Abstract
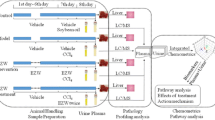
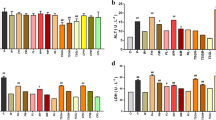
Metabolomics can provide an opportunity to develop the systematic analysis of the metabolites in biological samples and has been increasingly applied to discovering and identifying biomarkers and perturbed pathways. It enables us to better understand the metabolic pathways which can clarify the mechanism of traditional Chinese medicines (TCM). Yinchenhao (YCH, Artemisia annua L), a famous TCM plant, has been used clinically for more than a thousand years to relieve liver diseases in Asia, and its mechanisms are not still completely clear. Here, metabolomic techniques may provide additional insight, and our investigation was designed to assess the effects and possible mechanisms of YCH on α-naphthylisothiocyanate (ANIT)-induced liver injury. Metabolite profiling was performed by ultra-performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization quadruple time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC/ESI-Q-TOF/MS) combined with pathway analysis and pattern recognition approaches including independent component analysis (ICA) and partial least squares-discriminant analysis (PLS-DA). Biochemistry test was also performed for the liver tissue and plasma samples. The changes in metabolic profiling were restored to their baseline values after YCH treatment according to the ICA score plots. Of note, YCH has a potential pharmacological effect through regulating multiple perturbed pathways to normal state, correlating well to the assessment of biochemistry test. Five different potential biomarkers in the positive mode contributing to the treatment of YCH were discovered. Pathway analysis showed that these metabolites were associated with perturbations in pyrimidine metabolism, primary bile acid biosynthesis, and propanoate metabolism, which may be helpful to further understand the action mechanisms of YCH. It showed that changed biomarkers and pathways may provide evidence to insight into drug action mechanisms and drug discovery.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, X., Sun, H., Zhang, A., Sun, W., Wang, P., & Wang, Z. (2011). Potential role of metabolomics approaches in the area of traditional Chinese medicine: as pillars of the bridge between Chinese and Western medicine. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 55, 859–868.
Wang, X., Zhang, A., Han, Y., Wang, P., Sun, H., Song, G., et al. (2012). Urine metabolomics analysis for biomarker discovery and detection of jaundice syndrome in patients with liver disease. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, 11, 370–380.
Zhang, T., Watson, D. G., Wang, L., Abbas, M., Murdoch, L., Bashford, L., et al. (2013). Application of holistic liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry based urinary metabolomics for prostate cancer detection and biomarker discovery. PloS One, 8(6), e65880.
Castro, C., Krumsiek, J., Lehrbach, N. J., Murfitt, S. A., Miska, E. A., & Griffin, J. L. (2013). A study of Caenorhabditis elegans DAF-2 mutants by metabolomics and differential correlation networks. Molecular BioSystems, 9(7), 1632–1642.
Xu, J., Liu, C., Cai, S., Dong, J., Li, X., Feng, J., et al. (2013). Metabolomic profilings of urine and serum from high fat-fed rats via 1H NMR spectroscopy and pattern recognition. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 169(4), 1250–1261.
Wang, X., Yang, B., Sun, H., & Zhang, A. (2012). Pattern recognition approaches and computational systems tools for ultra performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry-based comprehensive metabolomic profiling and pathways analysis of biological data sets. Analytical Chemistry, 84, 428–439.
Yang, B., Zhang, A., Sun, H., Dong, W., Yan, G., Li, T., et al. (2012). Metabolomic study of insomnia and intervention effects of Suanzaoren decoction using ultra-performance liquid-chromatography/electrospray-ionization synapt high-definition mass spectrometry. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 58, 113–124.
OuYang, D., Xu, J., Huang, H., & Chen, Z. (2011). Metabolomic profiling of serum from human pancreatic cancer patients using 1H NMR spectroscopy and principal component analysis. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 165(1), 148–154.
Dong, H., Zhang, A., Sun, H., Wang, H., Lu, X., Wang, M., et al. (2012). Ingenuity pathways analysis of urine metabolomics phenotypes toxicity of Chuanwu in Wistar rats by UPLC-Q-TOF-HDMS coupled with pattern recognition methods. Molecular BioSystems, 8, 1206–1221.
Zhang, A., Sun, H., & Wang, X. (2012). Saliva metabolomics opens door to biomarker discovery, disease diagnosis, and treatment. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 168(6), 1718–1727.
Zhang, A., Sun, H., Wang, Z., Sun, W., Wang, P., & Wang, X. (2010). Metabolomics: towards understanding traditional Chinese medicine. Planta Medica, 76, 2026–2035.
van Vliet, E., Eixarch, E., Illa, M., Arbat-Plana, A., González-Tendero, A., Hogberg, H. T., et al. (2013). Metabolomics reveals metabolic alterations by intrauterine growth restriction in the fetal rabbit brain. PloS One, 8(5), e64545.
Zhang, A., Sun, H., Yuan, Y., Sun, W., Jiao, G., & Wang, X. (2011). An in vivo analysis of the therapeutic and synergistic properties of Chinese medicinal formula Yin-Chen-Hao-Tang based on its active constituents. Fitoterapia, 82, 1160–1168.
Ohta, Y., Kongo-Nishimura, M., Imai, Y., Matsura, T., Kitagawa, A., & Yamada, K. (2006). alpha-Tocopherol protects against alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate-induced hepatotoxicity in rats less effectively than melatonin. Chemico-Biological Interactions, 161, 115–124.
Hasegawa, M., Ide, M., Fujita, T., & Takenaka, S. (2008). Urinary metabolic fingerprinting for alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate-induced intrahepatic cholestasis in rats using Fourier transform-ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Toxicologic Pathology, 36, 818–826.
Ding, Y., Zhao, L., Mei, H., Zhang, S. L., Huang, Z. H., Duan, Y. Y., et al. (2008). Exploration of Emodin to treat alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate-induced cholestatic hepatitis via anti-inflammatory pathway. European Journal of Pharmacology, 590, 377–386.
Cui, Y. J., Aleksunes, L. M., Tanaka, Y., Goedken, M. J., & Klaassen, C. D. (2009). Compensatory induction of liver efflux transporters in response to ANIT-induced liver injury is impaired in FXR-null mice. Toxicological Sciences, 110, 47–60.
Wang, X., Sun, H., Zhang, A., Wang, P., & Han, Y. (2011). Ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry as a sensitive and powerful technology for metabolomic studies. Journal of Separation Science, 34, 3451–3459.
Qin, X., Dai, Y., Liu, N. Q., Li, Z., Liu, X., Hu, J., et al. (2012). Metabolic fingerprinting by 1HNMR for discrimination of the two species used as Radix Bupleuri. Planta Medica, 78, 926–933.
Zhang, A., Sun, H., Wang, P., Han, Y., & Wang, X. (2012). Modern analytical techniques in metabolomics analysis. Analyst, 137(2), 293–300.
Zhang, H. M., Li, S. L., Zhang, H., Wang, Y., Zhao, Z. L., Chen, S. L., et al. (2011). Holistic quality evaluation of commercial white and red ginseng using a UPLC-QTOF-MS/MS-based metabolomics approach. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 62, 258–273.
Zhang, A., Sun, H., Han, Y., Yan, G., & Wang, X. (2013). Urinary metabolic biomarker and pathway study of hepatitis B virus infected patients based on UPLC-MS system. PloS One, 8(5), e64381.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Key Program of Natural Science Foundation of State (Grant Nos. 90709019, 81173500, 81373930, 81302905, 81102556, and 81202639), National Key Technology Research and Development Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (Grant Nos. 2011BAI03B03, 2011BAI03B06, and 2011BAI03B08), and National Key Subject of Drug Innovation (Grant No. 2009ZX09502-005).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 118 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, H., Zhang, Ah., Zou, Dx. et al. Metabolomics Coupled with Pattern Recognition and Pathway Analysis on Potential Biomarkers in Liver Injury and Hepatoprotective Effects of Yinchenhao. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 173, 857–869 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-0903-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-0903-5