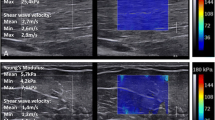
Abstract
The ability to measure and quantify the properties of skeletal muscle in vivo as a method for understanding its complex physiological and pathophysiological behavior is important in numerous clinical settings, including rehabilitation. However, this remains a challenge to date due to the lack of a “gold standard” technique. Instead, there are a myriad of measuring techniques each with its own set of pros and cons. This review discusses the current state-of-the-art in elastography imaging techniques, i.e., ultrasound and magnetic resonance elastography, as applied to skeletal muscle, and briefly reviews other methods of measuring muscle mechanical behavior in vivo. While in vivo muscle viscoelastic properties can be measured, these techniques are largely limited to static or quasistatic measurements. Emerging elastography techniques are able to quantify muscle anisotropy and large deformation effects on stiffness, but, validation and optimization of these newer techniques is required. The development of reliable values for the mechanical properties of muscle across the population using these techniques are required to enable them to become more useful in rehabilitation and other clinical settings.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afdhal, N. H. Fibroscan (transient elastography) for the measurement of liver fibrosis. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 8:605–607, 2012.
Alhusaini, A. A. A., J. Crosbie, R. B. Shepherd, C. M. Dean, and A. Scheinberg. No change in calf muscle passive stiffness after botulinum toxin injection in children with cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 53:553–558, 2011.
Basford, J. R., T. R. Jenkyn, K. N. An, R. L. Ehman, G. Heers, and K. R. Kaufman. Evaluation of healthy and diseased muscle with magnetic resonance elastography. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 83:1530–1536, 2002.
Bensamoun, S. F., S. I. Ringleb, Q. S. Chen, R. L. Ehman, K. N. An, and M. Brennan. Thigh muscle stiffness assessed with magnetic resonance elastography in hyperthyroid patients before and after medical treatment. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 26:708–713, 2007.
Bensamoun, S. F., S. I. Ringleb, L. Littrell, Q. Chen, M. Brennan, R. L. Ehman, and K. N. An. Determination of thigh muscle stiffness using magnetic resonance elastography. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 23:242–247, 2006.
Botar-Jid, C., L. Damian, S. M. Dudea, D. Vasilescu, S. Rednic, and R. Badea. The contribution of ultrasonography and sonoelastography in assessment of myositis. Med. Ultrason. 12:120–126, 2010.
Brodie, T. G. The extensibility of muscle. J. Anat. Physiol. 29:367, 1895.
Brown, E. C., S. Cheng, D. K. McKenzie, J. E. Butler, S. C. Gandevia, and L. E. Bilston. Respiratory movement of upper airway tissue in obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep 36:1069–1076, 2013.
Brown, E. C., S. Cheng, D. K. McKenzie, J. E. Butler, S. C. Gandevia, and L. E. Bilston. Tongue stiffness is lower in patients with obstructive sleep apnea during wakefulness compared with matched control subjects. Sleep 2014. (in press).
Castéra, L., J. Vergniol, J. Foucher, B. Le Bail, E. Chanteloup, M. Haaser, et al. Prospective comparison of transient elastography, fibrotest, apri, and liver biopsy for the assessment of fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology 128:343–350, 2005.
Cheng, S., J. E. Butler, S. C. Gandevia, and L. E. Bilston. Movement of the tongue during normal breathing in awake healthy humans. J. Physiol. 586:4283–4294, 2008.
Chuang, L.-L., C.-Y. Wu, and K.-C. Lin. Reliability, validity, and responsiveness of myotonometric measurement of muscle tone, elasticity, and stiffness in patients with stroke. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 93:532–540, 2012.
Clarke, E. C., S. Cheng, M. Green, R. Sinkus, and L. E. Bilston. Using static preload with magnetic resonance elastography to estimate large strain viscoelastic properties of bovine liver. J. Biomech. 44:2461–2465, 2011.
Dalkilic, I., and L. M. Kunkel. Muscular dystrophies: genes to pathogenesis. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 13:231–238, 2003.
Diong, J., L. A. Harvey, L. K. Kwah, J. L. Clarke, L. E. Bilston, S. C. Gandevia, and R. D. Herbert. Gastrocnemius muscle contracture after spinal cord injury: a longitudinal study. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 92:565–574, 2013.
Diong, J. H., R. D. Herbert, L. A. Harvey, L. K. Kwah, J. L. Clarke, P. D. Hoang, et al. Passive mechanical properties of the gastrocnemius after spinal cord injury. Muscle Nerve 46:237–245, 2012.
Drakonaki, E. E., and G. M. Allen. Magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasound and real-time ultrasound elastography of the thigh muscles in congenital muscle dystrophy. Skeletal Radiol. 39:391–396, 2010.
Drakonaki, E., G. Allen, and D. Wilson. Ultrasound elastography for musculoskeletal applications. Br. J. Radiol. 85:1435–1445, 2012.
Friedrich-Rust, M., M. F. Ong, S. Martens, C. Sarrazin, J. Bojunga, S. Zeuzem, and E. Herrmann. Performance of transient elastography for the staging of liver fibrosis: a meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 134(960–974):e968, 2008.
Friedrich-Rust, M., K. Wunder, S. Kriener, F. Sotoudeh, S. Richter, J. Bojunga, et al. Liver fibrosis in viral hepatitis: noninvasive assessment with acoustic radiation force impulse imaging vs. transient elastography 1. Radiology 252:595–604, 2009.
Fung, Y. C. Biomechanics: Mechanical Properties of Living Tissues. New York: Springer, 1993.
Gao, F., T. H. Grant, E. J. Roth, and L.-Q. Zhang. Changes in passive mechanical properties of the gastrocnemius muscle at the muscle fascicle and joint levels in stroke survivors. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 90:819–826, 2009.
Garteiser, P., R. S. Sahebjavaher, L. C. Ter Beek, S. Salcudean, V. Vilgrain, B. E. Van Beers, and R. Sinkus. Rapid acquisition of multifrequency, multislice and multidirectional MR elastography data with a fractionally encoded gradient echo sequence. NMR Biomed. 26:1326–1335, 2013.
Gennisson, J. L., C. Cornu, S. Catheline, M. Fink, and P. Portero. Human muscle hardness assessment during incremental isometric contraction using transient elastography. J. Biomech. 38:1543–1550, 2005.
Giacomozzi, C., E. D’Ambrogi, S. Cesinaro, V. Macellari, and L. Uccioli. Muscle performance and ankle joint mobility in long-term patients with diabetes. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 9:99, 2008.
Green, M. A., L. E. Bilston, and R. Sinkus. In vivo brain viscoelastic properties measured by magnetic resonance elastography. NMR Biomed. 21:755–764, 2008.
Green, M., G. Geng, E. Qin, R. Sinkus, S. Gandevia, and L. Bilston. Measuring anisotropic muscle stiffness properties using elastography. NMR Biomed. 26:1387–1394, 2013.
Green, M., R. Sinkus, S. Gandevia, R. Herbert, and L. Bilston. Measuring changes in muscle stiffness after eccentric exercise using elastography. NMR Biomed. 25:852–858, 2012.
Grounds, M. D., H. G. Radley, G. S. Lynch, K. Nagaraju, and A. De Luca. Towards developing standard operating procedures for pre-clinical testing in the mdx mouse model of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Neurobiol. Dis. 31:1–19, 2008.
Hafer-Macko, C. E., A. S. Ryan, F. M. Ivey, and R. F. Macko. Skeletal muscle changes after hemiparetic stroke and potential beneficial effects of exercise intervention strategies. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 45:261–272, 2008.
Hamhaber, U., I. Sack, S. Papazoglou, J. Rump, D. Klatt, and J. Braun. Three-dimensional analysis of shear wave propagation observed by in vivo magnetic resonance elastography of the brain. Acta Biomater. 3:127–137, 2007.
Hoang, P., R. Gorman, G. Todd, S. C. Gandevia, and R. Herbert. A new method for measuring passive length–tension properties of human gastrocnemius muscle in vivo. J. Biomech. 38:1333–1341, 2005.
Huwart, L., C. Sempoux, N. Salameh, J. Jamart, L. Annet, R. Sinkus, et al. Liver fibrosis: noninvasive assessment with MR elastography vs. aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index. Radiology 245:458–466, 2007.
Huwart, L., C. Sempoux, E. Vicaut, N. Salameh, L. Annet, E. Danse, et al. Magnetic resonance elastography for the noninvasive staging of liver fibrosis. Gastroenterology 135:32–40, 2008.
Kawakami, Y., H. Kanehisa, and T. Fukunaga. The relationship between passive ankle plantar flexion joint torque and gastrocnemius muscle and achilles tendon stiffness: implications for flexibility. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Therapy 38:269–276, 2008.
Klatt, D., C. Friedrich, Y. Korth, R. Vogt, J. Braun, and I. Sack. Viscoelastic properties of liver measured by oscillatory rheometry and multifrequency magnetic resonance elastography. Biorheology 47:133–141, 2010.
Krouskop, T. A., T. M. Wheeler, F. Kallel, B. S. Garra, and T. Hall. Elastic moduli of breast and prostate tissues under compression. Ultrason. Imaging 20:260–274, 1998.
Kwah, L. K., R. D. Herbert, L. A. Harvey, J. Diong, J. L. Clarke, J. H. Martin, et al. Passive mechanical properties of gastrocnemius muscles of people with ankle contracture after stroke. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehab. 93:1185–1190, 2012.
Kwon, D. R., G. Y. Park, and J. G. Kwon. The change of intrinsic stiffness in gastrocnemius after intensive rehabilitation with botulinum toxin a injection in spastic diplegic cerebral palsy. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 36:400–403, 2012.
Kwon, D. R., G. Y. Park, S. U. Lee, and I. Chung. Spastic cerebral palsy in children: dynamic sonoelastographic findings of medial gastrocnemius. Radiology 263:794–801, 2012.
Leonard, C. T., W. P. Deshner, J. W. Romo, E. S. Suoja, S. C. Fehrer, and E. L. Mikhailenok. Myotonometer intra-and interrater reliabilities. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 84:928–932, 2003.
Leonard, C. T., J. U. Stephens, and S. L. Stroppel. Assessing the spastic condition of individuals with upper motoneuron involvement: validity of the myotonometer. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 82:1416–1420, 2001.
Lieber, R. L., and S. C. Bodine-Fowler. Skeletal muscle mechanics: implications for rehabilitation. Phys. Ther. 73:844–856, 1993.
Lieber, R. L., S. Steinman, I. A. Barash, and H. Chambers. Structural and functional changes in spastic skeletal muscle. Muscle Nerve 29:615–627, 2004.
Linder-Ganz, E., and A. Gefen. Mechanical compression-induced pressure sores in rat hindlimb: muscle stiffness, histology, and computational models. J. Appl. Physiol. 96:2034–2049, 2004.
Lv, F., J. Tang, Y. Luo, Y. Ban, R. Wu, J. Tian, et al. Muscle crush injury of extremity: quantitative elastography with supersonic shear imaging. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 38:795–802, 2012.
Maïsetti, O., F. Hug, K. Bouillard, and A. Nordez. Characterization of passive elastic properties of the human medial gastrocnemius muscle belly using supersonic shear imaging. J. Biomech. 45:978–984, 2012.
Marusiak, J., A. Jaskólska, S. Budrewicz, M. Koszewicz, and A. Jaskólski. Increased muscle belly and tendon stiffness in patients with Parkinson’s disease, as measured by myotonometry. Mov. Disord. 26:2119–2122, 2011.
McCracken, P. J., A. Manduca, J. Felmlee, and R. L. Ehman. Mechanical transient-based magnetic resonance elastography. Magn. Reson. Med. 53:628–639, 2005.
McCullough, M. B., Z. J. Domire, A. M. Reed, S. Amin, S. R. Ytterberg, Q. Chen, and K. N. An. Evaluation of muscles affected by myositis using magnetic resonance elastography. Muscle Nerve 43:585–590, 2011.
Mezzanotte, W. S., D. J. Tangel, and D. P. White. Waking genioglossal electromyogram in sleep apnea patients vs. normal controls (a neuromuscular compensatory mechanism). J. Clin. Investig. 89:1571–1579, 1992.
Muraki, T., Z. J. Domire, M. B. McCullough, Q. Chen, and K.-N. An. Measurement of stiffness changes in immobilized muscle using magnetic resonance elastography. Clin. Biomech. 25:499–503, 2010.
Muthupillai, R., and R. L. Ehman. Magnetic resonance elastography. Nat. Med. 2:601–603, 1996.
Nightingale, K., M. S. Soo, R. Nightingale, and G. Trahey. Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging. In vivo demonstration of clinical feasibility. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 28:227–235, 2002.
Niitsu, M., A. Michizaki, A. Endo, H. Takei, and O. Yanagisawa. Muscle hardness measurement by using ultrasound elastography: a feasibility study. Acta Radiol. 52:99–105, 2011.
Nordez, A., J. Gennisson, P. Casari, S. Catheline, and C. Cornu. Characterization of muscle belly elastic properties during passive stretching using transient elastography. J. Biomech. 41:2305–2311, 2008.
Nordez, A., and F. Hug. Muscle shear elastic modulus measured using supersonic shear imaging is highly related to muscle activity level. J. Appl. Physiol. 108:1389–1394, 2010.
OpenStax College. 2014. Anatomy & Physiology. OpenStax CNX, Jul 31, 2014. http://cnx.org/contents/14fb4ad7-39a1-4eee-ab6e-3ef2482e3e22@6.27@6.27. Accessed 15 Sept 2014
Osman, N. F., W. S. Kerwin, E. R. McVeigh, and J. L. Prince. Cardiac motion tracking using cine harmonic phase (Harp) magnetic resonance imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 42:1048–1060, 1999.
Pastoret, C., and A. Sebille. Mdx mice show progressive weakness and muscle deterioration with age. J. Neurol. Sci. 129:97–105, 1995.
Proske, U., D. L. Morgan, and J. E. Gregory. Thixotropy in skeletal muscle and in muscle spindles: a review. Prog. Neurobiol. 41:705–721, 1993.
Purslow, P. P. Muscle fascia and force transmission. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 14:411–417, 2010.
Qin, E. C., L. Juge, S. A. Lambert, V. Paradis, R. Sinkus, and L. E. Bilston. In vivo anisotropic mechanical properties of dystrophic skeletal muscles measured by MR elastography with diffusion–tensor imaging: the mdx mouse model of muscular dystrophy. Radiology 2014. doi:10.1148/radiol.14132661.
Qin, E. C., R. Sinkus, G. Geng, S. Cheng, M. Green, C. D. Rae, and L. E. Bilston. Combining MR elastography and diffusion tensor imaging for the assessment of anisotropic mechanical properties: a phantom study. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 37:217–226, 2013.
Rydahl, S. J., and B. J. Brouwer. Ankle stiffness and tissue compliance in stroke survivors: a validation of myotonometer measurements. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 85:1631–1637, 2004.
Sandrin, L., M. Tanter, J. L. Gennisson, S. Catheline, and M. Fink. Shear elasticity probe for soft tissues with 1-D transient elastography. Trans. Ultrasonics Ferroelectr. Freq. Control IEEE 49:436–446, 2002.
Shinohara, M., K. Sabra, J. L. Gennisson, M. Fink, and M. Tanter. Real-time visualization of muscle stiffness distribution with ultrasound shear wave imaging during muscle contraction. Muscle Nerve 42:438–441, 2010.
Sinkus, R., M. Tanter, S. Catheline, J. Lorenzen, C. Kuhl, E. Sondermann, and M. Fink. Imaging anisotropic and viscous properties of breast tissue by magnetic resonance-elastography. Magn. Reson. Med. 53:372–387, 2005.
Talwalkar, J. A., M. Yin, J. L. Fidler, S. O. Sanderson, P. S. Kamath, and R. L. Ehman. Magnetic resonance imaging of hepatic fibrosis: emerging clinical applications. Hepatology 47:332–342, 2008.
Tian, M., R. D. Herbert, P. Hoang, S. C. Gandevia, and L. E. Bilston. Myofascial force transmission between the human soleus and gastrocnemius muscles during passive knee motion. J. Appl. Physiol. 113:517–523, 2012.
Tian, M., P. D. Hoang, S. C. Gandevia, L. E. Bilston, and R. D. Herbert. Stress relaxation of human ankles is only minimally affected by knee and ankle angle. J. Biomech. 43:990–993, 2010.
Torres, L., and L. Duchen. The mutant mdx: inherited myopathy in the mouse morphological studies of nerves, muscles and end-plates. Brain 110:269–299, 1987.
Vain, A. Estimation of the Functional State of Skeletal Muscle. In: Control of Ambulation Using Functional Neuromuscular Stimulation, edited by P. H. Veltink, and H. B. K. Boom. Enschede: University of Twente Press, 1995, pp. 51–55.
Van Houten, E. E. W., M. M. Doyley, F. E. Kennedy, J. B. Weaver, and K. D. Paulsen. Initial in vivo experience with steady-state subzone-based MR elastography of the human breast. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 17:72–85, 2003.
Van Houten, E., J. Weaver, M. Miga, F. Kennedy, and K. Paulsen. Elasticity reconstruction from experimental MR displacement data: initial experience with an overlapping subzone finite element inversion process. Med. Physics. 27:101–107, 2000.
Van Loocke, M., C. G. Lyons, and C. K. Simms. A validated model of passive muscle in compression. J. Biomech. 39:2999–3009, 2006.
van Turnhout, M., G. Peters, A. Stekelenburg, and C. Oomens. Passive transverse mechanical properties as a function of temperature of rat skeletal muscle in vitro. Biorheology 42:193–207, 2005.
Vasilescu, D., D. Vasilescu, S. Dudea, C. Botar-Jid, S. Sfrângeu, and D. Cosma. Sonoelastography contribution in cerebral palsy spasticity treatment assessment, preliminary report: a systematic review of the literature apropos of seven patients. Med. Ultrason. 12:306–310, 2010.
Veldi, M., V. Vasar, T. Hion, A. Vain, and M. Kull. Myotonometry demonstrates changes of lingual musculature in obstructive sleep apnoea. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 259:108–112, 2002.
Zerhouni, E. A., D. M. Parish, W. J. Rogers, A. Yang, and E. P. Shapiro. Human heart: tagging with MR imaging–a method for noninvasive assessment of myocardial motion. Radiology 169:59–63, 1988.
Zhijie, Z., K. Cw, L. Wc, and S. Fu. Shearwave ultrasound elastography of thigh muscles: intra- and inter-rater reliability. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 37:S141–S142, 2011.
Acknowledgments
Lynne Bilston is supported by an NHMRC senior research fellowship. The authors have no competing interests to declare. The authors would like to thank Professor Rob Herbert for his insightful comments on a draft of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Amit Gefen oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bilston, L.E., Tan, K. Measurement of Passive Skeletal Muscle Mechanical Properties In Vivo: Recent Progress, Clinical Applications, and Remaining Challenges. Ann Biomed Eng 43, 261–273 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-014-1186-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-014-1186-2