Abstract
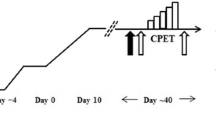
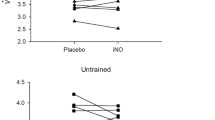
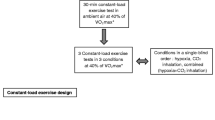
We sought to determine the influence of sildenafil on the diffusing capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxide (DLCO) and the components of DLCO (pulmonary capillary blood volume V c, and alveolar–capillary membrane conductance D M) at rest and following exercise with normoxia and hypoxia. This double-blind placebo-controlled, cross-over study included 14 healthy subjects (age = 33 ± 11 years, ht = 181 ± 8 cm, weight = 85 ± 14 kg, BMI = 26 ± 3 kg/m2, peak normoxic VO2 = 36 ± 6 ml/kg, mean ± SD). Subjects were randomized to placebo or 100 mg sildenafil 1 h prior to entering a hypoxic tent with an FiO2 of 12.5% for 90 min. DLCO, V c, and D M were assessed at rest, every 3 min during exercise, at peak exercise, and 10 and 30 min post exercise. Sildenafil attenuated the elevation in PAP at rest and during recovery with exposure to hypoxia, but pulmonary arterial pressure immediately post exercise was not different between sildenafil and placebo. Systemic O2 saturation and VO2peak did not differ between the two conditions. DLCO was not different between groups at any time point. V C was higher with exercise in the placebo group, and the difference in D M between sildenafil and placebo was significant only when corrected for changes in V c (D M/V c = 0.57 ± 0.29 vs. 0.41 ± 0.16, P = 0.04). These results suggest no effect of sildenafil on DLCO, but an improvement in D M when corrected for changes in V c during short-term hypoxic exposure with exercise.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldashev AA, Kojonazarov BK, Amatov TA, Sooronbaev TM, Mirrakhimov MM, Morrell NW, Wharton J, Wilkins MR (2005) Phosphodiesterase type 5 and high altitude pulmonary hypertension. Thorax 60:683–687
Bartsch P, Mairbaurl H, Maggiorini M, Swenson ER (2005) Physiological aspects of high-altitude pulmonary edema. J Appl Physiol 98:1101–1110
Bell C, Monahan KD, Donato AJ, Hunt BE, Seals DR, Beck KC (2003) Use of acetylene breathing to determine cardiac output in young and older adults. Med Sci Sports Exerc 35:58–64
Bland RD, Demling RH, Selinger SL, Staub NC (1977) Effects of alveolar hypoxia on lung fluid and protein transport in unanesthetized sheep. Circ Res 40:269–274
Borg GA (1982) Psychophysical bases of perceived exertion. Med Sci Sports Exerc 14:377–381
Chang HJ, Chung JH, Choi BJ, Choi TY, Choi SY, Yoon MH, Hwang GS, Shin JH, Tahk SJ, Choi BI (2003) Endothelial dysfunction and alteration of nitric oxide/cyclic GMP pathway in patients with exercise-induced hypertension. Yonsei Med J 44:1014–1020
Cohen AH, Hanson K, Morris K, Fouty B, McMurty IF, Clarke W, Rodman DM (1996) Inhibition of cyclic 3′-5′-guanosine monophosphate-specific phosphodiesterase selectively vasodilates the pulmonary circulation in chronically hypoxic rats. J Clin Invest 97:172–179
Faoro V, Lamotte M, Deboeck G, Pavelescu A, Huez S, Guenard H, Martinot JB, Naeije R (2007) Effects of sildenafil on exercise capacity in hypoxic normal subjects. High Alt Med Biol 8:155–163
Galie N, Ghofrani HA, Torbicki A, Barst RJ, Rubin LJ, Badesch D, Fleming T, Parpia T, Burgess G, Branzi A, Grimminger F, Kurzyna M, Simonneau G (2005) Sildenafil citrate therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension. N Engl J Med 353:2148–2157
Gallagher CG, Huda W, Rigby M, Greenberg D, Younes M (1988) Lack of radiographic evidence of interstitial pulmonary edema after maximal exercise in normal subjects. Am Rev Respir Dis 137:474–476
Ghofrani HA, Reichenberger F, Kohstall MG, Mrosek EH, Seeger T, Olschewski H, Seeger W, Grimminger F (2004) Sildenafil increased exercise capacity during hypoxia at low altitudes and at Mount Everest base camp: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover trial. Ann Intern Med 141:169–177
Grover RF (1965) Pulmonary circulation in animals and man at high altitude. Ann N Y Acad Sci 127:632–639
Guenette JA, Sporer BC, Macnutt MJ, Coxson HO, Sheel AW, Mayo JR, McKenzie DC (2007) Lung density is not altered following intense normobaric hypoxic interval training in competitive female cyclists. J Appl Physiol 103(3):875–882
Hanel B, Clifford PS, Secher NH (1994) Restricted postexercise pulmonary diffusion capacity does not impair maximal transport for O2. J Appl Physiol 77:2408–2412
Hansen JE, Sue DY, Wasserman K (1984) Predicted values for clinical exercise testing. Am Rev Respir Dis 129:S49–S55
Hodges AN, Sheel AW, Mayo JR, McKenzie DC (2007) Human lung density is not altered following normoxic and hypoxic moderate-intensity exercise: implications for transient edema. J Appl Physiol 103:111–118
Jackson G, Benjamin N, Jackson N, Allen MJ (1999) Effects of sildenafil citrate on human hemodynamics. Am J Cardiol 83:13C–20C
Johnson BD, Saupe KW, Dempsey JA (1992) Mechanical constraints on exercise hyperpnea in endurance athletes. J Appl Physiol 73:874–886
Johnson BD, Beck KC, Proctor DN, Miller J, Dietz NM, Joyner MJ (2000) Cardiac output during exercise by the open circuit acetylene washin method: comparison with direct Fick. J Appl Physiol 88:1650–1658
Levine BD, Kubo K, Kobayashi T, Fukushima M, Shibamoto T, Ueda G (1988) Role of barometric pressure in pulmonary fluid balance and oxygen transport. J Appl Physiol 64:419–428
MacNutt MJ, Guenette JA, Witt JD, Yuan R, Mayo JR, McKenzie DC (2007) Intense hypoxic cycle exercise does not alter lung density in competitive male cyclists. Eur J Appl Physiol 99:623–631
Maeda S, Tanabe T, Otsuki T, Sugawara J, Iemitsu M, Miyauchi T, Kuno S, Ajisaka R, Matsuda M (2004) Moderate regular exercise increases basal production of nitric oxide in elderly women. Hypertens Res 27:947–953
Michelakis E, Tymchak W, Lien D, Webster L, Hashimoto K, Archer S (2002) Oral sildenafil is an effective and specific pulmonary vasodilator in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension: comparison with inhaled nitric oxide. Circulation 105:2398–2403
Nagueh SF, Kopelen HA, Zoghbi WA (1996) Relation of mean right atrial pressure to echocardiographic and Doppler parameters of right atrial and right ventricular function. Circulation 93:1160–1169
Ommen SR, Nishimura RA, Hurrell DG, Klarich KW (2000) Assessment of right atrial pressure with 2-dimensional and Doppler echocardiography: a simultaneous catheterization and echocardiographic study. Mayo Clin Proc 75:24–29
Proctor DN, Beck KC (1996) Delay time adjustments to minimize errors in breath-by-breath measurement of VO2 during exercise. J Appl Physiol 81:2495–2499
Ricart A, Maristany J, Fort N, Leal C, Pages T, Viscor G (2005) Effects of sildenafil on the human response to acute hypoxia and exercise. High Alt Med Biol 6:43–49
Richalet JP, Gratadour P, Robach P, Pham I, Dechaux M, Joncquiert-Latarjet A, Mollard P, Brugniaux J, Cornolo J (2005) Sildenafil inhibits altitude-induced hypoxemia and pulmonary hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 171:275–281
Sartori C, Allemann Y, Trueb L, Lepori M, Maggiorini M, Nicod P, Scherrer U (2000) Exaggerated pulmonary hypertension is not sufficient to trigger high-altitude pulmonary oedema in humans. Schweiz Med Wochenschr 130:385–389
Sebkhi A, Strange JW, Phillips SC, Wharton J, Wilkins MR (2003) Phosphodiesterase Type 5 as a target for the treatment of hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Circulation 107:3230–3235
Snyder EM, Beck KC, Hulsebus ML, Breen JF, Hoffman EA, Johnson BD (2006) Short-term hypoxic exposure at rest and during exercise reduces lung water in healthy humans. J Appl Physiol 101:1623–1632
Tamhane RM, Johnson RL Jr, Hsia CC (2001) Pulmonary membrane diffusing capacity and capillary blood volume measured during exercise from nitric oxide uptake. Chest 120:1850–1856
Yock PG, Popp RL (1984) Noninvasive estimation of right ventricular systolic pressure by Doppler ultrasound in patients with tricuspid regurgitation. Circulation 70:657–662
Zhao L, Mason NA, Morrell NW, Kojonazarov B, Sadykov A, Maripov A, Mirrakhimov MM, Aldashev A, Wilkins MR (2001) Sildenafil inhibits hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Circulation 104:424–428
Zusman RM, Morales A, Glasser DB, Osterloh IH (1999) Overall cardiovascular profile of sildenafil citrate. Am J Cardiol 83:35C–44C
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant to Dr. Frantz from Pfizer, Inc., NIH Grant HL71478, and AHA Grant 56051Z. At the time the study was performed Dr. Snyder was supported by the Mayo Clinic Nephrology and Hypertension Training Grant (DK007013-31). We would like to thank Minelle Hulsebus and Kathy O’Malley for their help with data collection, as well as the efforts of the study participants. We would also like to thank the staff of the General Clinical Research Center (GCRC) for their assistance throughout this study. The Mayo Clinic GCRC is supported by US Public Health Service grant M01-RR00585.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Snyder, E.M., Olson, T.P., Johnson, B.D. et al. Influence of sildenafil on lung diffusion during exposure to acute hypoxia at rest and during exercise in healthy humans. Eur J Appl Physiol 103, 421–430 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-008-0735-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-008-0735-5