Abstract
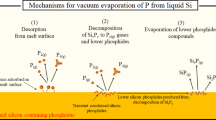
An experimental investigation into the mass transfer of phosphorus in molten silicon under vacuum induction refining has been carried out. In a pilot-scale experiment, in the temperature range 1773 K (1500 °C) to 1873 K (1600 °C) and a vacuum of 0.1 to 0.035 Pa smelting for 7200 seconds (2 hours), phosphorus is decreased from 15 ppmw to 0.08 ppmw, which achieved the target for solar-grade silicon of less than 0.1 ppmw. Lab-scale experiments are used to determine the effects of vacuum, refining time, and temperature on the rate of mass transfer of phosphorus during vacuum refining. Hardly any phosphorus was removed when the vacuum pressure is greater than 100 Pa. Mass-transfer coefficients are nearly independent of pressure at 1783 K (1510 °C) when pressures are below 0.1 Pa and are highly correlated with vacuum pressures above 0.1 Pa. A model of vacuum refining of inductively stirred silicon melts is discussed to explain the transfer path of phosphorus out of the melt.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
Surface area exposed to the vacuum, m2
- f P :
-
Henry activity coefficient of solute phosphorus
- \( P_{i}^{0} \) :
-
Vapor pressure of pure solute I, Pa
- p atm :
-
Atmospheric pressure, 101, 325 Pa
- △G 0 :
-
Gibbs energy change, J/mol
- R:
-
Gas constant, 8.31541 J/mol × K
- \( {\text{K}}_{F}^{0} \) :
-
Reaction equilibrium constant of phosphorus
- T :
-
Temperature, K
- K :
-
Overall mass transfer coefficient, m/s
- t 0 :
-
Starting time for vacuum refining, s
- M Si :
-
Molecular weight of silicon, g/mol
- T :
-
Current time during vacuum refining, s
- M i :
-
Molecular weight of solute i, g/mol
- V :
-
Volume of metal, m3
- m Si :
-
Mass of silicon, kg
- [wt pct P]0 :
-
Phosphorus content of silicon at time t 0, ppmw
- P :
-
Element phosphorus
- [wt pct P] t :
-
Phosphorus content of silicon at time t, ppmw
- \( P_{\text{Si}}^{ 0} \) :
-
Vapor pressure of silicon, Pa
- x P :
-
Mole fraction of solute phosphorus
- p P :
-
Dimensionless pressure of phosphorus
- x i :
-
Mole fraction of solute i
- \( p_{P}^{{^{e} }} \) :
-
Equilibrium partial pressure of solute phosphorus, Pa
- A :
-
Evaporation coefficient
- \( p_{i}^{e} \) :
-
Equilibrium partial pressure of solute i, Pa
- γ i :
-
Raoultian activity coefficient of solute i
References
M.G. Mauk: JOM, 2003, vol. 5, pp. 38–42.
B.R. Bathey and M.C. Cretella: J. Mater. Sci., 1982, vol. 17, pp. 3077–96.
B.G. Gribov and K.V. Zinov’ev: Inorg. Mater., 2003, vol. 39, pp. 653–62.
J. Dietl: Sol. Cell., 1983, vol. 10, pp. 145–54.
S. Zheng, J. Cai, C. Chen, and X. Luo: 3rd Int. Workshop on Science and Technology of Crystalline Si Solar Cells (CSSC-3), 2009.
M. Miyake, T. Hiramatsu, and M. Maeda: J. Japan Inst. Metals, 2006, vol. 70, pp. 43–46.
N. Yuge, K. Hanazawa, K. Nishikawa, and H. Terashima: J. Japan Inst. Metals, 1997, vol. 61, pp. 1086–93.
K. Suzuki, K. Sakaguchi, T. Nakagiri, and N. Sano, J. Japan Inst. Metals, 1990, vol. 54, pp. 161–67.
J.C.S. Pires, J. Otubo, A.F.B. Braga, and P.R. Mei: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2005, vol. 169, pp. 16–20.
T. Ikeda and M. Maeda: ISIJ Int., 1992, vol. 32, pp. 635–42.
T. Miki, K. Morita, and N. Sano, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1996, vol. 27B, pp. 937–41.
A.I. Zaitsev, N.E. Shelkova, and A.A. Kodentsov: J. Phase Equil., 2000, vol. 21, pp. 528–33.
C. Mosselman, W.H.V. Vugt, and H. Vos: J. Chem. Eng. Data, 1982, vol. 27, pp. 246–51.
O. Kubaschewski, E.LL. Evans, and C.B. Alcock: Metallurgical Thermo-Chemistry, 4th ed., Pergamon Press, Oxford, UK, 1979, pp. 408–20.
R.G. Ward and T.D. Aurini: J. Iron Steel Inst., 1966, vol. 208, pp. 920–23.
R.G. Ward and T.D. Aurini: J. Iron Steel Inst., 1963, vol. 201, pp. 11–15.
Acknowledgments
The project is supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province of China (No. 2007J0012) and the Key Technological Program of Fujian Province of China (No. 2007HZ0005-2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted June 28, 2009.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, SS., Chen, WH., Cai, J. et al. Mass Transfer of Phosphorus in Silicon Melts Under Vacuum Induction Refining. Metall Mater Trans B 41, 1268–1273 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-010-9422-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-010-9422-0