Abstract
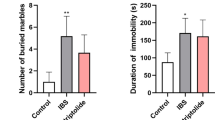
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is induced by dysfunction of central nervous and peripheral intestinal systems, which affects an estimated 10–15 % population worldwide annually. Stress-related psychiatric disorders including depression and anxiety are often comorbid with gastrointestinal function disorder, such as IBS. However, the mechanism of IBS still remains unknown. Curcumin is a biologically active phytochemical presents in turmeric and has pharmacological actions that benefit patients with depression and anxiety. Our study found that IBS rats showed depression- and anxiety-like behaviors associated with decreased 5-HT (serotonin), BDNF (Brain-derived neurotrophic factor) and pCREB (phosphorylation of cAMP response element-binding protein) expression in the hippocampus after chronic acute combining stress (CAS). However, these decreased parameters were obviously increased in the colonic after CAS. Curcumin (40 mg/kg) reduced the immobility time of forced swimming and the number of buried marbles in behavioral tests of CAS rats. Curcumin also decreased the number of fecal output and abdominal withdrawal reflex (AWR) scores in response to graded distention. Moreover, curcumin increased serotonin, BDNF and pCREB levels in the hippocampus, but they were decreased in the colonic of CAS rats. 5-HT1A receptor antagonist NAN-190 reversed the effects of curcumin on behaviors and the changes of intestine, pCREB and BDNF expression, which are related to IBS. These results suggested that curcumin exerts the effects on IBS through regulating neurotransmitters, BDNF and CREB signaling both in the brain and peripheral intestinal system.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul-Baki H, El Ihab I, Hajj LEZ, Azar C, Aoun E, Skoury A, Chaar H, Sharara AI (2009) A randomized controlled trial of imipramine in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. World J Gastroenterol 15:3636–3642
Al-Chaer ED, Kawasaki M, Pasricha PJ (2000) A new model of chronic visceral hypersensitivity in adult rats induced by colon irritation during postnatal development. Gastroenterology 119:1276–1285
Bambico FR, Nguyen NT, Gobbi G (2009) Decline in serotonergic firing activity and desensitization of 5-HT1A autoreceptors after chronic unpredictable stress. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 19:215–228
Barone FC, Deegan JF, Price WJ, Fowler PJ, Fondacaro JD, Ormsbee HS 3rd (1990) Cold-restraint stress increases rat fecal pellet output and colonic transit. Am J Physiol 258:G329–G337
Bian ZX, Zhang M, Han QB, Xu HX, Sung JJ (2010) Analgesic effects of JCM-16021 on neonatal maternal separation-induced visceral pain in rats. World J Gastroenterol 16:837–845
Bueno L, Fioramonti J (2002) Visceral perception: inflammatory and non-inflammatory mediators. Gut 51(Suppl 1):i19–i23
Clouse RE (2003) Antidepressants for irritable bowel syndrome. Gut 52:598–599
Drossman DA, Camilleri M, Mayer EA, Whitehead WE (2002) AGA technical review on irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 123:2108–2131
Dunlop SP, Coleman NS, Blackshaw E, Perkins AC, Singh G, Marsden CA, Spiller RC (2005) Abnormalities of 5-hydroxytryptamine metabolism in irritable bowel syndrome. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 3:349–357
Franklin KPG (1997) The rat brain in tereotaxic coordinates
Friedrich M, Grady SE, Wall GC (2010) Effects of antidepressants in patients with irritable bowel syndrome and comorbid depression. Clin Ther 32:1221–1233
Garnett WR (1999) Management of irritable bowel syndrome. J Am Soc Consult Pharmac 14(suppl 8)
Gershon MD, Tack J (2007) The serotonin signaling system: from basic understanding to drug development for functional GI disorders. Gastroenterology 132:397–414
Holt PR, Katz S, Kirshoff R (2005) Curcumin therapy in inflammatory bowel disease: a pilot study. Dig Dis Sci 50:2191–2193
Jailwala J, Imperiale TF, Kroenke K (2000) Pharmacologic treatment of the irritable bowel syndrome: a systematic review of randomized, controlled trials. Ann Intern Med 133:136–147
Johansson M, Norrgard O, Forsgren S (2007) Study of expression patterns and levels of neurotrophins and neurotrophin receptors in ulcerative colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 13:398–409
Kirkup AJ, Brunsden AM, Grundy D (2001) Receptors and transmission in the brain-gut axis: potential for novel therapies. I. Receptors on visceral afferents. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 280:G787–G794
Li Y, Deuring J, Peppelenbosch MP (2012) STAT1, STAT6 and Adenosine 3′,5 ′-Cyclic Monophosphate (cAMP) Signaling Drive SOCS3 Expression in Inactive Ulcerative Colitis. Mol Med 18:1412–1419
Longstreth GF, Thompson WG, Chey WD, Houghton LA, Mearin F, Spiller RC (2006) Functional bowel disorders. Gastroenterology 130:1480–1491
Lydiard RB (2001) Irritable bowel syndrome, anxiety, and depression: What are the links? J Clin Psychiatry 62(suppl 8):38–45
Mattson MP, Maudsley S, Martin B (2004) BDNF and 5-HT: a dynamic duo in age-related neuronal plasticity and neurodegenerative disorders. Trends Neurosci 27:589–594
Ness TJGG (1988) Colorectal distension as a noxious visceral stimulus: physiologic and pharmacologic characterization of pseudaffective reflexes in the rat. Brain Res 450:153–169
Nitta A, Furukawa Y, Hayashi K, Hiramatsu M, Kameyama T, Hasegawa T, Nabeshima T (1992) Denervation of dopaminergic neurons with 6-hydroxydopamine increases nerve growth factor content in rat brain. Neurosci Lett 144:152–156
Njung’e K, Handley SL (1991) Effects of 5-HT uptake inhibitors, agonists and antagonists on the burying of harmless objects by mice; a putative test for anxiolytic agents. Br J Pharmacol 104:105–112
Porsolt RD, Bertin A, Jalfre M (1977) Behavioral despair in mice: a primary screening test for antidepressants. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 229:327–336
Porsolt RD, Bertin A, Jalfre M (1978) “Behavioural despair” in rats and mice: strain differences and the effects of imipramine. Eur J Pharmacol 51:291–294
Qiao LY, Gulick MA, Bowers J, Kuemmerle JF, Grider JR (2008) Differential changes in brain-derived neurotrophic factor and extracellular signal-regulated kinase in rat primary afferent pathways with colitis. Neurogastroenterol Motil 20:928–938
Rahimi R, Nikfar S, Rezaie A, Abdollahi M (2009) Efficacy of tricyclic antidepressants in irritable bowel syndrome: A meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol 15:1548–1553
Ren TH, Wu J, Yew D, Ziea E, Lao L, Leung WK, Berman B, Hu PJ, Sung JJ (2007) Effects of neonatal maternal separation on neurochemical and sensory response to colonic distension in a rat model of irritable bowel syndrome. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 292:G849–G856
Schneider T, Popik P (2007) Attenuation of estrous cycle-dependent marble burying in female rats by acute treatment with progesterone and antidepressants. Psychoneuroendocrinology 32:651–659
Siuciak JA, Altar CA, Wiegand SJ, Lindsay RM (1994) Antinociceptive effect of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3. Brain Res 633:326–330
Siuciak JA, Boylan C, Fritsche M, Altar CA, Lindsay RM (1996) BDNF increases monoaminergic activity in rat brain following intracerebroventricular or intraparenchymal administration. Brain Res 710:11–20
Talley NJ, Owen BK, Boyce P, Paterson K (1996) Psychological treatments for irritable bowel syndrome: a critique of controlled treatment trials. Am J Gastroenterol 91:277–283
Wheatcroft J, Wakelin D, Smith A, Mahoney CR, Mawe G, Spiller R (2005) Enterochromaffin cell hyperplasia and decreased serotonin transporter in a mouse model of postinfectious bowel dysfunction. Neurogastroenterol Motil 17:863–870
Wu JC, Ziea ET, Lao L, Lam EF, Chan CS, Liang AY, Chu SL, Yew DT, Berman BM, Sung JJ (2010) Effect of electroacupuncture on visceral hyperalgesia, serotonin and fos expression in an animal model of irritable bowel syndrome. J Neurogastroenterol Motil 16:306–314
Xu YX, Pindolia KR, Janakiraman N, Noth CJ, Chapman RA, Gautam SC (1997) Curcumin, a compound with anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant properties, down-regulates chemokine expression in bone marrow stromal cells. Exp Hematol 25:413–422
Xu Y, Ku BS, Yao HY, Lin YH, Ma X, Zhang YH, Li XJ (2005a) Antidepressant effects of curcumin in the forced swim test and olfactory bulbectomy models of depression in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 82:200–206
Xu Y, Ku BS, Yao HY, Lin YH, Ma X, Zhang YH, Li XJ (2005b) The effects of curcumin on depressive-like behaviors in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 518:40–46
Xu Y, Ku B, Tie L, Yao H, Jiang W, Ma X, Li X (2006) Curcumin reverses the effects of chronic stress on behavior, the HPA axis, BDNF expression and phosphorylation of CREB. Brain Res 1122:56–64
Xu Y, Ku B, Cui L, Li X, Barish PA, Foster TC, Ogle WO (2007) Curcumin reverses impaired hippocampal neurogenesis and increases serotonin receptor 1A mRNA and brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in chronically stressed rats. Brain Res 1162:9–18
Yeo ABP, Lumsden S (2004) Association between a functional polymorphism in the serotonin transporter gene and diarrhea predominant irritable bowel syndrome in women. Gut 53:1452Y–1458Y
Yu YB, Zuo XL, Zhao QJ, Chen FX, Yang J, Dong YY, Wang P, Li YQ (2012) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor contributes to abdominal pain in irritable bowel syndrome. Gut 61:685–694
Zou N, Lv H, Li J, Yang N, Xue H, Zhu J, Qian J (2008) Changes in brain G proteins and colonic sympathetic neural signaling in chronic-acute combined stress rat model of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Transl Res 152:283–289
Acknowledgments
The authors do not have financial or personal conflicts of interest associated with this work.
The project was sponsored by the foundation of Science Technology Department of Zhejiang Province (No. 2012C33118) and Natural Science and Technology Foundation of Zhejiang Province (No. Y2110896).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, Y., Wu, S., Li, J. et al. The effect of curcumin on the brain-gut axis in rat model of irritable bowel syndrome: involvement of 5-HT-dependent signaling. Metab Brain Dis 30, 47–55 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-014-9554-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-014-9554-z