Abstract
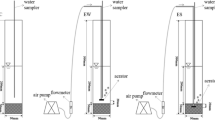
San Vicente Bay is a coastal shallow embayment in Central Chile with multiple uses, one of which is receiving wastewater from industrial fisheries, steel mill effluents, and domestic sewage. A simulation model was developed and applied to dissolved oxygen consumption by organic residues released into this embayment. Three compartments were established as function of: depth, circulation and outfall location. The model compartments had different volumes, and their oxygen saturation value was used as baseline. The parameters: (a) BOD5 of the industrial and urban effluents, (b) oxygen demand by organic sediments, (c) respiration, (d) photosynthesis and (e) re-aeration were included in the model. Iteration results of the model showed severe alterations in Compartment 1, with a decrease of 65% in the oxygen below saturation. Compartment 2 showed a small decline (10%) and compartment 3 did not show apparent changes in oxygen values. Measures recommended for remediation were to decrease the BOD5 loading by 30% in the affected sector. Iteration of the model for 200 h following recommendations derived from the preceding results produced an increase in saturation of 60% (5 ml O2 L−1), which suggested an improvement of the environmental conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- V :
-
volume of the compartment
- c :
-
oxygen saturation for temperature and salinity (Lm−3) for the compartment (n)
- Q :
-
inflows (e) or arrow/outflows (s) or arrow for the compartment (n)
- S :
-
Oxygen sources and sinks within the compartment
- Uw :
-
wind velocity at 10 m above the water surface (m s−1)
- kL :
-
reaeration constant, ms−1
- A :
-
surface and bottom areas of compartments (m2) ( n ) = compartment
- k 1 :
-
deoxygenating constant, 1/day
- BOD5 :
-
biochemical oxygen demand
- SB:
-
sediment oxygen demand [ml O2 m−2 s−1]
References
Ahumada, R.: 1992, ‘Patrones de distribución de metales traza (Cr, Ni, Zn, Cu, Cd y Pb) en sedimentos superficiales de Bahía San Vicente, Chile’, Revista Biología Marina Valparaíso 27(2), 265–282.
Ahumada, R.: 1995, ‘Bahías: áreas de uso múltiple, un enfoque holístico al problema de contaminación’, Ciencia y Tecnología del Mar, Cona. No. Especial, 59–68.
Ahumada, R. and Rudolph, A.: 1989, ‘Residuos líquidos de la industria pesquera: Alteraciones ambientales y estrategias de eliminación’, Amb. y Des. 5(1), 147–161.
Ahumada, R. and Vargas, J.: 2004, ‘Sedimentation rate of trace metals in San Vicente Bay, Chile’, Environ. Monit. Assess. 100, 11–22.
Ahumada, R., Rudolph, A., Madariaga, S. and Carrasco, F.: 1989, ‘Descripción de las condiciones oceanográficas de la Bahía San Vicente y antecedentes sobre los efectos de la contaminación’, Biología Pesquera 18, 37–52.
Ahumada, R., Pinto, L. and Camus, P.: 2000, ‘The Chilean Coast’, in: Ch. R. C. Sheppard (ed.). The Seas at the Millenium: An Environmental Evaluation. Elsevier Science, Pergamon Press, London, I, Chapter 45, pp. 699–717.
Ahumada, R., Rudolph, A. and Contreras, S.: 2004, ‘Evaluation of coastal waters receiving fish procesing waste: Lota bay as a case of study’, Environ. Monit. Assess. 90, 89–99.
Arcos, D., Ahumada, R., Nuñez, S., Furet, L. and Vargas, L.: 1992, ‘Evaluación de impacto ambiental entorno al ecosistema de Bahía de San Vicente, Chile', Informe Técnico. Instituto de Investigación Pesquera, Derechos de Autor No. 83602, 700 pp.
Byers, Sch., Mills, C. E. L. and Steward, P. L.: 1978, ‘A comparison of methods of determining organic carbon in marine sediments, with suggestion for a standard method’, Hidrobiologia 58(1), 43–47.
Carrasco, F. D. and Carbajal, W.: 1995, ‘Enriquecimiento orgánico de los sedimentos y el tamaño de los organismos macrobentónicos de la Bahía de San Vicente, Chile central’, Gayana Oceanol. 3, 89–98.
Carrasco, F. D. and Gallardo, V. A.: 1989, ‘La contaminación marina y el valor de la macrofauna bentónica en su evaluación y monitoreo: Casos de estudio en el litoral de Concepción, Chile’, Biología Pesquera 18, 15–27.
Clesceri, L., Greenberg, A. and Eaton, A.: 1999, Standard Methods for Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC, 1268 pp.
Chapra, S.: 1997, Surface Water Quality Modeling, Ed. WCB/McGraw-Hill, 844 pp.
Díaz, R. J. and Rosenberg, R.: 1995, ‘Marine Benthic Hypoxia: A review of its ecological effects and the behavioral responses of benthic macrofauna’, Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Ann. Rev. 33, 215–303.
Pradenas, E. and Rudolph, A.: 1989, ‘Comparación del impacto ambiental en Bahía Concepción producido por los residuos de las plantas de harina, aceite y congelados’, Biología Pesquera 18, 115–122.
Rudolph, A.: 1995, ‘Alteraciones en el ambiente costero producido por material orgánico proveniente de la industria pesquera: un caso de estudio’, Ciencia y Tecnología del Mar, CONA No. Especial, pp. 69–78.
Rudolph, A., Ahumada, R. and Pérez C.: 2002, ‘Dissolved oxygen content as an index of water quality in San Vicente Bay, Chile (36°45′S)’, Environ. Monit. Assess. 78, 89–100.
SERNAPESCA: 2000, Anuario estadístico, Servicio Nacional de Pesca. Chile. 46 pp.
SERNAPESCA: 2002, Anuario estadístico, Servicio Nacional de Pesca. Chile. 50 pp.
Siemens, R. A., Mudge, S. M. and Cancino, J. M.: 2001. ‘The effect of physical and chemical parameters on the macroinfaunal community structure of San Vicente Bay, Chile’, Revista Chilena de Historia Natural 74, 429–444.
Theede, H., Ponat, A., Hiroki, K. and Schlieper, C.: 1969, ‘Studies on resistance of marine bottom invertebrates to oxygen—deficiency and hydrogen sulphide’. Mar. Biol. 2, 325–337.
Thomann, R. and Mueller, J.: 1987, ‘Principles of Surface Water Quality Modeling and Control’, in: Harper and Row Publishers (eds), Dissolved Oxygen, Chapter 6, New York, pp. 261–384.
Water Quality for River-Reservoir System: 1988, Manual Water Quality for River-reservoir Systems. Hydrologic Engineering Center. CPD-8. US Army Corps of Engineers. 288 pp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahumada, R., Vargas, J. & Pagliero, L. Simple Model of Dissolved Oxygen Consumption in a Bay within High Organic Loading: An Applied Remediation Tool. Environ Monit Assess 118, 179–193 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-1489-3
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-1489-3