Abstract
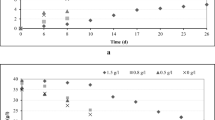
The ability of Aspergillus niger GH1 in converting creosote bush ellagitannins into ellagic acid (EA) was evaluated in solid state culture. Creosote bush leaves were used to extract the ellagitannins fraction, which was impregnated in polyurethane foam used as support of solid state culture. Ellagitannins content, EA accumulation, and the related enzymatic activities were evaluated. A. niger GH1 was able to completely degrade creosote bush ellagitannins with an EA yield of 23.1% at 36 h of culture. The ability to degrade creosote bush ellagitannins exhibited by A. niger GH1 was clearly associated to an ellagitannin-hydrolysing enzyme with a maximum activity of 43 U/l, while that ability was not associated to tannase activity that was detected in the culture extract. This study demonstrated the great ability of A. niger GH1 to hydrolyze ellagitannins and the potential of solid state culture to produce the antioxidant EA by degradation of creosote bush ellagitannins.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilar, C. N., Augur, C., Viniegra-González, G., & Favela, E. (1999). A comparison of methods to determine tannin acyl hydrolase activity. Brazilian Archives in Biology and Technology, 42, 355–361.
Aguilar, C. N., Rodríguez, R., Gutierrez-Sanchez, G., Augur, C., Favela-Torres, E., Prado Barragán, L. A., et al. (2007). Microbial tannases: Advances and perpectives. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 76(1), 47–59.
Aguilera-Carbo, A. F., Augur, C., Prado-Barragan, L. A., Favela-Torres, E., & Aguilar, C. N. (2008). Microbial production of ellagic acid and biodegradation of ellagitannins. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology (in press). DOI 10.1007/s00253-007-1276-2.
Aguilera-Carbo, A. F., Robledo-Olivo, A., Augur, C., Prado-Barragán, L. A., Favela-Torres, E., & Aguilar, C. N. (2007). Method for ellagic acid quantification in novel sources of this natural antioxidant. Proceedings of the 5th International Congress on Food Technology, Thessaloniki, Greece.
Ascacio, J., Prieto-Nieto, A., Hernández-Rivera, J. S., Aguilera-Carbo, A., & Aguilar, C. N. (2007). Determination of ellagitannins in native plants of Mexican semiarid zone, relationship between two analytical methods. Proceedings of the Third Mexican Congress on Biopolymers: Advances and perspectives (p. 25).
Bath, T. K., Singh, B., & Sharma, O. P. (1998). Microbial degradation of tannins—A current perspective. Biodegradation, 9, 345–357.
Cerdá, B., Cerón, J. J., Tomás-Barberán, F. A., & Espín, J. C. (2003). Repeated oral administration of doses of the pomegranate ellagitannins punicalagin to rats for 37 days is not toxic. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 51, 3493–3501.
Cruz-Hernández, M., Contreras-Esquivel, J. C., Lara, F., Rodríguez, R., & Aguilar, C. N. (2005). Isolatation and evaluation of tannin-degrading fungal starins from the Mexican desert. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung, 60, 844–848.
Daniel, M. E., Ratnayake, S., Kinstle, T., & Stoner, G. D. (1991). The effects of pH and intestinal contents on the liberation of ellagic acid from purified and crude ellagitannins. Journal of Natural Products, 54, 946–952.
Divipriya, N., Srinivasan, M., Sudheer, A. R., & Menon, V. P. (2007). Effect of ellagic acid, a natural polyphenol, on alcohol-induced prooxidant imbalance: A drug dose dependent study. Singapore Medical Journal, 48(4), 311–318.
Dubois, M., Guiles, K. A., Hamiton, J. K., Rebers, P. A., & Smith, F. (1956). Colorimetric method for determination of sugar and related substances. Analytical Chemistry, 21, 145–149.
Fukuda, T., Ito, H., & Yoshida, T. (2003). Antioxidative polyphenols from walnuts (Junglans regia L.). Phytochemistry, 63, 795–801.
Huang, W., Ni, J., & Borthwick, A. G. L. (2005). Biosynthesis of valonia tannin hydrolase and hydrolysis of valonia tannin to ellagic acid by A.niger SHL 6. Process Biochemistry, 40, 1245–1249.
Huang, W., Niu, H., Gong, G., Lu, Y., Li, Z., & Li, H. (2007a). Individual and combined effects on physicochemical parameters on ellagitannin acyl hydrolase and ellagic acid production from ellagitannin by Aspergillus oryzae. Bioprocess Biosystems Engineering, 30, 281–288.
Huang, W., Niu, H., Li, Z., He, Y., Gong, W., & Gong, G. (2007c). Optimization of ellagic acid production from ellagitannins by co-culture and correlations between its yield and activities of relevant enzymes. Bioresource Technology, 99, 769–775.
Huang, W., Niu, H., Li, Z. m., Lin, W., Gong, G., & Wang, W. (2007b). Effect of ellagitannin acyl hydrolase, xylanase and cellulase on ellagic acid production from cups extract of Valona acorns. Process Biochemistry, 42, 1291–1295.
Huang, W., Niu, H., Li, Z., & Wang, W. (2007d). Ellagic acid from acorn fringe by enzymatic hydrolysis and combined effects of operational variable and enzymes on yield of the production. Bioresource Technology, 99, 1518–1525.
Huetz, P., Mavaddat, N., & Mavri, J. (2005). Reaction between ellagic acid and ultimate carcinogen. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 45, 1564–1570.
Koponen, J. M., Happonen, A. M., Mattila, P. H., & Törrönen, A. R. (2007). Contents of anthocyanins and ellagitannins in selected foods consumed in Finland. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 55, 1612–1619.
Makkar, H. P. S., Blümmel, M., Borowy, N. K., & Becker, K. (1993). Gravimetric determination of tannins and their correlations with chemical and protein precipitation methods. Journal of Science and Food Agriculture, 61, 161–165.
Martens-Talcott, S. U., Talcott, S. T., & Percival, S. S. (2003). Low concentrations of quercitin and ellagic acid synergistically influence proliferation, cytotoxicity and apoptosis in MOLT-4 human leukemia cells1–3. Journal of Nutrition, 133, 2669–2674.
Okuda, T. (2005). Systematics and Health effects of chemically distinct tannins in medicinal plants. Phytochemistry, 66, 2012–2031.
Olsson, M. E., Ekvall, J., Gustavsson, T.-E., Nilsson, J., Pillai, D., Sjöholm, I., et al. (2004). Antioxidants, low molecular weight carbohydrates, and total antioxidant capacity in strawberries (Fragaria x annanassa): Effects of cultivar, ripening, and storage. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 52, 2490–2498.
Robledo, A., Aguilera-Carbo, A., Rodríguez, R., Martinez, J. L., Garza, Y., & Aguilar, C. N. (2008). Ellagic acid production by Aspergillus niger in solid state fermentation of pomegranate residues. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology (in press). DOI 10.1007/s10295-008-0309-x.
Ruibal, B. I. J., Dubed, E. M., Martínez, L. F., Noa, R. E., Vargas, G. L. M., & Santana, R. J. L. (2003). Inhibición de la replicación del virus de inmunodeficiencia humana por extractos de Pinus caribaea Morelet. Revista Cubana de Farmacia, 37(2), 1–8.
Saavedra, P. G. A., Couri, S., Ferreira, L. S. G., & de Brito, E. S. (2005). Tanase: Conceitos, produçao e aplicaçao. B. CEPPA. Curitiba, 23, 435–462.
Seeram, N. P., Lee, R., Hardy, M., & Herber, D. (2005). Rapid large scale purification of ellagitannins from pomegranate husk, a by-product of the commercial juice industry. Separation and Purification Technology, 41, 49–55.
Seeram, N. P., Lee, R., & Herber, D. (2004). Bioavailability of ellagic acid in human plasma after consumption of ellagitannins from pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) juice. Clinical Chimica Acta, 348, 63–68.
Shi, B., He, Q., Yao, K., Huang, W., & Li, Q. (2005). Production of ellagic acid from degradation of valonea tannins by Aspergillus niger and Candida utilis. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 80, 1154–1159.
Vattem, D. A., & Shetty, K. (2002). Solid-state production of phenolic antioxidants from cranberry pomace by Rhizophus oliogosporus. Food Biotechnology, 16(3), 189–210.
Vattem, D. A., & Shetty, K. (2003). Ellagic acid production and phenolic antioxidant activity in cranberry pomace (Vaccinium macrocarpon) mediated by Lentinus edodes using a solid-state system. Process Biochemistry, 39, 367–379.
Vivas, N., Laguerre, M., Pianet de Boissel, I., Vivas de Gaulejac, N., & Nonier, M. F. (2004). Conformational interpretation of vascalagin and castalagin physicochemical properties. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 52, 2073–2078.
Wang, C. C., Chen, L. G., & Yang, L. L. (1999). Antitumor actitvity of four macrocyclic ellagitannins from Cuphea Hyssopifolia. Cancer Letters, 140, 195–200.
Zhang, Y. J., Abe, T., Tanaka, T., Yang, C. R., & Kouna, I. (2001). Phyllanemblinins A-F, nre ellagitannins from Phyllanthus emplica. Journal of Natural Products, 64, 1527–1532.
Acknowledgment
Financial support of this research was from the National Council of Science and Technology of Mexico with grant no. SEP-CONACYT-J-51360. Authors A. Aguilera-Carbo and J. S. Hernández-Rivera are graduate students supported by CONACYT, Mexico.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aguilera-Carbo, A., Hernández, J.S., Augur, C. et al. Ellagic Acid Production from Biodegradation of Creosote Bush Ellagitannins by Aspergillus niger in Solid State Culture. Food Bioprocess Technol 2, 208–212 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-008-0063-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-008-0063-0