Abstract
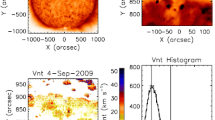
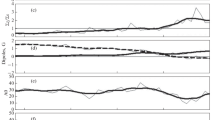
We compare the shape and position of some plasma formations visible in the polar corona with the cyclic evolution of the global magnetic field. The first type of object is polar crown prominences. A two-fold decrease of the height of polar crown prominences was found during their poleward migration from the middle latitudes to the poles before a polar magnetic field reversal. The effect could be assigned to a decrease of the magnetic field scale. The second type of object is the polar plumes, ray like structures that follow magnetic field lines. Tangents to polar ray structures are usually crossed near some point, “a magnetic focus,” below the surface. The distance q between the focus and the center of the solar disk changes from the maximum value about 0.65 R ⊙ at solar minimum activity to the minimum value about 0.45 R ⊙ at solar maximum. At first glance this behaviour seems to be contrary to the dynamics of spherical harmonics of the global magnetic field throughout a cycle. We believe that the problem could be resolved if one takes into account not only scale changes in the global magnetic field but also the phase difference in the cyclic variations of large-scale and small-scale components of the global field.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, J. and Pneuman, G. W.: 1976, Solar Phys. 46, 185.
Altschuler, M. D. and Newkirk, G. Jr.: 1969, Solar Phys. 9, 131.
Altschuler, M. D., Levine, R. H., Stix, M., and Harvey, J. W.: 1977, Solar Phys. 51, 345.
Boguslavskaya, E. Ya.: 1958, in Total solar eclipses of 25 Feb. 1952 and 30 June 1954, Sov. Acad Sci. Press, p. 100.
Bravo, S., Stewart, G. A., and Blanco-Cano, X.: 1998, Solar Phys. 179, 223.
Chapman, S. and Bartels, J.: 1940, Geomagnetism, Oxford University Press, London.
Dzubenko, N. I.: 1957, Astron. Zh. 34, 379.
Ermakov, F. A., Obridko, V. N., and Shelting B. D.: 1995, Astron. Rep. 39, 672.
Filippov, B. P. and Den, O. G.: 2000, Astron. Lett. 26, 322.
Filippov, B. P. and Den, O. G.: 2001, J. Geophys. Res. 106, 25177.
Filippov, B. P., Platov, Yu. V., Ajabshirizadeh, A., and Klepikov D. V.: 2004, Astron. Rep. 48, 781.
Gulyaev, R. A.: 1998, in Solar Jets and Coronal Plumes, ESA SP-421, p. 277.
Hoeksema, J. T., Wilcox, J. M., and Scherrer, P. H.: 1982, J. Geophys. Res. 87, 10331.
Koutchmy, S. and Bocchialini, K.: 1998, in Solar Jets and Coronal Plumes, ESA SP-421, p. 51.
Makarov, V. I.: 1994, Solar Phys. 150, 359.
Makarov, V. I.: 1998, in K. S. Balasubramaniam, J. Harvey and D. Rabin (eds.), Proc. 18th NSO Workshop, ASP Conference Series, 140, p. 83.
Makarov, V. I. and Filippov, B. P.: 2003, Solar Phys. 214, 55.
Makarov, V. I. and Sivaraman, K. R.: 1983, Solar Phys. 85, 227.
Makarov, V. I., Tlatov, A. G., and Sivaraman, K. R.: 2001, Solar Phys. 202, 11.
McIntosh, P. S.: 1972, Rev. Geophys. Space Phys. 10, 837.
McIntosh, P. S.: 1992, in K. L. Harvey (ed.), The Solar Cycle, Astron. Soc. Pac. Conf. Ser. 27, Astron. Soc. of the Pacific, San Francisco, Calif., 14.
Nesmyanovich, A. T.: 1962, Astron. Zh., 39, 996.
Nikolsky, G. M.: 1953, Astron. Zh. 30, 286.
Saito, K.: 1958, PASJ 10, 49.
Schatten, K. H., Wilcox, J. M., and Ness, N. F.: 1969, Solar Phys. 6, 442.
Svalgaard, L., Duvall, T. L., Jr., and Scherrer, P. H.: 1978, Solar Phys. 58, 225.
Tsubaki, T., Tominaya, S., Kubota, J., and Kawagushi, I.: 1964, PASJ 16, 13.
Vsekhsviatsky, S. K. and Nikolsky, G. M.: 1955, Astron. Zh. 32, 354.
Waldmeier, M.: 1965, Zs. Astrophys. 61, 186.
Wang, Y.-M. and Sheeley, N. R, Jr.: 1992, Astrophys. J. 392, 310.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Filippov, B.P., Platov, Y.V., Ajabshirizadeh, A. et al. Polar Coronal Structures and the Global Magnetic Field Evolution Through the Cycle. Sol Phys 224, 277–284 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-005-4280-7
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-005-4280-7