Abstract
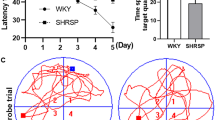
(1) The role of activation of Rho-kinase in the pathogenesis of cognitive deficit and neuronal damage caused by chronic global ischemia is not clear. In this study, hydroxyfasudil, a Rho-kinase inhibitor, was found to improve the learning and memory performance significantly in rats with ischemia induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion after permanent bilateral carotid artery ligation (BCAL). This was observed by the administration of hydroxyfasudil (1 mg/kg or 10 mg/kg, once per day for 30 days) to ischemic rats and the measurements of escape latency and time spent in the target quadrant among the ischemic, sham, and ischemic plus hydroxyfasudil rats by the method of Morris water maze. (2) In electrophysiological study, hydroxyfasudil abolished the inhibition of long-term potentiation (LTP) in rats with ischemia. Morphologically, it also markedly reduced pathological changes such as neuronal cells loss and nuclei shrinkage in cortex and hippocampus of ischemic rats. Biochemical analysis showed that the inhibition of Rho-kinase by hydroxyfasudil reduced the amount of MDA and increased the activities of SOD and GPx in ischemic rats that had increased MDA and decreased SOD and GPx activities. (3) To explore mechanism (s) of the beneficial effects of hydroxyfasudil in ischemia, we performed immunohistochemistry and RT-PCR analyses of NMDA NR2B subunit and for the first time found that hydroxyfasudil increased the expression of NR2B in cortex and hippocampus at both protein and mRNA levels. (4) Taken together, our data further support the notion that the inhibition of Rho-kinase provides neuroprotective effects in cerebral ischemia.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailey SR, Mitra S, Flavahan S, Flavahan NA (2005) Reactive oxygen species from smooth muscle mitochondria initiate cold-induced constriction of cutaneous arteries. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 289:H243–H250
Berberich S, Punnakkal P, Jensen V, Pawlak V, Seeburg PH, Hvalby O, Köhr G (2005) Lack of NMDA receptor subtype selectivity for hippocampal long-term potentiation. J Neurosci 25:6907–6910
Berzhanskaya J, Urban NN, Barrionuevo G (1998) Electrophysiological and pharmacological characterization of the direct perforant path input to hippocampal area CA3. J Neurophysiol 79:2111–2118
Bliss TVP, Lomo T (1973) Long-lasting potentiation of synaptic transmission in the denate area of the perforant path. J Physiol 232:331–56
Bliss TVP, Collingridge GL (1993) A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature 361(6407):31–39
Bombi L, YoungKook C, Hocheol K (2003) Protective effects of methanol extract of Acori graminei rhizome and Uncariae Ramulus et Uncus on ischemia-induced neuronal death and cognitive impairments in the rat. Life Sciences 74:435–450
Coyle JT, Puttfarcken P (1993) Oxidative stress, glutamate, and neurodegenerative disorders. Science 262:689–695
Do VH, Martinez CO, Martinez JL, Derrick BE (2002) Long-term potentiation in direct perforant path projections to the hippocampal CA3 region in vivo. J Neurophysiol 87:669–678
Fournier AE, Takizawa BT, Strittmatter SM (2003) Rho kinase inhibition enhances axonal regeneration in the injured CNS. J Neurosci 23:1416–1423
Fukata Y, Amano M, Kaibuchi K (2001) Rho-Rho-kinase pathway in smooth muscle contraction and cytoskeletal reorganization of non-muscle cells. Trends Pharmacol Sci 22:32–39
Higashi M, Shimokawa H, Hattori T, Hiroki J, Mukai Y, Morikawa K, Ichiki T, Takahashi S, Takeshita A (2003) Long-term inhibition of Rho-kinase suppresses angiotensin II-induced cardiovascular hypertrophy in rats in vivo: effect on endothelial NAD (P) H oxidase system. Circ Res 93: 767–775
Horwitz AR, Parsons JT (1999) Cell migration: movein’ on. Science 286:1102–1103
Jennifer ML, Aaron J (2003) The N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor subunit NR2B: localization, functional properties, regulation, and clinical implications. Pharmacol Therap 97:55–85
Juurlink BH, Sweeney MI (1997) Mechanisms that result in damage during and following cerebral ischemia. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 21:121–128
Kiyoshi M, Hiroko T, Ken-ichi, Ueno, Machiko M, Mitsuhiro Y (2001) Aminoguanidine prevented the impairment behavior and hippocampal long-term potentiation following transient cerebral ishemia. Behavioural. Brain Research 120:159–169
Lai SK, Wong CKC, Yang MS, Yung KKL (2000) Changes in expression of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor subunits in the rat neostriatum after a single dose of antisense oligonucleotide specific for N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor 1 subunit. Neuroscience 98:493–500
Lehmann M, Fournier A, Selles-Navarro I, Dergham P, Sebok A, Leclerc N, Tigyi G, McKerracher L (1999) Inactivation of Rho signaling pathway promotes CNS axon regeneration. J. Neurosci 19:7537–7547
Lyubkin M, Durand DM, Haxhiu MA (1997) Interaction between tetanus Long-termpotentiation and hypoxia-induced potentiation in the rat hippocampus. Neurophysiol 78(5):2475–2482
Martinez CO, Do VH, Martinez JL, Derrick BE (2002) Associative long-term potentiation (LTP) among extrinsic afferents of the hippocampal CA3 region in vivo. Brain Res 940:86–94
Masumoto A, Hirooka Y, Shimokawa H, Hironaga K, Setoguchi S, Takeshita A (2001) Possible involvement of Rho-kinase in the pathogensis of hypertension in humans. Hypertension 38:1307–1310
Nakayama AY, Harms MB, Luo L (2000) Small GTPases Rac and Rho in the maintenance of dendritic spines and branches in hippocampal pyramidal neurons. J Neurosci 20:5329–5338
Nakazawa T, Watabe AM, Tezuka T, Yoshida Y, Yokoyama K, Umemori H, Inoue A, Okabe S, Manabe T, Yamamoto T (2003) p250GAP, a novel brain-enriched GTPase-activating protein for Rho family GTPases, is involved in the N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor signaling. Mol Biol Cell 14:2921–2934
Narumiya S (1996) The small GTPase Rho: cellular functions and signal transduction. J Biochem (Tokyo) 120:215–228
Noerenberg W, Hofmann F, Illes P, Aktories K, Meyer DK (1999) Rundown of somatodendritic N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor channels in rat hippocampal neurones: evidence for a role of the small GTPase RhoA. Br J Pharmacol 127:1060–1063
Satoh S, Ikegaki I, Suzuki Y, Asano T, Shibuya M, Hidaka H (1996) Neuroprotective properties of a protein kinase inhibitor against ischaemia-induced neuronal damage in rats and gerbils. Br J Pharmacol 118:1592–1596
Shimokawa H, Hiramori K, Iinuma H, Hosoda S, Kishida H, Osada H, Katagiri T, Yamauchi K, Yui Y, Minamino T, Nakashima M, Kato K (2002) Anti-anginal effect of fasudil, a Rho-kinase inhibitor, in patients with stable effort angina: a multicenter study. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 40:751–761
Shin-ichi S, Tatsuma U, Kazuyuki T, Teruki K, Ichiro I, Yasuo S, Toshio A (2001) Pharmacological profile of hydroxy fasudil as a selective rho kinase inhibitor on ischemic brain damage. Life Sciences 69:1441–1453
Stephen PD, Helen R, Matilde C, Philip C (2000) Specificity and mechanism of action of some commonly used protein kinase inhibitors. Biochem 351:95–105
Sun T, Hu HZ, Xu XL, Yu SB, Ouyang CH, Qu L, Lv Q, Guo LJ (2004) Effects of glutamic acid and its receptor antagonist on evoked potentials in hippocampus CA3region in rats. Chinese Pharmacol Bull 20l:414–417
Sung JK, Miao L, Calvert JW, Huang L, Harkey HL, Zhang JH (2003) A possible role of RhoA/Rho-kinase in experimental spinal cord injury in rat. Brain Res 959:29–38
Tachibana E, Harada T, Shibuya M, Saito K, Takayasu M, Suzuki Y, Yoshida J (1999) Intra-arterial infusion of fasudil hydrochloride for treating vasospasm following subarachnoid haemorrhage. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 141:13–19
Takemoto M, Sun J, Hiroki J, Shimokawa H, Liao JK (2002) Rho-kinase mediates hypoxia-induced downregulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Circulation 106:57–62
Tang YP, Shimizu E, Dube GR, Rampon C, Kerchner GA, Zhuo M, Liu G, Tsien JZ (1999) Genetic enhancement of learning and memory in mice. Nature 401:63–69
Tang YP, Wang H, Feng R, Kyin M, Tsien JZ (2001) Differential effects of enrichment on learning and memory function in NR2B transgenic mice. Neuropharmacology 41(6):779–790
van Nieuw Amerongen GP, van Hinsbergh VWM (2001) Cytoskeletal effects of Rho-like small guanine nucleotide-binding proteins in the vascular system. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 21:300–311
Wang LM, Han YF, Tang XC (2000) Huperzine A improves cognitive deficits caused by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 398:65–72
Wong H, Anderson WD, Cheng T, Riabowol KT (1994) Monitoring mRNA expression by polymerase chain reaction: the “primer-dropping” method. Anal Biochem 223:251–258
Yoshiyuki R, Hyung HK, Huang ZH, Minoru S, Kazuo Y, Toshio A, Michael A, Moskowitz, James KL (2005) Inhibition of Rho Kinase (ROCK) leads to increased cerebral blood flow and stroke protection. Stroke 36:2251–2257
Zhao MG, Toyoda H, Lee YS, Wu LJ, Ko SW, Zhang XH, Jia Y, Shum F, Xu H, Li BM, Kaang BK, Zhuo M (2005) Roles of NMDA NR2B subtype receptor in prefrontal long-term potentiation and contextual fear memory. Neuron 47:859–872
Zheng M, Guo LJ, Xu XL, Hu HZ, Zong XG (2006) ZD7288 inhibits the synaptic transmission of the pathway from perforant pathway (PP) fibers to CA3 region in rat hippocampus. Acta Pharmaceutica Sin 41:565–571
Zhou M, Baudry M (2006) Developmental changes in NMDA neurotoxicity reflect developmental changes in subunit composition of NMDA receptors. J Neurosci 26(11):2956–2963
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Lin Huang and Zhi He contribute equally to the paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, L., He, Z., Guo, L. et al. Improvement of Cognitive Deficit and Neuronal Damage in Rats with Chronic Cerebral Ischemia via Relative Long-term Inhibition of Rho-kinase. Cell Mol Neurobiol 28, 757–768 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-007-9157-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-007-9157-x