Abstract
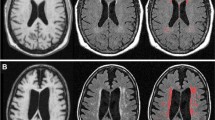
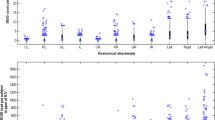
Iron deposition increases in normal aging, has its greatest presence in structures of the extrapyramidal system, and may contribute to functional decline. MR imaging provides a method for indexing iron deposition in brain structures because of iron’s ferromagnetic properties, which interact with the MRI environment to cause signal intensity attenuation that is quantifiable by comparing images collected at 1.5 and 3.0 T. We tested functional correlates of an MR-based iron index in 10 healthy, elderly individuals previously reported to have a higher iron burden in the putamen and lower in the thalamus than young individuals. Lower scores on the Dementia Rating Scale and longer reaction times on a two-choice attention test correlated with higher iron estimates in the caudate nucleus and putamen; poorer Mini-Mental State Examination and Digit Symbol scores correlated with lower iron estimates in the thalamus. Further analyses based on multiple regression, which considered regional FDRI estimates and volume measures as predictors of performance, identified iron but not the sampled volume as the unique predictor in each case. These exploratory correlations suggest a substrate of performance degradation in aging and have implications for regional signal darkening in an array of MR-based imaging protocols.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggleton, J. P., & Sahgal, A. (1993). The contribution of the anterior thalamic nuclei to anterograde amnesia. Neuropsychologia, 31(10), 1001–1019. doi:10.1016/0028-3932(93)90029-Y.
Bartzokis, G., Aravagiri, M., Oldendorf, W. H., Mintz, J., & Marder, S. R. (1993). Field dependent transverse relaxation rate increase may be a specific measure of tissue iron stores. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 29, 459–464. doi:10.1002/mrm.1910290406.
Bartzokis, G., Mintz, J., Sultzer, D., Marx, P., Herzberg, J. S., Phelan, C. K., et al. (1994). In vivo MR evaluation of age-related increases in brain iron. AJNR. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 15(6), 1129–1138.
Bartzokis, G., Tishler, T. A., Lu, P. H., Villablanca, P., Altshuler, L. L., Carter, M., et al. (2007). Brain ferritin iron may influence age- and gender-related risks of neurodegeneration. Neurobiology of Aging, 28(3), 414–423. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2006.02.005.
Bizzi, A., Brooks, R. A., Brunetti, A., Hill, J. M., Alger, J. R., Miletich, R. S., et al. (1990). Role of iron and ferritin in MR imaging of the brain: a study in primates at different field strengths. Radiology, 177(1), 59–65.
Bizzi, A., Armstrong, M., Dietz, M., Fulmah, M., Frank, J., DeChiro, G., et al. (1992). Proton spectroscopic imaging of frontal and parietal lobes in normal human brain. Proceedings of Annual Meeting of Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 1906.
Brass, S. D., Chen, N. K., Mulkern, R. V., & Bakshi, R. (2006). Magnetic resonance imaging of iron deposition in neurological disorders. Topics in Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 17(1), 31–40. doi:10.1097/01.rmr.0000245459.82782.e4.
Cahn, D. A., Sullivan, E. V., Shear, P. K., Heit, G., Lim, K. O., Marsh, L., et al. (1998). Neuropsychological and motor functioning following unilateral anatomically-guided posterior ventral pallidotomy: preoperative performance and three-month follow-up. Neuropsychiatry, Neuropsychology, and Behavioral Neurology, 11(3), 136–145.
Cooper, J. A., Sagar, H. J., Jordan, N., Harvey, N., & Sullivan, E. V. (1991). Cognitive impairment in early, untreated Parkinson’s disease and its relationship to motor disability. Brain, 114, 2095–2122. doi:10.1093/brain/114.5.2095.
Corkin, S., Growdon, J. H., Sullivan, E. V., Nissen, M. J., & Huff, F. J. (1986). Assessing treatment effects from a neuropsychological perspective. In L. Poon (Ed.), Handbook of clinical memory assessment in older adults (pp. 156–167). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
DeCarli, C., Massaro, J., Harvey, D., Hald, J., Tullberg, M., Au, R., et al. (2005). Measures of brain morphology and infarction in the Framingham heart study: establishing what is normal. Neurobiology of Aging, 26(4), 491–510. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2004.05.004.
Folstein, M. F., Folstein, S. E., & McHugh, P. R. (1975). Mini-mental state: a practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 12, 189–198. doi:10.1016/0022-3956(75)90026-6.
Glover, G. H., & Lai, S. (1998). Self-navigated spiral fMRI: interleaved versus single-shot. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 39, 361–368. doi:10.1002/mrm.1910390305.
Gomori, J. M., & Grossman, R. I. (1993). The relation between regional brain iron and T2 shortening. AJNR. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 14, 1049–1050.
Good, C. D., Johnsrude, I. S., Ashburner, J., Henson, R. N., Friston, K. J., & Frackowiak, R. S. (2001). A voxel-based morphometric study of ageing in 465 normal adult brains. NeuroImage, 14, 21–36. doi:10.1006/nimg.2001.0786.
Haacke, E. M., Cheng, N. Y., House, M. J., Liu, Q., Neelavalli, J., Ogg, R. J., et al. (2005). Imaging iron stores in the brain using magnetic resonance imaging. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 23, 1–25. doi:10.1016/j.mri.2004.10.001.
Hallgren, B., & Sourander, P. (1958). The effect of age on the non-haemin iron in the human brain. Journal of Neurochemistry, 3(1), 41–51. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.1958.tb12607.x.
Harding, A., Halliday, G., Caine, D., & Kril, J. (2000). Degeneration of anterior thalamic nuclei differentiates alcoholics with amnesia. Brain, 123(Pt 1), 141–154. doi:10.1093/brain/123.1.141.
Jernigan, T. L., Archibald, S. L., Fennema-Notestine, C., Gamst, A. C., Stout, J. C., Bonner, J., et al. (2001). Effects of age on tissues and regions of the cerebrum and cerebellum. Neurobiology of Aging, 22(4), 581–594. doi:10.1016/S0197-4580(01)00217-2.
Killiany, R. J. (2006). Why is the study of iron important for magnetic resonance imaging? Topics in Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 17, 1–3. doi:10.1097/RMR.0b013e31802c14e6.
Lezak, M. D., Howieson, D. B., & Loring, D. W. (2004). Neuropsychological assessment (4th ed.). New York: Oxford University Press.
Majumdar, S., Zoghbi, S., Pope, C. F., & Gore, J. C. (1989). A quantitative study of relaxation rate enhancement produced by iron oxide particles in polyacrylamide gels and tissue. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 9(2), 185–202. doi:10.1002/mrm.1910090205.
Mattis, S. (1988). Dementia Rating Scale (DRS) professional manual. Odessa, FL: Psychological Assessment Resources.
Pascual-Leone, A., Grafman, J., Clark, K., Stewart, M., Massaquoi, S., Lou, J. S., et al. (1993). Procedural learning in Parkinson’s disease and cerebellar degeneration. Annals of Neurology, 34(4), 594–602. doi:10.1002/ana.410340414.
Pfefferbaum, A., Mathalon, D. H., Sullivan, E. V., Rawles, J. M., Zipursky, R. B., & Lim, K. O. (1994). A quantitative magnetic resonance imaging study of changes in brain morphology from infancy to late adulthood. Archives of Neurology, 51, 874–887.
Pfefferbaum, A., Adalsteinsson, E., Rohlfing, T., & Sullivan, E. V. (2008). Diffusion tensor imaging of deep gray matter brain structures: effects of age and iron concentration. Neurobiology of Aging, doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2008.04.013.
Pfeuffer, J., Van de Moortele, P. F., Ugurbil, K., Hu, X., & Glover, G. H. (2002). Correction of physiologically induced global off-esonance effects in dynamic echo-planar and spiral functional imaging. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 47(2), 344–353. doi:10.1002/mrm.10065.
Pujol, J., Junque, C., Vendrell, P., Grau, J. M., Marti-Vilalta, J. L., Olive, C., et al. (1992). Biological significance of iron-related magnetic resonance imaging changes in the brain. Archives of Neurology, 49(7), 711–717.
Raz, N., & Rodrigue, K. M. (2006). Differential aging of the brain: patterns, cognitive correlates and modifiers. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 30, 730–748. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2006.07.001.
Raz, N., Lindenberger, U., Rodrigue, K. M., Kennedy, K. M., Head, D., Williamson, A., et al. (2005). Regional brain changes in aging healthy adults: general trends, individual differences, and modifiers. Cerebral Cortex (New York, N.Y.), 15, 1676–1689. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhi044.
Raz, N., Rodrigue, K. M., & Haacke, E. M. (2007a). Brain aging and its modifiers: insights from in vivo neuromorphometry and susceptibility weighted imaging. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1097, 84–93. doi:10.1196/annals.1379.018.
Raz, N., Rodrigue, K. M., Kennedy, K. M., & Acker, J. D. (2007b). Vascular health and longitudinal changes in brain and cognition in middle-aged and older adults. Neuropsychology, 21(2), 149–157. doi:10.1037/0894-4105.21.2.149.
Rohlfing, T., & Maurer, C. R. (2003). Nonrigid image registration in shared-memory multiprocessor environments with application to brains, breasts, and bees. IEEE Transactions on Information Technology in Biomedicine, 7(1), 16–25. doi:10.1109/TITB.2003.808506.
Rohlfing, T., Zahr, N. M., Sullivan, E. V., & Pfefferbaum, A. (2008). The SRI24 multi-channel brain atlas: construction and applications. In J. M. Reinhardt, & J. P. W. Pluim (Eds.), Medical imaging 2008: image processing, vol. 6914 of Proceedings of SPIE. Bellingham, WA, EID 691409 doi:10.1117/12.770441.
Saint-Cyr, J. A., Taylor, A. E., & Lang, A. E. (1988). Procedural learning and neostriatal dysfunction in man. Brain, 111, 941–959. doi:10.1093/brain/111.4.941.
Sassoon, S. A., Fama, R., Rosenbloom, M. J., O’Reilly, A., Pfefferbaum, A., & Sullivan, E. V. (2007). Component cognitive and motor processes of the Digit Symbol Test: differential deficits in alcoholism, HIV infection and their comorbidity. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research, 31, 1315–1324. doi:10.1111/j.1530-0277.2007.00426.x.
Sullivan, E. V., & Pfefferbaum, A. (2007). Neuroradiological characterization of normal adult aging. The British Journal of Radiology, 60, S99–S108. doi:10.1259/bjr/22893432.
Thomas, L. O., Boyko, O. B., Anthony, D. C., & Burger, P. C. (1993). MR detection of brain iron. AJNR. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 14(5), 1043–1048.
Wechsler, D. (1981). Wechsler adult intelligence scale—revised. San Antonio, TX: The Psychological Corporation.
Yin, H. H., & Knowlton, B. J. (2006). The role of the basal ganglia in habit formation. Nature Reviews. Neuroscience, 7(6), 464–476. doi:10.1038/nrn1919.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by U.S. National Institutes of Health grants AG17919 and AA05965.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sullivan, E.V., Adalsteinsson, E., Rohlfing, T. et al. Relevance of Iron Deposition in Deep Gray Matter Brain Structures to Cognitive and Motor Performance in Healthy Elderly Men and Women: Exploratory Findings. Brain Imaging and Behavior 3, 167–175 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-008-9059-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-008-9059-7