Abstract
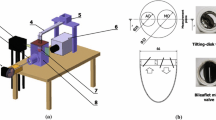
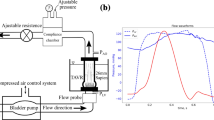
New dynamic particle image velocimetry (PIV) technology was applied to the study of the flow field associated with prosthetic heart valves. Four bileaflet prostheses, the St. Jude Medical (SJM) valve, the On-X valve with straight leaflets, the Jyros (JR) valve, and the Edwards MIRA (MIRA) valve with curved leaflets, were tested in the mitral position under pulsatile flow conditions to find the effect of the leaflet shape and overall valve design on the flow field, particularly in terms of the turbulent stress distribution, which may influence hemolysis, platelet activation, and thrombus formation. Comparison of the time-resolved flow fields associated with the opening, accelerating, peak, and closing phases of the diastolic flow revealed the effects of the leaflet shape and overall valve design on the flow field. Anatomically and antianatomically oriented bileaflet valves were also compared in the mitral position to study the effects of the orientation on the downstream flow field. The experimental program used a dynamic PIV system utilizing a high-speed, high-resolution video camera to map the true time-resolved velocity field inside the simulated ventricle. Based on the experimental data, the following general conclusions can be made. High-resolution dynamic PIV can capture true chronological changes in the velocity and turbulence fields. In the vertical measuring plane that passes the centers of both the aortic and mitral valves (A-A section), bileaflet valves show clear and simple circulatory flow patterns when the valve is installed in the antianatomical orientation. The SJM, the On-X, and the MIRA valves maintain a relatively high velocity through the central orifice. The curved leaflets of the JR valve generate higher velocities with a divergent flow during the accelerating and peak flow phases when the valve is installed in the anatomical orientation. In the velocity field directly below the mitral valve and normal to the previous measuring plane (B-B section), where characteristic differences in valve design on the three-dimensional flow should be visible, the symmetrical divergent nature of the flow generated by the two inclined half-disks installed in the antianatomical orientation was evident. The SJM valve, with a central downward flow near the valve, is contrasted with the JR valve, which has a peripherally strong downward circulation with higher turbulent stresses. The On-X valve has a strong central downward flow attributable to its large opening angle and flared inlet shape. The MIRA valve also has a relatively strong downward central flow. The MIRA valve, however, diverts the flow three-dimensionally due to its peripherally curved leaflets.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
CA Hufnagel WP Harvey PJ Rabil TF McDermott (1954) ArticleTitleSurgical correction of aortic insufficiency Surgery 35 673–683 Occurrence Handle13156880 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaG2c%2Fns1ymsA%3D%3D
A Starr ML Edwards CW McCord HE Griswold (1963) ArticleTitleAortic replacement clinical experience with a semirigid ball-valve prosthesis Circulation 27 779–783
N Aoyagi I Tanaka Y Nishi M Yamashita A Oryouji T Hara K Kosuga K Ooishi (1991) ArticleTitleLong-term results of MRV using the SJM valve J Jpn Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 39 1126–1130 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK38%2Fktl2muw%3D%3D
EM Baudet CC Oca XF Roques MN Laborde AS Hafez MA Collot IM Ghidoni (1985) ArticleTitleA 5.5 Year experience with the St. Jude Medical cardiac valve prosthesis. Early and late results of 737 valve replacements in 671 patients J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 90 137–144 Occurrence Handle3874324 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL2M3jvV2rtg%3D%3D
Duveau D, Michaud JL, Despins P, Patra P, Train M, Dupon H, Rozo L, Carlier R. Mitral valve replacement with the St. Jude Medical prosthesis: 242 cases with clinical results and an evaluation of prosthesis positioning. In: DeBakey ME (ed) Advances in cardiac valves, clinical perspectives (Proceedings of the Third International Symposium on the St. Jude Valve, November 1982, Scottsdale, Arizona), New York: Yorke Medical Books, 1983;183–190
T Akutsu D Higuchi (1999) ArticleTitleEffect of mechanical prosthetic heart valve orientation on the flow field inside a simulated ventricle: comparison between St. Jude Medical valve and Medtronic-Hall valve J Artif Organs 2 39–45 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01235523
T Akutsu D Higuchi (2000) ArticleTitleEffect of the mechanical prosthetic mono- and bi-leaflet heart valve orientation on the flow field inside a simulated ventricle J Artif Organs 3 126–135 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF02479979
T Akutsu D Higuchi (2001) ArticleTitleFlow analysis of bi-leaflet mechanical prosthetic heart valves using laser Doppler anemometry: effect of the valve design and installed orientation on the flow inside a simulated left ventricle J Artif Organs 4 113–125 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF02481421
T Akutsu T Masuda (2003) ArticleTitleThree-dimensional flow analysis of a mechanical bi-leaflet mitral prostheses J Artif Organs 6 112–123 Occurrence Handle14598112
T Akutsu T Fukuda (2005) ArticleTitleTime-resolved particle image velocimetry and laser Doppler anemometry study of the turbulent flow field of bileaflet mechanical mitral prostheses J Artif Organs 8 171–183 Occurrence Handle16235034 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10047-005-0298-8
VJ Modi WF Bishop T Akutsu (1991) ArticleTitleUnsteady fluid dynamics of three contemporary heart valves using a two-component LDA system Artif Organs 14 103–107
T Akutsu VJ Modi (1997) ArticleTitleUnsteady fluid dynamics of several mechanical prosthetic heart valves using a two-component laser Doppler anemometer system Artif Organs 21 1110–1120 Occurrence Handle9335370 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2svnsVentA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1525-1594.1997.tb00451.x
LA Du Plessis P Marchand (1964) ArticleTitleThe anatomy of the mitral valve and its associated structures Thorax 19 221–227 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaF2c7gtFChug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1136/thx.19.3.221
N Westerhof G Elzinga P Sipkema (1971) ArticleTitleAn artificial arterial system for the pumping heart J Appl Physiol 31 776–781 Occurrence Handle5117196 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaE38%2FjtlyitA%3D%3D
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akutsu, T., Saito, J. Dynamic particle image velocimetry flow analysis of the flow field immediately downstream of bileaflet mechanical mitral prostheses. J Artif Organs 9, 165–178 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10047-006-0340-5
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10047-006-0340-5