Abstract
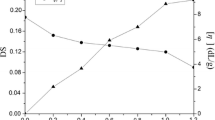
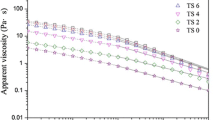
In this study, various modified xanthan gums (MXG) were prepared by deacetylation under alkali treatment at certain temperature. The molecular weight of xanthan gum decreased after alkali modification. Rheological properties such as flowability, thixotropy and viscoelasticity were investigated via steady-shear, transient and dynamic oscillatory tests. The results showed that the flowability and viscous effect of MXG increased, while the structural viscosity and elastic effect decreased with increasing degrees of modification. Compared to xanthan gum, printing performances using MXG as a thickener were improved, especially the screenability, color yield and penetration. In addition, the quantitative interpretation of the rheological parameters, which are strongly associated with the quality-determining parameters, was obtained using rheological models (the power-law and Friedrich-Braun models). Excellent printing performances were achieved by applying MXG under the appropriate modification conditions. These thickeners, which have better flowability, more viscous behavior and smaller structural viscosity, might be good pastes to meet the the requirements of cotton printing with reactive dyes.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Halim ES, Emam HE, El-Rafie MH (2008) Utilization of hydroxypropyl cellulose and poly (acrylic acid)-hydroxypropyl cellulose composite as thickeners for textile printing. Carbohydr Polym 74:938–941
Alves VD, Freitas F, Costa N, Carvalheira M, Oliveira R, Gonçalves MP, Reis MAM (2010) Effect of temperature on the dynamic and steady-shear rheology of a new microbial extracellular polysaccharide produced from glycerol byproduct. Carbohydr Polym 79:981–988
Baranov AV, Dymnikova NS, ll’in AV (2002) Alkali cellulose as a regulator of the rheological behavior of solutions of dyes. Fiber Chem 34(1):38–40
Clark AH, Ross-Murphy SB (1987) Structural and mechanical properties of biopolymer gels. Adv Polym Sci 83:57–192
Dang TL, Prasil M (2001) Rheological behavior of reactive printing pastes and its effects on print parameters. Texsc’ 98(3):508–511
Durairaj R, Ekere NN, Salam B (2004) Thixotropy flow behavior of solder and conductive adhesive pastes. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 15:677–683
Fijan R, Šostar-Turk S, Lapasin R (2007) Rheological study of interactions between non-ionic surfactants and polysaccharide thickeners used in textile printing. Carbohydr Polym 68:708–717
Fijan R, Basile M, Lapasin R, Šostar-Turk S (2009) Rheological properties of printing pastes and their influence on quality-determining parameters in screen printing of cotton with reactive dyes using recycled polysaccharide thickeners. Carbohydr Polym 78:25–35
Fitzgerald EE (1983) Xanthan gum in textile printing applications. In: Paper presented at the meeting of American Association of Textile Chemists and Colorists (AATCC), New Orleans, USA
Friedrich C, Braun H (1992) Generalized cole–cole behavior and its rheological relevance. Rheol Acta 31:309–322
García-Ochoa F, Santos VE, Casas JA, Gómez E (2000) Xanthan gum: production, recovery, and properties. Biotechnol Adv 15:549–579
Ibrahim NA, Abo-Shosha MH, Allam EA, El-Zairy EM (2010) New thickening agents based on tamarind seed gum and karaya gum polysaccharides. Carbohydr Polym 81:402–408
Khouryieh HA, Herald TJ, Aramouni F, Alavi S (2007) Intrinsic viscosity and viscoelastic properties of xanthan/guar mixtures in dilute solutions: effect of salt concentration on the polymer interactions. Food Res Int 40:883–893
Kumbasar EPA, Bide M (2000) Reactive dye printing with mixed thickeners on viscose. Dyes Pigment 47:189–199
Mallik S, Ekere NN, Marks AE, Seman A, Durairaj R (2010) Modeling the structural breakdown of solder paste using the structural kinetic model. J Mater Eng Perform 19:40–45
Mezger TG (2002) Rotational tests. In: Zorll U (ed) The rheology handbook: for users of rotational and oscillatory rheometers. Vincentz Verlag, Hannover, pp 55–68
Oblonšek M, Šostar-Turk S, Lapasin R (2003) Rheological studies of concentrated guar gum. Rheol Acta 42:491–499
Paradossi G, Brant DA (1982) Light scattering studies of a series of xanthan fractions in aqueous solution. Macromolecules 15:874–879
Razavi SMA, Karazhiyan H (2009) Flow properties and thixotropy of selected hydrocolloids: experimental and modeling studies. Food Hydrocoll 23:908–912
Ross-Murphy SB (1984) Rheological methods. In: Chan HW-S (ed) Biophysical methods in food research. Blackwell, Palo Alto, pp 138–199
Sato T, Norisuye T, Fujita H (1984) Double-stranded helix of xanthan: dimensional and hydrodynamic properties in 0.1 m aqueous sodium chloride. Macromolecules 17:2696–2700
Shatwell KP, Sutherland IW, Dea ICM, Ross-Murphy SB (1990) The influence of acetyl and pyruvate substituents on the helix–coil transition behavior of xanthan. Carbohydr Res 206:87–103
Smith IH, Symes KC, Lawson CJ (1981) Influence of the pyruvate content of xanthan on macromolecular association in solution. Int J Biol Macromol 3:129–134
Šostar S, Schneider R (1998) Guar gum as an environment-friendly alternative thickener in printing with reactive dyes. Dyes Pigment 39:211–221
Šostar-Turk S, Schneider R (2000) Printing properties of a high substituted guar gum and its mixture with alginate. Dyes Pigment 47:269–275
Southwick JG, Jamieson AM, Blackwell J (1982) Conformation of xanthan dissolved in aqueous urea and sodium chloride solution. Carbohydr Res 99:117–127
Tako M, Nakamura S (1984) Rheological properties of deacetylated xanthan in aqueous media. Agric Biol Chem 40:2987–2993
Wang LL, Zhu FR, Lu DN (2013) Rheological properties of sodium alginate and xanthan pastes on cotton with reactive dye in screen printing. Text Res J (accept)
Xu XJ, Liu W, Zhang LN (2006) Rheological behavior of Aeromonas gum in aqueous solutions. Food Hydrocoll 20:723–729
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Key Laboratory of Science and Technology of Eco-Textiles, Ministry of Education, Donghua University, for their support. Financial support given by the Innovation Foundation for PhD Candidates of Donghua University (CUSF-DH-D-2013046) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Zhu, F., Yang, Q. et al. Rheological properties of modified xanthan and their influence on printing performances on cotton with reactive dyes in screen printing. Cellulose 20, 2125–2135 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-9968-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-9968-5