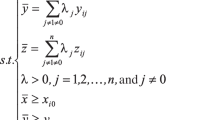Abstract
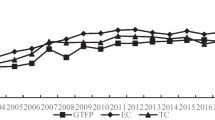
The sustainable development of the economy is a key issue of global concern. Green total factor productivity (GTFP) combining economic growth with resources and the environment can evaluate the quality of economic development comprehensively and accurately. In this paper, super slack-based measure (Super-SBM) model and Malmquist-Luenberger (ML) index were used to calculate GTFP. The trend of industrial GTFP in China’s 30 provinces from 2006–2015 was analyzed. Furtherly, a dynamic panel model was used to discuss the impact of trade openness on GTFP. The results showed that (1) the growth rate of GTFP rose from 2007 to 2011 and declined significantly from 2011 to 2015, and GTFP only achieved positive growth in 2011; (2) the growth rate of GTFP in the eastern region was higher than that in the central and western regions; (3) the trend of technical progress change (MLTECH) index was highly consistent with that of ML index. That was, technical progress played a major role in the variation of GTFP; (4) trade openness could significantly improve China’s GTFP. Every 1% increase in trade openness could increase GTFP by 0.097% on average. It is advisable to implement differentiated economic development and environmental policies in different regions. Meanwhile, relevant measures can be taken to promote import and export trade, such as encouraging companies to increase investment in green technology research and development, optimizing the trade environment.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Afzal M, Hussain I (2010) Export-led growth hypothesis: evidence from Pakistan. J Quant Econ 8(1):130–147
Ahmed EM (2012) Green TFP intensity impact on sustainable East Asian productivity growth. Econ Anal Policy 42(1):67–78
Al-Mulali U, Ozturk I, Lean HH (2015) The influence of economic growth, urbanization, trade openness, financial development, and renewable energy on pollution in Europe. Nat Hazards 79(1):621–644
Baek J, Cho Y, Koo WW (2009) The environmental consequences of globalization: a country-specific time-series analysis. Ecol Econ 68(8-9):2255–2264
Blundell R, Bond S (1998) Initial conditions and moment restrictions in dynamic panel data models. J Econ 87(1):115–143
Charnes A, Cooper WW, Rhodes E (1978) Measuring the efficiency of decision making units. Eur J Oper Res 2(6):429–444
Chen C, Lan Q, Gao M, Sun Y (2018) Green total factor productivity growth and its determinants in China’s industrial economy. Sustainability 10(4):1052
Chung YH, Färe R, Grosskopf S (1997) Productivity and undesirable outputs: a directional distance function approach. J Environ Manag 51(3):229–240
Destek MA, Sinha A (2020) Renewable, non-renewable energy consumption, economic growth, trade openness and ecological footprint: evidence from organisation for economic Co-operation and development countries. J Clean Prod 242:118537
Du KR, Li JL (2019) Towards a green world: how do green technology innovations affect total-factor carbon productivity. Energy Policy 131:240–250
Färe R, Grosskopf S, Pasurka CA Jr (2007) Environmental production functions and environmental directional distance functions. Energy 32(7):1055–1066
Feng C, Huang JB, Wang M (2018) Analysis of green total-factor productivity in China’s regional metal industry: A meta-frontier approach. Res Policy 58:219–229
Feng YJ, Zhong SY, Li QY, Zhao XM, Dong X (2019) Ecological well-being performance growth in China (1994-2014): From perspectives of industrial structure green adjustment and green total factor productivity. J Clean Prod 236:117556
Fu J, Liu Y, Chen R, Yu X, Tang W (2020) Trade openness, internet finance development and banking sector development in China. Econ Model 91:670–678
Hdom HA, Fuinhas JA (2020) Energy production and trade openness: assessing economic growth, CO2 emissions and the applicability of the cointegration analysis. Energy Strateg Rev 30:100488
He W, Tan L, Liu J, Zhang H (2020) Property rights protection, environmental regulation and corporate financial performance: revisiting the Porter Hypothesis. J Clean Prod 264:121615
Hou BQ, Wang B, Du MZ, Zhang N (2020) Does the SO2 emissions trading scheme encourage green total factor productivity? An empirical assessment on China’s cities. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(6):6375–6388
Hye QMA (2012) Long term effect of trade openness on economic growth in case of Pakistan. Qual Quant 46(4):1137–1149
Jiang Y, Wang H, Liu Z (2021) The impact of the free trade zone on green total factor productivity--evidence from the shanghai pilot free trade zone. Energy Policy 148:112000
Keho Y (2017) The impact of trade openness on economic growth: the case of Cote d’Ivoire. Cogent Econ Finance 5(1):1332820
Kim D-H, Lin S-C, Suen Y-B (2016) Trade, growth and growth volatility: new panel evidence. Int Rev Econ Financ 45:384–399
Kong Q, Peng D, Ni Y, Jiang X, Wang Z (2020) Trade openness and economic growth quality of China: empirical analysis using ARDL model. Financ Res Lett 38:101488
Le T-H, Chang Y, Park D (2016) Trade openness and environmental quality: international evidence. Energy Policy 92:45–55
Lei XB, Wu SS (2019) Nonlinear effects of governmental and civil environmental regulation on green total factor productivity in China. Adv Meteorol 2019:8351512
Li B, Wu SS (2017) Effects of local and civil environmental regulation on green total factor productivity in China: a spatial Durbin econometric analysis. J Clean Prod 153(1):342–353
Li H, Fang K, Yang W, Wang D, Hong X (2013) Regional environmental efficiency evaluation in China: analysis based on the Super-SBM model with undesirable outputs. Math Comput Model 58(5-6):1018–1031
Li PS, Chen YY (2019) The influence of enterprises’ bargaining power on the green total factor productivity effect of environmental regulation-evidence from China. Sustainability 11(18):4910
Li TH, Liao GK (2020) The heterogeneous impact of financial development on green total factor productivity. Front Energy Res 8:29
Li XM, Shi PF, Han YZ, Deng AM, Liu D (2020) Measurement and spatial variation of green total factor productivity of the tourism industry in China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(4):1159
Lin BQ, Chen ZY (2018) Does factor market distortion inhibit the green total factor productivity in China? J Clean Prod 197:25–33
Lin BQ, Xu MM (2019) Exploring the green total factor productivity of China’s metallurgical industry under carbon tax: a perspective on factor substitution. J Clean Prod 233:1322–1333
Liu ZK, Xin L (2019) Has China’s Belt and Road Initiative promoted its green total factor productivity ? - Evidence from primary provinces along the route. Energy Policy 129:360–369
Lu XH, Jiang X, Gong MQ (2020) How land transfer marketization influence on green total factor productivity from the approach of industrial structure? Evidence from China Land Use Policy 95:104610
Majumder MK, Raghavan M, Vespignani J (2020) Oil curse, economic growth and trade openness. Energy Econ 91:104896
Managi S, Hibiki A, Tsurumi T (2009) Does trade openness improve environmental quality? J Environ Econ Manag 58(3):346–363
Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China (2020) China environmental bulletin 2019. http://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/sthjzk/zghjzkgb/202006/P020200602509464172096.pdf. Accessed 04 November 2020
National Bureau of Statistics (2020) Growth rate of industrial added value of Industrial enterprises above designated size. https://data.stats.gov.cn/tablequery.htm?code=AD01. Accessed 04 Nov 2020
Rahman MM, Mamun SAK (2016) Energy use, international trade and economic growth nexus in Australia: new evidence from an extended growth model. Renew Sust Energ Rev 64:806–816
Rahman MM, Saidi K, Mbarek MB (2020) Economic growth in South Asia: the role of CO2 emissions, population density and trade openness. Heliyon 6(5):e03903
Ramzan M, Sheng B, Shahbaz M, Song J, Jiao Z (2019) Impact of trade openness on GDP growth: does TFP matter? J Int Trade Econ Dev 28(8):960–995
Shahbaz M (2012) Does trade openness affect long run growth? Cointegration, causality and forecast error variance decomposition tests for Pakistan. Econ Model 29(6):2325–2339
Shahbaz M, Tiwari AK, Nasir M (2013) The effects of financial development, economic growth, coal consumption and trade openness on CO2 emissions in South Africa. Energy Policy 61:1452–1459
Shen N, Liao H, Deng R, Wang Q (2019) Different types of environmental regulations and the heterogeneous influence on the environmental total factor productivity: empirical analysis of China's industry. J Clean Prod 211:171–184
Solarin SA, Shahbaz M (2015) Natural gas consumption and economic growth: the role of foreign direct investment, capital formation and trade openness in Malaysia. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 42:835–845
Solow RM (1957) Technical change and the aggregate production function. Rev Econ Stat 39:312–320
Song ML, Du JT, Tan KH (2018) Impact of fiscal decentralization on green total factor productivity. Int J Prod Econ 205:359–367
Tiba S, Belaid F (2020) The pollution concern in the era of globalization: do the contribution of foreign direct investment and trade openness matter? Energy Econ 92:104966
Tone K (2001) A slacks-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur J Oper Res 130(3):498–509
Tone K (2002) A slacks-based measure of super-efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur J Oper Res 143(1):32–41
Tone K (2004) Dealing with undesirable outputs in DEA: a slacks-based measure (SBM) approach. Presentation At NAPW, Toronto, pp 44–45
Wang K-L, Pang S-Q, Ding L-L, Miao Z (2020) Combining the biennial Malmquist–Luenberger index and panel quantile regression to analyze the green total factor productivity of the industrial sector in China. Sci Total Environ 739:140280
Wang XL, Sun CZ, Wang S, Zhang ZX, Zou W (2018) Going green or going away? A spatial empirical examination of the relationship between environmental regulations, biased technological progress, and green total factor productivity. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15(9):1917
Wen H, Dai J (2020) Trade openness, environmental regulation, and human capital in China: based on ARDL cointegration and Granger causality analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(2):1789–1799
World Bank (2014a) CO2 intensity (kg per kg of oil equivalent energy use). https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/EN.ATM.CO2E.EG.ZS?view=chart. Accessed 04 Nov 2020
World Bank (2014b) Energy use (kg of oil equivalent per capita). https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/EG.USE.PCAP.KG.OE?view=chart. Accessed 04 Nov 2020
World Bank (2016) PM2.5 air pollution, mean annual exposure (micrograms per cubic meter). https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/EN.ATM.PM25.MC.M3?end=2016&start=1990&view=chart. Accessed 04 Nov 2020
World Bank (2020) GDP per capita growth (annual %). https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GDP.PCAP.KD.ZG?end=2019&locations=CN&start=1960&view=chart. Accessed 04 Nov 2020
Wu H, Ren S, Yan G, Hao Y (2020) Does China’s outward direct investment improve green total factor productivity in the “Belt and Road” countries? Evidence from dynamic threshold panel model analysis. J Environ Manag 275:111295
Xin BG, Qu YM (2019) Effects of smart city policies on green total factor productivity: evidence from a quasi-natural experiment in China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16(13):2396
Yuan B, Zhang Y (2020) Flexible environmental policy, technological innovation and sustainable development of China’s industry: The moderating effect of environment regulatory enforcement. J Clean Prod 243:118543
Zhang C, Liu H, Bressers HTA, Buchanan KS (2011) Productivity growth and environmental regulations - accounting for undesirable outputs: Analysis of China’s thirty provincial regions using the Malmquist–Luenberger index. Ecol Econ 70(12):2369–2379
Zhang S (2018) Is trade openness good for environment in South Korea? The role of non-fossil electricity consumption. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(10):9510–9522
Zhang W, Meng J, Tian X (2020) Does de-capacity policy enhance the total factor productivity of China’s coal companies? A Regression Discontinuity design. Res Policy 68:101741
Zhou YY, Xu YR, Liu CZ, Fang ZQ, Fu XY, He MZ (2019) The threshold effect of China’s financial development on green total factor productivity. Sustainability 11(14):3776
Zhu XH, Chen Y, Feng C (2018) Green total factor productivity of China’s mining and quarrying industry: a global data envelopment analysis. Res Policy 57:1–9
Acknowledgements
The authors greatly appreciate useful discussion of Yun Pan of Shanghai University, and we are very grateful to the reviewers for their insightful comments and careful review.
Funding
This research was funded by the Green Manufacturing System Integration Project in 2018 of the Jiangnan Shipyard (Group) Corporation Limited.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Lili Ding, Mingliang Wu, Zheng Jiao, and Yongyou Nie. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Lili Ding and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Nicholas Apergis
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Table 6 displays the correlation coefficients of the variables used in this paper.
Table 7 presents the descriptive statistics of the variables in the east, central and west regions.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, L., Wu, M., Jiao, Z. et al. The positive role of trade openness in industrial green total factor productivity—provincial evidence from China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 6538–6551 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16164-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16164-8