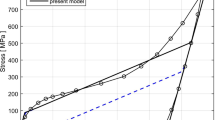
Abstract
This paper focuses on the numerical simulation of martensitic transformations in shape memory alloys (SMAs) using a phase-field model. We developed a dynamic thermo-mechanical model for SMAs, using strain based order parameter, having a bi-directional coupling between structural and thermal physics via strain, strain rate and temperature. The model involves fourth order spatial derivatives representing a domain wall. We propose an isogeometric analysis numerical formulation for straightforward solution to the fourth order differential equations. We present microstructure evolution under different loading conditions and dynamic loading simulations of the evolved microstructures of SMAs of different geometries to illustrate the flexibility, accuracy and stability of our numerical method. The simulation results are in agreement with the numerical and experimental results from the literature.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahluwalia R, Lookman T, Saxena A (2006) Dynamic strain loading of cubic to tetragonal martensites. Acta Mater 54(8):2109–2120
Ahluwalia R, Lookman T, Saxena A, Shenoy S (2004) Pattern formation in ferroelastic transitions. Phase Trans 77(5–7):457–467
Auricchio F, Da Veiga LB, Hughes TJR, Reali A, Sangalli G (2010) Isogeometric collocation methods. Math Models Methods Appl Sci 20(11):2075–2107
Auricchio F, da Veiga LB, Hughes T, Reali A, Sangalli G (2012) Isogeometric collocation for elastostatics and explicit dynamics. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 249252:2–14
Auricchio F, da Veiga LB, Kiendl J, Lovadina C, Reali A (2013) Locking-free isogeometric collocation methods for spatial Timoshenko rods. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 263:113–126
Bazilevs Y, Calo V, Cottrell J, Evans J, Hughes T, Lipton S, Scott M, Sederberg T (2010) Isogeometric analysis using T-splines. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 199(58):229–263
Bhattacharya K (2003) Microstructure of martensite: why it forms and how it gives rise to the shape-memory effect. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Borden MJ, Verhoosel CV, Scott MA, Hughes TJ, Landis CM (2012) A phase-field description of dynamic brittle fracture. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 217:77–95
Bouville M, Ahluwalia R (2008) Microstructure and mechanical properties of constrained shape memory alloy nanograins and nanowires. Acta Mater 56(14):3558–3567
Chen L (2002) Phase-field models for microstructure evolution. Annu Rev Mater Res 32(1):113–140
Chen L, Shen J (1998) Applications of semi-implicit Fourier-spectral method to phase field equations. Comput Phys Commun 108(2):147–158
Comsol multiphysics finite element analysis software. http://www.comsol.com
Cottrell J, Hughes T, Reali A (2007) Studies of refinement and continuity in isogeometric structural analysis. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 196(4144):4160–4183
Cottrell J, Reali A, Bazilevs Y, Hughes T (2006) Isogeometric analysis of structural vibrations. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 195(4143):5257–5296
Cottrell JA, Hughes TJR, Bazilevs Y (2009) Isogeometric analysis: toward integration of CAD and FEA. Wiley, New York
De Lorenzis L, Temizer I, Wriggers P, Zavarise G (2011) A large deformation frictional contact formulation using NURBS-based isogeometric analysis. Int J Numer Methods Eng 87(13):1278–1300
Dedè L, Borden MJ, Hughes TJ (2012) Isogeometric analysis for topology optimization with a phase field model. Arch Comput Methods Eng 19(3):427–465
Dhote R, Gomez H, Melnik R, Zu J (2013) Isogeometric analysis of coupled thermo-mechanical phase-field models for shape memory alloys using distributed computing. Procedia Comput Sci 18:1068–1076
Dhote R, Melnik R, Zu J (2012) Dynamic thermo-mechanical coupling and size effects in finite shape memory alloy nanostructures. Comput Mater Sci 63:105–117
Elguedj T, Bazilevs Y, Calo V, Hughes T (2008) B and F projection methods for nearly incompressible linear and non-linear elasticity and plasticity using higher-order NURBS elements. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 197(3340):2732–2762
Falk F (1980) Model free energy, mechanics, and thermodynamics of shape memory alloys. Acta Metall 28(12):1773–1780
Gadaj S, Nowacki W, Pieczyska E (2002) Temperature evolution in deformed shape memory alloy. Infrared Phys Technol 43(3–5):151–155
Gomez H, Calo V, Bazilevs Y, Hughes T (2008) Isogeometric analysis of the Cahn–Hillard phase-field model. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 197(49–50):4333–4352
Gomez H, Hughes TJ, Nogueira X, Calo VM (2010) Isogeometric analysis of the isothermal Navier–Stokes–Korteweg equations. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 199(2528):1828–1840
Gomez H, Nogueira X (2012) An unconditionally energy-stable method for the phase field crystal equation. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 249252:52–61
Gomez H, Paris J (2011) Numerical simulation of asymptotic states of the damped Kuramoto–Sivashinsky equation. Phys Rev E 83:046702
Greer J, Bertozzi A, Sapiro G (2006) Fourth order partial differential equations on general geometries. J Comput Phys 216(1):216–246
Hughes T, Cottrell J, Bazilevs Y (2005) Isogeometric analysis: CAD, finite elements, NURBS, exact geometry and mesh refinement. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 194(3941):4135–4195
Kiendl J, Bazilevs Y, Hsu MC, Wchner R, Bletzinger KU (2010) The bending strip method for isogeometric analysis of Kirchhoff–Love shell structures comprised of multiple patches. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 199(3740):2403–2416
Kim JY, Youn SK (2012) Isogeometric contact analysis using mortar method. Int J Numer Methods Eng 89(12):1559–1581
Levitas V, Preston D (2002) Three-dimensional Landau theory for multivariant stress-induced martensitic phase transformations. I. Austenite \(\leftrightarrow \) martensite. Phys Rev B 66(134206):1–9
Liu J, Dede L, Evans JA, Borden MJ, Hughes TJ (2013) Isogeometric analysis of the advective Cahn–Hilliard equation: spinodal decomposition under shear flow. J Comput Phys 242:321–350
Mamivand M, Zaeem MA, El Kadiri H (2013) A review on phase field modeling of martensitic phase transformation. Comput Mater Sci 77:304–311
Melnik R, Roberts A, Thomas KA (2000) Computing dynamics of copper-based SMA via center manifold reduction models. Comput Mater Sci 18:255–268
Ng N, Ahluwalia R, Srolovitz D (2012) Domain patterns in free-standing nanoferroelectrics. Acta Mater 60(8):3632–3642
Pieczyska E, Tobushi H (2010) Temperature evolution in shape memory alloy during loading in various conditions. In 10th international conference on quantitative infrared thermography, p 5–10
Provatas N, Elder K (2010) Phase-field methods in materials science and engineering. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim
Raknes S, Deng X, Bazilevs Y, Benson D, Mathisen K, Kvamsdal T (2013) Isogeometric rotation-free bending-stabilized cables: statics, dynamics, bending strips and coupling with shells. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 263:127–143
Salje E, Buckley A, Van Tendeloo G, Ishibashi Y, Nord G (1998) Needle twins and right-angled twins in minerals: comparison between experiment and theory. Am Mineral 83(7–8):811–822
Schillinger D, Ded L, Scott MA, Evans JA, Borden MJ, Rank E, Hughes TJ (2012) An isogeometric design-through-analysis methodology based on adaptive hierarchical refinement of NURBS, immersed boundary methods, and T-spline CAD surfaces. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 249252:116–150
Scott M, Simpson R, Evans J, Lipton S, Bordas S, Hughes T, Sederberg T (2013) Isogeometric boundary element analysis using unstructured T-splines. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 254:197–221
Steinbach I (2009) Phase-field models in materials science. Model Simul Mater Sci Eng 17:073001–073031
Steinbach I, Shchyglo O (2011) Phase-field modelling of microstructure evolution in solids: perspectives and challenges. Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci 15(3):87–92
Vilanova G, Colominas I, Gomez H (2013) Capillary networks in tumor angiogenesis: from discrete endothelial cells to phase-field averaged descriptions via isogeometric analysis. Int J Numer Methods Biomed Eng 29(10):1015–1037
Wang L, Melnik R (2007) Model reduction applied to square to rectangular martensitic transformations using proper orthogonal decomposition. Appl Numer Math 57(5):510–520
Yamanaka A, Takaki T, Tomita Y (2008) Elastoplastic phase-field simulation of self- and plastic accommodations in cubic tetragonal martensitic transformation. Mater Sci Eng A 491(1):378–384
Acknowledgments
RD and RM have been supported by NSERC and CRC program, Canada, and JZ by NSERC. HG was partially supported by the European Research Council through the FP7 Ideas Starting Grant program (Project # 307201) and by Consellería de Educación e Ordenación Universitaria (Xunta de Galicia). Their support is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dhote, R.P., Gomez, H., Melnik, R.N.V. et al. Isogeometric analysis of a dynamic thermo-mechanical phase-field model applied to shape memory alloys. Comput Mech 53, 1235–1250 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-013-0966-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-013-0966-0