Abstract
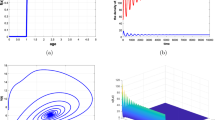
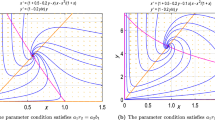
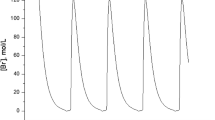
This paper studies systematically a Bedd-ington–DeAngelis prey–predator system with harvesting and impulsive state feedback control. Conditions for existence and stability of predator-free periodic solution are obtained. When the predator-free periodic solution loses its stability, the existence and stability of nontrivial period solution are also established. Furthermore, computer simulations show that this impulsive system displays a series of complex phenomena, including period-doubling bifurcation and cascade, period window, and chaotic bands. Through numerical simulation, it is also observed that capture capability can influence the amount of predator released and the interval of the stability for nontrivial period-1 solution. Moreover, the superiority of impulsive state feedback control strategy is also exhibited over the impulsive fixed-time control.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kar, T.K., Pahari, U.K.: Modeling and analysis of a prey-predator system with stage-structure and harvesting. Nonlinear Anal., Real World Appl. 8(2), 601–609 (2007)
Lenzini, P., Rebaza, J.: Nonconstant preydator harvesting on ratio-dependent predator-prey models. Appl. Math. Sci. 4(16), 791–803 (2010)
Xiao, D.M., Li, W.X., Han, M.A.: Dynamics in ratio-dependent predator-prey model with predator harvesting. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 324(1), 14–29 (2006)
Liu, Z.J., Tan, R.H.: Impulsive harvesting and stocking in a Monod–Haldane functional response predator-prey system. Chaos Solitons Fractals 34(2), 454–464 (2007)
Vayenas, D.V., Pavlou, S.: Chaotic dynamics of a food web in a chemostat. Math. Biosci. 162(1–2), 69–84 (1999)
Wang, F.Y., Hao, C.P., Chen, L.S.: Bifurcation and chaos in a Monod–Haldene type food chain chemostat with pulsed input and washout. Chaos Solitons Fractals 32(1), 181–194 (2007)
Geritz, S.A.H., Kisdi, É., Yan, P.: Evolutionary branching and long-term coexistence of cycling predators: critical function analysis. Theor. Popul. Biol. 71(4), 424–435 (2007)
Haque, M., Venturino, E.: The role of transmissible diseases in the Holling–Tanner predator-prey model. Theor. Popul. Biol. 70(3), 273–288 (2006)
Huang, Y.J., Chen, F.D., Zhong, L.: Stability analysis of a prey-predator model with Holling type III response function incorporating a prey refuge. Appl. Math. Comput. 182(1), 672–683 (2006)
Jiang, G.R., Lu, Q.S.: Impulsive state feedback control of a predator-prey model. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 200(1), 193–207 (2007)
Jiang, G.R., Lu, Q.S., Qian, L.N.: Complex dynamics of a Holling type II prey-predator system with state feedback control. Chaos Solitons Fractals 31(2), 448–461 (2007)
Jiao, J.J., Meng, X.Z., Chen, L.S.: A stage-structured Holling mass defence predator-prey model with impulsive perturbations on predators. Appl. Math. Comput. 189(2), 1448–1458 (2007)
Xu, R., Chaplain, M.A.J., Davidson, F.A.: Periodic solutions for a predator-prey model with Holling-type functional response and time delays. Appl. Math. Comput. 161(2), 637–654 (2005)
Kooij, R.E., Zegeling, A.: A predator-prey model with Iliev’s functional response. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 198(2), 473–489 (1996)
Sugie, J.: Two-parameter bifurcation in a predator-prey system of Ivlev type. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 217(2), 349–371 (1998)
Cantrell, R.S., Cosner, C.: On the dynamics of predator-prey models with the Beddington–DeAngelis functional response. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 257(1), 206–222 (2001)
Lu, Z.H., Chi, X.B., Chen, L.S.: Impulsive control strategies in biological control of pesticide. Theor. Popul. Biol. 64(1), 39–47 (2003)
Simeonov, P.E., Bainov, D.D.: Orbital stability of periodic solutions of autonomous systems with impulse effect. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 19, 2562–2585 (1988)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (60974004) and Liaoning Provincial Foundation of Science and Technology (20082023).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Zhang, Q. & Zhang, X. Dynamical behavior of a class of prey-predator system with impulsive state feedback control and Beddington–DeAngelis functional response. Nonlinear Dyn 70, 1511–1522 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-012-0551-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-012-0551-7