Abstract
Objective
The present work was carried out to investigate the effects of temperature, initial pH, initial concentration, and contact time on the biosorption of lead (Pb) and cadmium (Cd) by modified stalk sponge of Zea mays using a batch technique.
Methods
The biomass was chemically modified with a 0.1 M NaCl solution. The lead and cadmium sorption process was evaluated at 20°C, 30°C, 40°C, and 50°C.
Results
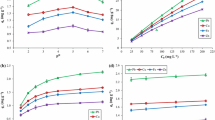
The results showed that the modified stalk sponge of Z. mays had a good capacity for biosorption of Pb(II) and Cd(II). The kinetic behavior was described by the pseudo-second-order model for both metallic species. The experimental isotherms obtained at different temperatures were fit with Langmuir and Freundlich models. Thermodynamic parameters ΔH 0 and ΔS 0 were calculated using the van’t Hoff equation, and the results show that Pb(II) and Cd(II) sorption by modified stalk sponge of Z. mays is an exothermic and spontaneous process.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abia AA, Igwe JC (2005) Sorption kinetics and intraparticulate diffusivities of Cd, Pb and Zn ions on maize cob. Afr J Biotechnol 4:509–512
Adebajo MO, Frost RL (2004) Infrared and 13 C MAS nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopic study of acetylation of cotton. Spectrochim Acta A 60:449–453
Apiratikul R, Pavasant P (2008) Batch and column studies of biosorption of heavy metals by Caulerpa lentillifera. Bioresour Technol 99:2766–2777
Babarinde NAA, Babalola JO, Adegboye KA (2008) Kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic studies of the biosorption of cadmium (II) by snail (Lymnaea rufescens) shell. J Appl Sci Res 4:1420–1427
Chen G, Zeng G, Tang L, Du C, Jiang X, Huang G, Liu H, Shen G (2008) Cadmium removal from simulated wastewater to biomass byproduct of Lentinus edodes. Bioresour Technol 99:7034–7040
Dabrowski A (2001) Adsorption—from theory to practice. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 93:135–224
Doyurum S, Çelik A (2006) Pb(II) and Cd(II) removal from aqueous solutions by olive cake. J Hazard Mater 138:22–28
El-Sherif IY, Ashmawy A, Badr S (2008) Biosorption of cadmium and nickel by Nile water algae. J Appl Sci Res 4:391–396
Garg U, Kaur MP, Jawa GK, Sud D, Garg VK (2008) Removal of cadmium (II) from aqueous solutions by adsorption on agricultural waste biomass. J Hazard Mater 154:1149–1157
Hashem MA (2007) Adsorption of lead ions from aqueous solution by okra wastes. Int J Phys Sci 2:178–184
Ho YS, Ng JCY, McKay G (2001) Removal of lead(II) from effluents by sorption on peat using second-order kinetics. Separ Sci Technol 36:241–261
Horn JR, Russell D, Lewis EA, Murphy KP (2001) Van’t Hoff and calorimetric enthalpies from isothermal titration calorimetry: are there significant discrepancies? Biochemistry 40:1774–1778
Izanloo H, Nasseri S (2005) Cadmium removal from aqueous solutions by Ground Pine Cone. Iran J Environ Health Sci Eng 2:33–42
Li S, Jin-lan X, Huan H, Zhen-yuan N (2008) Comparative study on biosorption of Pb(II) and Cr(VI) by Synechococcus sp. T Nonferr Metal Soc 18:1336–1342
Liang CY, Marchessault RH (1959) Infrared spectra of crystalline polysaccharides. I. Hydrogen bonds in native cellulose. J Polym Sci 37:385–395
Llanes-Monter MM, Olguín MT, Solache-Ríos MJ (2006) Lead sorption by a Mexican, clinoptilolite-rich tuff. Environ Sci Pollut R 14:397–403
Mane VS, Babu PVV (2011) Studies on the adsorption of brilliant green dye from aqueous solution onto low-cost NaOH treated saw dust. Desalination 273:321–329
Müllerová H, Kruml O, Vybíhal K, Zeman J, Müller P (2003) Adsorption of copper and cadmium from aqueous solution by various types of sediments under static and dynamic conditions. B Geosci 78:169–178
Nuhoglu Y, Malkoc E, Gürses A, Canpolat N (2002) The removal of Cu (II) from aqueous solutions by Ulothrix zonata. Bioresour Technol 85:331–333
Park D, Yun YS, Park JM (2005) Studies on hexavalent chromium biosorption by chemically-treated biomass of Ecklonia. Chemosphere 60:1356–1364
Pehlivan E, Altun T, Parlayıcı S (2009) Utilization of barley straws as biosorbents for Cu2+ and Pb2+ ions. J Hazard Mater 164:982–986
Rudziński W, Panas G, Charmas R (2000) A combined temperature–calorimetric study of ion adsorption at the hematite–electrolyte interface: I. Model of a homogeneous oxide surface. J Phys Chem B 104:11912–11922
Shin EW, Rowell RM (2005) Cadmium ion sorption onto lignocellulosic biosorbent modified by sulfonation: the origin of sorption capacity improvement. Chemosphere 60:1054–1061
Sun Y, Lin L, Deng H, Li J, He B, Sun R, Ouyang P (2008) Structural changes of bamboo cellulose in formic acid. Bioresources 3:297–315
Tsai SC, Juang KW, Jan YL (2005) Sorption of cesium on rocks using heterogeneity based isotherm models. J Radioanal Nucl Ch 266:101–105
Vilar VJP, Botelho CMS, Boaventura RAR (2007) Kinetics and equilibrium modelling of lead uptake by algae Gelidium and algal waste from agar extraction industry. J Hazard Mater 143:396–408
Vilar VJP, Santos SCR, Martins RJE, Botelho CMS, Boaventura RAR (2008) Cadmium uptake by algal biomass in batch and continuous (CSTR and packed bed column) adsorbers. Biochem Eng J 42:276–289
Yan G, Viraraghavan T (2000) Effect of pretreatment on the bioadsorption of heavy metals on Mucor rouxii. Water SA 26:119–123
Yu XZ, Gu JD (2010) Effect of temperature on removal of iron cyanides from solution by maize plants. Environ Sci Pollut R 17:106–114
Yuan HP, Zhang JH, Lu ZM, Min H, Wu C (2009) Studies on biosorption equilibrium and kinetics of Cd2+ by Streptomyces sp. K33 and HL-12. J Hazard Mater 164:423–431
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the technician in the laboratory of the Department of Electron Microscopy. M. T. Olguin thanks the partial financial support of CONACyT (project 131174-Q).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Vera Slaveykova
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
García-Rosales, G., Olguin, M.T., Colín-Cruz, A. et al. Effect of the pH and temperature on the biosorption of lead(II) and cadmium(II) by sodium-modified stalk sponge of Zea mays . Environ Sci Pollut Res 19, 177–185 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-011-0537-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-011-0537-x