Abstract
Purpose
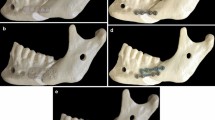
Relapse caused by clockwise (opening) rotation of the distal segment (dentate segment) in the sagittal plane is one of the postoperative complications sometimes seen after sagittal split ramus osteotomy. The force involved in this movement is primarily exerted by the masticatory and suprahyoid muscles. For postoperative stability, we have used two plates on each side: a straight plate placed over the vertical osteotomy line at the buccal surface of the first molar and an L-shaped plate placed at the distal or lateral part of the last molar over the osteotomy line, just crossing over the upper-lateral edge of the buccal shelf, to prevent the tail of the distal segment from moving upward. Although postoperative stability was clinically fine, experimental evaluations have not previously been performed. To clarify the effects of the L-shaped plate, we performed an experimental study using a bioabsorbable plate system.
Methods
A custom-fabricated jig was made to simulate rotational movement of the segments. Two segments made from polyoxymethylene resin were fixed with a four-hole straight or four-hole box poly-l-lactate bioabsorbable plate. An L-shaped plated was then added for rigidity, and mechanical testing was performed.
Results
The yield load exerted by the four-hole straight plate alone was 152.4 ± 11.0 N. This increased significantly to 273.8 ± 43.7 N with addition of an L-shaped plate (P < 0.05).
Conclusion
Addition of an L-shaped plate significant improves the rigidity of four-hole straight plate fixation in a bioabsorbable plate system.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Spiessl B (1974) Osteosynthese bei sagittaler Osteotomie nach Obwegeser/Dal pont. In: Schuchardt K (ed) Fortschritte in Kiefer-und Gesichtschirurgie. Thieme, Stuttgart, pp 145–148
Michelet FX, Deymes J, Dessus B (1973) Osteosynthesis with miniaturized screwed plates in maxillo-facial surgery. J Maxillofac Surg 1:79–84
Reyneke JP, Ferretti C (2007) Anterior open bite correction by Le Fort I or bilateral sagittal split osteotomy. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am 19:321–338
Ellis E, Esmail N (2009) Malocclusions resulting from loss of fixation after sagittal split ramus osteotomies. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 67:2528–2533
Epker BN (1977) Modifications in the sagittal osteotomy of the mandible. J Oral Surg 35:157–159
Murphy MT, Haug RH, Barber JE (1997) An in vitro comparison of the mechanical characteristics of three sagittal ramus osteotomy fixation techniques. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 55:489–494
Haug RH, Barber JE, Punjabi AP (1999) An in vitro comparison of the effect of number and pattern of positional screws on load resistance. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 57:300–308
Foley WL, Beckman TW (1992) In vitro comparison of screw versus plate fixation in the sagittal split osteotomy. Int J Adult Orthodon Orthognath Surg 7:147–151
Anucul B, Waite PD, Lemons JE (1992) In vitro strength analysis of sagittal split osteotomy fixation: noncompression monocortical plates versus bicortical position screws. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 50:1295–1299
Peterson GP, Haug RH, Van Sickels J (2005) A biomechanical evaluation of bilateral sagittal ramus osteotomy fixation techniques. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 63:1317–1324
Joss CU, Vassalli IM (2008) Stability after bilateral sagittal split osteotomy setback surgery with rigid internal fixation: a systematic review. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 66:1634–1643
Aymach Z, Nei H, Kawamura H, Bell W (2010) Biomechanical evaluation of a T-shaped miniplate fixation of a modified sagittal split ramus osteotomy with buccal step, a new technique for mandibular orthognathic surgery. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. doi:10.1016/j.tripleo.2010.03.028
Ribeiro-Junior PD, Magro-Filho O, Shastri KA, Papageorge MB (2010) In vitro biomechanical evaluation of the use of conventional and locking miniplate/screw systems for sagittal split ramus osteotomy. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 68:724–730
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank Hitoshi Ohtani of Gunze Co., Ltd (Kyoto, Japan) for providing PLLA materials, engaging in customization of a new jig and assisting with the laboratory testing.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsushita, K., Inoue, N. & Totsuka, Y. In vitro biomechanical evaluation of the effect of an additional L-shaped plate on straight or box plate fixation in sagittal split ramus osteotomy using a bioabsorbable plate system. Oral Maxillofac Surg 15, 139–146 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10006-011-0266-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10006-011-0266-9