Abstract
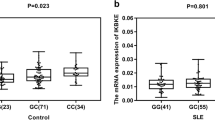
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a systemic autoimmune and inflammatory disease with a strong genetic contribution and characterized by kinds of immune reactions. Our previous genome-wide association studies have identified IL-28RA as a susceptibility gene for SLE. In this study, we performed a quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) in 62 patients with SLE and 69 controls to investigate the different expression levels of IL-28RA in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from SLE patients and healthy controls and the association between IL-28RA expression and systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity index (SLEDAI) or the variant of the single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs4649203. The expression levels of IL-28RA messenger RNA (mRNA) in SLE patients were significantly increased compared with those of healthy controls. In addition, there were also significant differences in the expression levels of IL-28RA between active (SLEDAI ≥ 6) or inactive (SLEDAI < 6) SLE groups and healthy controls. However, no correlation was observed between IL-28RA mRNA expression level and SLEDAI. There was no association between the variant of the SNP rs4649203 and IL-28RA mRNA expression levels neither. These results indicated that expression of IL-28RA mRNA may be correlated with the pathogenesis of SLE.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wong CK, Ho CY, Li EK, Lam CW (2000) Elevation of proinflammatory cytokine (IL-18, IL-17, IL-12) and Th2 cytokine (IL-4) concentrations in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 9(8):589–593
Li Y, Cheng H, Zuo XB, Sheng YJ, Zhou FS, Tang XF, Tang HY, Gao JP, Zhang Z, He SM, Lv YM, Zhu KJ, Hu DY, Liang B, Zhu J, Zheng XD, Sun LD, Yang S, Cui Y, Liu JJ, Zhang XJ (2013) Association analyses identifying two common susceptibility loci shared by psoriasis and systemic lupus erythematosus in the Chinese Han population. J Med Genet 50(12):812–818. doi:10.1136/jmedgenet-2013-101787
Dumoutier L, Lejeune D, Hor S, Fickenscher H, Renauld JC (2003) Cloning of a new type II cytokine receptor activating signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)1, STAT2 and STAT3. Biochem J 370(Pt 2):391–396. doi:10.1042/BJ20021935
Kotenko SV, Gallagher G, Baurin VV, Lewis-Antes A, Shen M, Shah NK, Langer JA, Sheikh F, Dickensheets H, Donnelly RP (2003) IFN-lambdas mediate antiviral protection through a distinct class II cytokine receptor complex. Nat Immunol 4(1):69–77. doi:10.1038/ni875
Sheppard P, Kindsvogel W, Xu W, Henderson K, Schlutsmeyer S, Whitmore TE, Kuestner R, Garrigues U, Birks C, Roraback J, Ostrander C, Dong D, Shin J, Presnell S, Fox B, Haldeman B, Cooper E, Taft D, Gilbert T, Grant FJ, Tackett M, Krivan W, McKnight G, Clegg C, Foster D, Klucher KM (2003) IL-28, IL-29 and their class II cytokine receptor IL-28R. Nat Immunol 4(1):63–68. doi:10.1038/ni873
Hochberg MC (1997) Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 40(9):1725. doi:10.1002/1529-0131(199709)40:9<1725::AID-ART29>3.0.CO;2-Y
Bombardier C, Gladman DD, Urowitz MB, Caron D, Chang CH (1992) Derivation of the SLEDAI. A disease activity index for lupus patients. The Committee on Prognosis Studies in SLE. Arthritis Rheum 35(6):630–640
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25(4):402–408. doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Mok CC, Lau CS (2003) Pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Pathol 56(7):481–490
Dumoutier L, Tounsi A, Michiels T, Sommereyns C, Kotenko SV, Renauld JC (2004) Role of the interleukin (IL)-28 receptor tyrosine residues for antiviral and antiproliferative activity of IL-29/interferon-lambda 1: similarities with type I interferon signaling. J Biol Chem 279(31):32269–32274. doi:10.1074/jbc.M404789200
Cui Y, Sheng Y, Zhang X (2013) Genetic susceptibility to SLE: recent progress from GWAS. J Autoimmun 41:25–33. doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2013.01.008
Ank N, Iversen MB, Bartholdy C, Staeheli P, Hartmann R, Jensen UB, Dagnaes-Hansen F, Thomsen AR, Chen Z, Haugen H, Klucher K, Paludan SR (2008) An important role for type III interferon (IFN-lambda/IL-28) in TLR-induced antiviral activity. J Immunol 180(4):2474–2485
Cao Y, Zhang R, Zhang W, Zhu C, Yu Y, Song Y, Wang Q, Bai L, Liu Y, Wu K, Wu J (2014) IL-27, a cytokine, and IFN-lambda1, a type III IFN, are coordinated to regulate virus replication through type I IFN. J Immunol 192(2):691–703. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1300252
Ding S, Khoury-Hanold W, Iwasaki A, Robek MD (2014) Epigenetic reprogramming of the type III interferon response potentiates antiviral activity and suppresses tumor growth. PLoS Biol 12(1):e1001758. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1001758
O’Connor KS, Ahlenstiel G, Suppiah V, Schibeci S, Ong A, Leung R, van der Poorten D, Douglas MW, Weltman MD, Stewart GJ, Liddle C, George J, Booth DR (2013) IFNL3 mediates interaction between innate immune cells: implications for hepatitis C virus pathogenesis. Innate Immun 20(6):598–605
Tezuka Y, Endo S, Matsui A, Sato A, Saito K, Semba K, Takahashi M, Murakami T (2012) Potential anti-tumor effect of IFN-lambda2 (IL-28A) against human lung cancer cells. Lung Cancer 78(3):185–192. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2012.09.005
Maher SG, Sheikh F, Scarzello AJ, Romero-Weaver AL, Baker DP, Donnelly RP, Gamero AM (2008) IFNalpha and IFNlambda differ in their antiproliferative effects and duration of JAK/STAT signaling activity. Cancer Biol Ther 7(7):1109–1115
de Veer MJ, Holko M, Frevel M, Walker E, Der S, Paranjape JM, Silverman RH, Williams BR (2001) Functional classification of interferon-stimulated genes identified using microarrays. J Leukoc Biol 69(6):912–920
Fensterl V, Sen GC (2009) Interferons and viral infections. Biofactors 35(1):14–20. doi:10.1002/biof.6
Acknowledgments
We thank all the study participants and all the volunteers who have so willingly participated in this study, thus making this study possible. This work was supported by grants from the National Key Basic Research Program of China (2014CB541901, 2012CB722404, and 2011CB512103), the Research Project of Chinese Ministry of Education (No. 213018A) and the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (NCET-12-0600), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81402590, 81371722, 81320108016, and 81171505), the Natural Science Fund of Anhui province (1408085MKL27) and the Youth Science Training Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (2010kj10).
Disclosures
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Yu-Yan Cheng, Yu-Jun Sheng and Yan Chang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, YY., Sheng, YJ., Chang, Y. et al. Increased expression of IL-28RA mRNA in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol 34, 1807–1811 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-015-2947-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-015-2947-5