invariant gamma delta antigen receptors. Ann. Rev. Immunol. 9, 679–705.
Bonneville, M., O’Brien, R.L., and Born, W.K. 2010. Gammadelta T cell effector functions: a blend of innate programming and acquired plasticity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 10, 467–478.
Capone, M., Hockett, R.D., Jr., and Zlotnik, A. 1998. Kinetics of T cell receptor beta, gamma, and delta rearrangements during adult thymic development: T cell receptor rearrangements are present in CD44(+)CD25(+) Pro-T thymocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 12522–12527.
Chen, Y., Chou, K., Fuchs, E., Havran, W.L., and Boismenu, R. 2002. Protection of the intestinal mucosa by intraepithelial gamma delta T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 14338–14343.
Chien, Y.H., Iwashima, M., Wettstein, D.A., Kaplan, K.B., Elliott, J.F., Born, W., and Davis, M.M. 1987. T-cell receptor delta gene rearrangements in early thymocytes. Nature 330, 722–727.
Chien, Y.H. and Konigshofer, Y. 2007. Antigen recognition by gammadelta T cells. Immunol. Rev. 215, 46–58.
Garman, R.D., Doherty, P.J., and Raulet, D.H. 1986. Diversity, rearrangement, and expression of murine T cell gamma genes. Cell. 45, 733–742.
Haas, W., Pereira, P., and Tonegawa, S. 1993. Gamma/delta cells. Ann. Rev. Immunol. 11, 637–685.
Hayday, A.C. 2009. Gammadelta T cells and the lymphoid stress-surveillance response. Immunity 31, 184–196.
Hayday, A.C., Saito, H., Gillies, S.D., Kranz, D.M., Tanigawa, G., Eisen, H.N., and Tonegawa, S. 1985. Structure, organization, and somatic rearrangement of T cell gamma genes. Cell. 40, 259–269.
Hayday, A. and Tigelaar, R. 2003. Immunoregulation in the tissues by gammadelta T cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 3, 233–242.
Hayden, M.S. and Ghosh, S. 2011. NF-kappaB in immunobiology. Cell Res. 21, 223–244.
Holtmeier, W. and Kabelitz, D. 2005. Gammadelta T cells link innate and adaptive immune responses. Chem. Immunol. Allergy 86, 151–183.
Howe, C.J., LaHair, M.M., Maxwell, J.A., Lee, J.T., Robinson, P.J., Rodriguez-Mora, O., McCubrey, J.A., and Franklin, R.A. 2002. Participation of the calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinases in hydrogen peroxide-induced Ikappa B phosphorylation in human T lymphocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 30469–30476.
Inagaki-Ohara, K., Chinen, T., Matsuzaki, G., Sasaki, A., Sakamoto, Y., Hiromatsu, K., Nakamura-Uchiyama, F., Nawa, Y., and Yoshimura, A. 2004. Mucosal T cells bearing TCRgammadelta play a protective role in intestinal inflammation. J. Immunol. 173, 1390–1398.
Ito, Y., Usui, T., Kobayashi, S., Iguchi-Hashimoto, M., Ito, H., Yoshitomi, H., Nakamura, T., Shimizu, M., Kawabata, D., Yukawa N., and et al. 2009. Gamma/delta T cells are the predominant source of interleukin-17 in affected joints in collagen-induced arthritis, but not in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 60, 2294–2303.
Livak, F., Tourigny, M., Schatz, D.G., and Petrie, H.T. 1999. Characterization of TCR gene rearrangements during adult murine T cell development. J. Immunol. 162, 2575–2580.
Pardoll, D.M., Fowlkes, B.J., Lew, A.M., Maloy, W.L., Weston, M.A., Bluestone, J.A., Schwartz, R.H., Coligan, J.E., and Kruisbeek, A.M. 1988. Thymus-dependent and thymus-independent developmental pathways for peripheral T cell receptor-gamma delta-bearing lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 140, 4091–4096.
Park, S.G., Mathur, R., Long, M., Hosh, N., Hao, L., Hayden, M.S., and Ghosh, S. 2010. T regulatory cells maintain intestinal homeostasis by suppressing gammadelta T cells. Immunity 33, 791–803.
Park, S.G., Schulze-Luehrman, J., Hayden, M.S., Hashimoto, N., Ogawa, W., Kasuga, M., and Ghosh, S. 2009. The kinase PDK1 integrates T cell antigen receptor and CD28 coreceptor signaling to induce NF-kappaB and activate T cells. Nat. Immunol. 10, 158–166.
Sutton, C.E., Lalor, S.J., Sweeney, C.M., Brereton, C.F., Lavelle, E.C., and Mills, K.H. 2009. Interleukin-1 and IL-23 induce innate IL-17 production from gammadelta T cells, amplifying Th17 responses and autoimmunity. Immunity 31, 331–341.
Turchinovich, G. and Pennington, D.J. 2011. T cell receptor signalling in gammadelta cell development: strength isn’t everything. Trends Immunol. 32, 567–573.
Weigmann, B., Tubbe, I., Seidel, D., Nicolaev, A., Becker, C., and Neurath, M.F. 2007. Isolation and subsequent analysis of murine lamina propria mononuclear cells from colonic tissue. Nature Protocols 2, 2307–2311.
Yamashita, S., Tanaka, Y., Tsutsumi, S., Aburatani, H., Minato, N., and Ihara, S. 2005. Analysis of mechanism for human gammadelta T cell recognition of nonpeptide antigens. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 334, 349–360.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeong, S.P., Kang, JA. & Park, SG. Intestinal intraepithelial TCRγδ+ T cells are activated by normal commensal bacteria. J Microbiol. 50, 837–841 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-012-2468-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-012-2468-8