Abstract
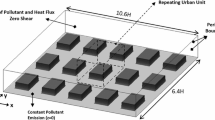
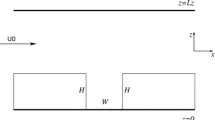
A validated large-eddy simulation model was employed to study the effect of the aspect ratio and ground heating on the flow and pollutant dispersion in urban street canyons. Three ground-heating intensities (neutral, weak and strong) were imposed in street canyons of aspect ratio 1, 2, and 0.5. The detailed patterns of flow, turbulence, temperature and pollutant transport were analyzed and compared. Significant changes of flow and scalar patterns were caused by ground heating in the street canyon of aspect ratio 2 and 0.5, while only the street canyon of aspect ratio 0.5 showed a change in flow regime (from wake interference flow to skimming flow). The street canyon of aspect ratio 1 does not show any significant change in the flow field. Ground heating generated strong mixing of heat and pollutant; the normalized temperature inside street canyons was approximately spatially uniform and somewhat insensitive to the aspect ratio and heating intensity. This study helps elucidate the combined effects of urban geometry and thermal stratification on the urban canyon flow and pollutant dispersion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad K, Khare M, Chaudhry KK (2005) Wind tunnel simulation studies on dispersion at urban street canyons and intersections—a review. J Wind Eng Ind Aerodyn 93: 697–717
Belcher SE (2005) Mixing and transport in urban areas. Phil Trans Roy Soc A 363: 2947–2968
Blocken B, Stathopoulos T, Saathoff P, Wang X (2008) Numerical evaluation of pollutant dispersion in the built environment: comparisons between models and experiments. J Wind Eng Ind Aerodyn 96: 1817–1831
Bottema M (1993) Wind climate and urban geometry. Eindhoven University of Technology, Netherlands
Britter RE, Hanna SR (2003) Flow and dispersion in urban areas. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 35: 469–496
Buccolieri R, Sandberg M, Di Sabatino S (2010) City breathability and its link to pollutant concentration distribution within urban-like geometries. Atmos Environ 44: 1894–1903
Ca VT, Asaeda T, Ito M, Armfield S (1995) Characteristics of wind field in a street canyon. J Wind Eng Ind Aerodyn 57(1): 63–80
Cai XM, Barlow JF, Belcher SE (2008) Dispersion and transfer of passive scalars in and above street canyons—large-eddy simulations. Atmos Environ 42: 5885–5895
Cheng WC, Liu CH (2011) Large-eddy simulation of turbulent transports in urban street canyons in different thermal stabilities. J Wind Eng Ind Aerodyn. doi:10.1016/j.jweia.2010.12.009
Cheng H, Hayden P, Robins AG, Castro IP (2007) Flow over cube arrays of different packing densities. J Wind Eng Ind Aerodyn 95: 715–740
Cheng WC, Liu CH, Leung DYC (2009) On the correlation of air and pollutant exchange for street canyons in combined wind-buoyancy-driven flow. Atmos Environ 43: 3682–3690
Coceal O, Thomas TG, Belcher SE (2007) Spatial variability of flow statistics within regular building arrays. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 125: 537–552
Cui Z, Cai XM, Baker CJ (2004) Large eddy simulation of turbulent flow in a street canyon. Q J R Meteorol Soc 599: 1373–1394
Fackrell JE, Robins AG (1982) The effects of source size on concentration fluctuations in plumes. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 22(3): 335–350
Fernando HJS, Lee SM, Anderson J, Princevac M, Pardyjak E, Grossman-Clarke S (2001) Urban fluid mechanics: air circulation and contaminant dispersion in cities. Environ Fluid Mech 1: 107–164
Hamlyn D, Hilderman T, Britter R (2007) A simple network approach to modelling dispersion among large groups of obstacles. Atmos Environ 41: 5848–5862
Kang YS, Baik JJ, Kim JJ (2008) Further studies of flow and reactive pollutant dispersion in a street canyon with bottom heating. Atmos Environ 42: 4964–4975
Kim JJ, Baik JJ (2001) Urban street-canyon flows with bottom heating. Atmos Environ 35: 3395–3404
Letzel MO, Krane M, Raasch S (2008) High resolution urban large-eddy simulation studies from street canyon to neighbourhood scale. Atmos Environ 42: 8770–9784
Li XX (2008) Large-eddy simulation of wind flow and air pollutant transport inside urban street canyons of different aspect ratios. PhD thesis, The University of Hong Kong, 205 pp
Li XX, Liu CH, Leung DYC, Lam KM (2006) Recent progress in CFD modelling of wind field and pollutant transport in street canyons. Atmos Environ 40(29): 5640–5658
Li XX, Liu CH, Leung DYC (2008) Large-eddy simulation of flow and pollutant dispersion in urban street canyons with wall model. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 129(2): 249–268
Li XX, Liu CH, Leung DYC (2009) Numerical investigation of pollutant transport characteristics inside deep urban street canyons. Atmos Environ 43(15): 2410–2418
Li XX, Britter RE, Koh TY, Norford LK, Liu CH, Entekhabi D, Leung DYC (2010) Large-eddy simulation of flow and pollutant transport in urban street canyons with ground heating. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 137(2): 187–204. doi:10.1007/s10546-010-9534-8
Liu CH, Barth MC (2002) Large-eddy simulation of flow and scalar transport in a modeled street canyon. J Appl Meteorol 41(6): 660–673
Liu CH, Barth MC, Leung DYC (2004) Large-eddy simulation of flow and pollutant transport in street canyons of different building-height-to-street-width ratios. J Appl Meteorol 43: 1410–1424
Liu CH, Leung DYC, Barth MC (2005) On the prediction of air and pollutant exchange rates in street canyons of different aspect ratios using large-eddy simulation. Atmos Environ 39: 1567–1574
Nakamura Y, Oke TR (1988) Wind, temperature, and stability conditions in an east-west-oriented urban canyon. Atmos Environ 22: 2691–2700
Oke T (1988) Street design and urban canopy layer climate. Energy Build 11: 103–113
Reynolds RT, Castro IP (2008) Measurements in an urban-type boundary layer. Exp Fluids 45: 141–156
Sini JF, Anquetin S, Mestayer PG (1996) Pollutant dispersion and thermal effects in urban street canyons. Atmos Environ 30: 2659–2677
Solazzo E, Britter RE (2007) Transfer processes in a simulated urban street canyon. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 124(1): 43–60
Uehara K, Murakami S, Oikawa S, Wakamatsu S (2000) Wind tunnel experiments on how thermal stratification affects flow in and above urban street canyons. Atmos Environ 34: 1553–1562
Vardoulakis S, Fisher BEA, Pericleous K, Gonzalez-Flesca N (2003) Modelling air quality in street canyons: a review. Atmos Environ 37: 155–182
Xie X, Huang Z, Wang J, Xie Z (2005) Thermal effects on vehicle emission dispersion in an urban street canyon. Transp Res D 10: 197–212
Xie X, Liu CH, Leung DYC, Leung MKH (2006) Characteristics of air exchange in a street canyon with ground heating. Atmos Environ 40(33): 6396–6409
Xie X, Liu CH, Leung DYC (2007) Impact of building facades and ground heating on wind flow and pollutant transport in street canyons. Atmos Environ 41: 9030–9049
Yoshie R, Jiang G, Shirasawa T, Chung J (2011) CFD simulations of gas dispersion around high-rise building in non-isothermal boundary layer. J Wind Eng Ind Aerodyn. doi:10.1016/j.jweia.2011.01.006
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, XX., Britter, R.E., Norford, L.K. et al. Flow and Pollutant Transport in Urban Street Canyons of Different Aspect Ratios with Ground Heating: Large-Eddy Simulation. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 142, 289–304 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-011-9670-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-011-9670-9