Abstract
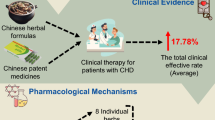
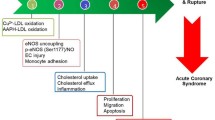
This article presents an integrated overview of Guanxin II (冠心II号) regarding its quality control, pharmacokinetics, pharmacology, clinical studies, adverse events, dosage and administration, and its pharmacoeconomic assessment. It has been demonstrated that Guanxin II has beneficial effects on coronary heart disease (CHD). The underlying mechanism was proved to be its anti-ischemic, anti-apoptotic, antioxidative, antiplatelet and anti-inflammatory effects, and so on. Tanshinol, hydroxysafflor yellow A and ferulic acid might be responsible for the cardioprotective effect of Guanxin II. In terms of acquisition cost, Guanxin II is cheaper than other drugs currently available for CHD. Guanxin II is safe, cheap, and effective in the management of CHD. However, the mechanism of its cardioprotective effects has not been completely understood because of limitations in the research methodologies of Chinese medicine. Further work should be carried out with single components such as tanshinol, hydroxysafflor yellow A and ferulic acid, using modern biochemical and molecular methods.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheng JW. Ranolazine for the management of coronary artery disease. Clin Ther 2006;28:1996–2007.
Nabel EG. Cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med 2003;349:60–72.
Thom T, Haase N, Rosamond W, Howard VJ, Rumsfeld J, Manolio T, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2006 update. A report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation 2006;113:85–1
Abrams J. Clinical practice. Chronic stable angina. N Engl J Med 2005;352:2524–2533.
Chen KJ, Qian ZZ, Liu WL. Observation on long-term effects of Guanxin II in treating 164 patients with angina pectoris of coronary heart disease. J Cardiovasc Dis (Chin) 1978;6:22–24.
Zhao J, Huang X, Tang W, Ren P, Xing Z, Tian X, et al. Effect of oriental herbal prescription Guan-Xin-Er-Hao on coronary flow in healthy volunteers and anti-apoptosis on myocardial ischemiareperfusion in rat models. Phytother Res 2007;21:926–931.
Makino T, Wakushima H, Okamoto T, Okukubo Y, Deguchi Y, Kano Y. Pharmacokinetic interactions between warfarin and kangen-karyu, a Chinese traditional herbal medicine, and their synergistic action. J Ethnopharmacol 2002;82:35–40.
The Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China. 2005 ed. Vol. 1. Beijng: Chemical Industry Press; 2005:653–654.
Huang J, Tian J, Zhu W. Content determination of danshensu and protocatechuic aidehyde contents of Salvia Milfiorrhiza and Coronary Heart No II Decoction in different decocting methods by HPLC respectively. Chin J Inf Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2005;12:44–46.
Gan HQ, Huang X, Qu Y, Ren P, Zhang S, Mei Q. Simultaneous determination of danshensu, protocatechuic aldehyde, paeoniflorin and ferulic acid in Guan-Xin-II Decoction by RP-HPLC. J Fourth Milit Med Univ (Chin) 2004;25:772–775.
Gan HQ, Mei QB, Qu Y, Huang X. Quality study on Guanxin II Decoction. Chin Pharm (Chin) 2005;16:1695–1696.
Wang LL, Huang X, Ren P, Zhang L, Zhang HX. Determination of contents of paeoniflorin and ferulic acid in No. 2 Decoction of coronary heart by reversed phase supercritical fluid extraction and chromatography. J Chengdu Univ Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2001;24:51–52.
Wang J, Feng W, Tong Y, Yan J, Wang Z, Zhu X, et al. Comparative studies on the purifying conditions of the elixation of the Guanxin II Decoction. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Form (Chin) 2007;13:14–16.
Tong Y, Wang J, Feng W, Yan J, Wang Z, Zhu X, et al. Effect of the two kinds of decocting methods on contents of main active components in Guanxin II Decoctions. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Form (Chin) 2007;13:24–26.
Qiao X, Han J, Xu M, Zhang ZC, Sun SF, Li HF, et al. Characterization of chemical constituents in Guan Xin II Decoction by liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry. Planta Med 2008;74:1720–1729.
Qiao X, Xu M, Han J, Guo DA. Progresses: constituents and pharmacological analyses of Guan Xin Er Hao Decoction. World Sci Tech-Mod Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2007;9:86–95.
Qin F, Huang X, Zhang HM, Ren P. Pharmacokinetic comparison of puerarin after oral administration of Jiawei-Xiaoyao-San in healthy volunteers and functional dyspepsia patients: influence of disease state. J Pharm Pharmacol 2009;61:125–129.
Gan HQ, Mei QB, Wang Y, Huang X. Serum pharmacochemistry changes of Guanxin II Oral Decoction in healthy volunteers. Chin Pharm (Chin) 2006;17:173–177.
Ye G, Li YZ, Li YY, Guo HZ, Guo DA. SPE-HPLC method for the determination and pharmacokinetic studies on paeoniflorin in rat serum after oral administration of traditional Chinese medicinal preparation Guan-Xin-Er-Hao Decoction. J Pharm Biomed Anal 2003;33:521–527.
Hu Y, Chen W, Zhang Y, Li L, Zhang GM, Yang W, et al. Degradation of paeoniflorin in Guanxin II prescription by intestinal bacteria. Chin Pharm J (Chin) 2007;42:1813–1818.
Yang XG, Peng B, Zhang GH, Wei LL, Nie SF, Pan WS. Studies of the pharmacokinetics of paeoniflorin in two Jing-Zhi-Guan-Xin formulations after oral administration to beagle dogs. J Pharm Biomed Anal 2006;41:320–324.
Gan HQ, Mei QB, Zhu W, Huang X. Pharmacokinetics of ferulic acid in serum of healthy male volunteers after oral administration of Guanxin II Decoction. Chin Pharm (Chin) 2007;18:109–111.
Ren P, Huang X, Chen K, Zhang L, Wang LL, Ma XC. Comparison of ferulic acid concentration-time profiles absorbed into serum between oral ligusticum wallichi and Guanxin II Decoctions. Chin Heart J (Chin) 2000;12:253–254.
Huang X, Qin F, Zhang HM, Xiao HB, Wang LX, Zhang XY. Cardioprotection by Guanxin II in rats with acute myocardial infarction is related to its three compounds. J Ethnopharmacol 2009;121:268–273.
Zeng X, He H, Yang J, Yang X, Wu L, Yu J. Temporal effect of Guanxin No. 2 on cardiac function, blood viscosity and angiogenesis in rats after long-term occlusion of the left anterior descending coronary artery. J Ethnopharmacol 2008;118:485–494.
Gan HQ, Huang X, Tian XQ, Zhu YS, Zhang SH, Li J, et al. Effect of oral administration of Guanxin II Decoction on coronary blood flow and cardiac systolic/diastolic function in healthy males. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med (Chin) 2004;24:785–789.
Tian X, Qian Y, Huang X, Zhu Y, Gan H, Li J, et al. Evaluating effects of Guan-Xin-Er-Hao Decoction on coronary artery hemodynamics in healthy men using coronary artery flow imaging. Chin J Ultrasound Med (Chin) 2004;20:936–939.
Tang W, Chen D, Huang X, Ren P, Xia Q, Wan M, et al. Effect of Coronary Heart No. 2 on the hemodynamics of inferior mesentery artery in healthy male volunteers. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Form (Chin) 2006;12:70–72.
Xu LN, Yin ZZ, Ou YR. The effect of compositus Guan-Xin No. 2 on myocardial ischemia and hypoxia in experimental animals. Atca Pharm Sin (Chin) 1979;14:461–466.
Zhao HW, Qin F, Liu YX, Huang X, Ren P. Antiapoptotic mechanisms of Chinese medicine formula, Guan-Xin-Er-Hao, in the rat ischemic heart. Tohoku J Exp Med 2008;216:309–316.
Wei H, Yang L, Li Q, Li L. Efects of Guanxin II formula on myocardial apoptosis of acute myocardial ischemia in rats. Pharmacol Clin Chin Mater Med (Chin) 2008;24:1–4.
Qin F, Liu YX, Zhao HW, Huang X, Ren P, Zhu ZY. Chinese medicinal formula Guan-Xin-Er-Hao protects the heart against oxidative stress induced by acute ischemic myocardial injury in rats. Phytomedicine 2009;16:215–221.
Wei H, Yang L, Li L. Effect of Guanxin II on myocardial pathological injury and myocardial enzymes in acute myocardial infarction rats. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res (Chin) 2008;19:1552–1553.
Wang ZY, Qian RQ, Guan SH, Feng XZ, Guo DA, Yan JJ, et al. Study on free radical mechanism of Guanxin II in antagonizing ischemic myocardial damage. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med (Chin) 2003;23:363–366.
Su Y, Li Y, Li P, Li L. Effects of blood serum of different officinal forms of Guanxin II formula on ischemiareperfusion injury in cultured rat myocardial cells. Pharmacol Clin Chin Mater Med (Chin) 2007;23(3):1–4.
Gao H, Li Y, Li L. Comparative study on the protective effects of different Guanxin II formula on acute myocardial ischemia in dogs. Pharmacol Clin Chin Mater Med (Chin) 2007;23(5):1–4.
Zhang WX, Bai Y, Yue FZ. Influence of Guanxin II on plasma lysophosphatidic acid level in patients with unstable angina. Shaanxi J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2006;27:150–151.
Wang Y, Liu J, Weng Z. Effect of Guanxin No. 2 combination herb on hemorheology. Prac Clin J Integr Tradit Chin West Med (Chin) 1997;10:1427–1430.
Zhang M, Wen JK, Chen X, Xu Z. Experimental study on effects of Guanxin II on plasma lipid, TNF-α, NO and TXA2/ PGI2 in rats. Chin J Tradit Med Sci Technol 2008;15:20–21.
Zeng X, Yang J, Yang X, Hong D, Wu L, Yu J. Effect of Guanxin No. 2 Decoction on gene expression in different areas of the myocardial infarcted heart of rats using microarray technology. J Pharm Pharmacol 2009;61:213–219.
Yu CY, Liu Z, Xu XM, Li YK, Li LD. Effects of Guanxin II on crdiac protein expression after acute myocardial ischemia on rats. China J Chin Mater Med (Chin) 2008;33:1605–1609.
Yu CY, Gao HL, Liu Z, Xu XM, Li YQ, Li LD. Effect of Guanxin No. 2 on gene variant expression profile in rats after myocardial ischemia. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med (Chin) 2008;28:426–430.
Tune JD, Gorman MW, Feigl EO. Matching coronary blood flow to myocardial oxygen consumption. J Appl Physiol 2004;97:404–415.
Razavi HM, Hamilton JA, Feng Q. Modulation of apoptosis by nitric oxide: implications in myocardial ischemia and heart failure. Pharmacol Ther 2005;106:147–162.
Kehrer JP. Cause-effect of oxidative stress and apoptosis. Teratology 2000;62:235–236.
Wattanapitayakul SK, Bauer JA. Oxidative pathways in cardiovascular disease: roles, mechanisms, and therapeutic implications. Pharmacol Ther 2001;89:187–206.
Angiolillo DJ, Guzman LA, Bass TA. Current antiplatelet therapies: benefits and limitations. Am Heart J 2008;156:S3–S9
Haensel A, Mills PJ, Nelesen RA. The relationship between heart rate variability and inflammatory markers in cardiovascular diseases. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2008;33:1305–1312.
Li LD, Liu JX. The pharmacology studies of Jingzhi-Guanxin. J Trad Chin Med (Chin) 1994;5:32.
Chen KJ, Tao SQ, Chen ZJ. The double-blind trial of Jingzhi-Guanxin granula for angina pectoris 112 cases. Chin J Cardiol (Chin) 1982;10:85.
Qu SJ. Therapeutic effect of purified Guanxin Soft Capsule in the treatment of angina of coronary heart disease. J Pract Med Tech (Chin) 2007;14:1425–1426.
Xu R, Huang X, Li Y, Zhang L, Wang L, Cui P. Clinical observation of treating coronary heart disease with Guanxinerhao. J Chengdu Univ Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2001;24:17–19.
Zhu AM, Huo P. Treating 42 cases of senile coronary heart disease with Guanxin-II prescription. Hunan Guid J Tradit Chin Med Pharmacol (Chin) 2002;8:63.
Wang HJ. Clinical obseveration of Guanxin II for angina pectoris in 122 cases. J Pract Med Tech (Chin) 2006;13:3428–3429.
Chen KJ, Qian ZZ, Weng WL. Clinical observation of treating coronary heart disease 100 cases with Huoxue-Chongji. In: Chen KJ, ed. The research of blood stasis syndrome and activating blood to remove blood stasis. Beijing: Peking Medical College & Peking Union Medical College Press;1993:290.
Zhao HL, Liu JL. Clinical observation of treating coronary heart disease with Jiawei Guanxin 2 in 160 cases. J Sichuan Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2006;24:60.
Peng B, Zhao Z. Guanxin II curing coronary heart disease angina pectoris 60 case clinic study. Chin J Pract Chin Modern Med (Chin) 2005;18:948–949.
Yang HW, Yang ZQ, Zhao LC. Angina pectoris of coronary heart disease treated by Shengmai-san and Guanxin II in 109 cases. Guangming J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2005;20:60–61.
Drugs price of Sichuan province. Sichuan Province Medicine Company;2007:23.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30572339 and No. 30325045)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, F., Huang, X. Guanxin II (冠心II号) for the management of coronary heart disease. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 15, 472–476 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-009-0472-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-009-0472-6