Abstract
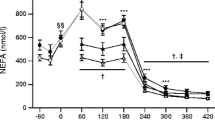
This study determined the effects of exercise training on adaptations of skeletal muscle including fibre composition, capillarity, intra-muscular triglyceride concentration (IMTG), as well as glucose transporter 4 protein (GLUT4) and metabolic enzyme activities. Percutaneous muscle biopsies from the vastus lateralis muscle were obtained from non-obese elderly Korean men (n=10; age range 58–67 years) with impaired glucose tolerance. Subjects performed 12 weeks of endurance exercise training (60–70% of the heart rate reserve). The training program improved the total GLUT4 protein expression (P<0.01), decreased the IMTG, increased the fatty acid oxidation capacity, and the number of capillaries around type 1 fibres (P<0.05), whereas no significant alteration was observed around type II fibres. All data are presented as the means together with the standard deviation. The results suggest that endurance training evokes morphological and biochemical changes in the skeletal muscle of elderly men with impaired glucose tolerance that may be considered to limit the development of type 2 diabetes.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen P (1975) Capillary density in skeletal muscle of man. Acta Physiol Scand 95:203–205
Beck-Nielsen H (1998) Mechanisms of insulin resistance in non-oxidative glucose metabolism: the role of glycogen synthase. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 9:255–279
Bergström J (1962) Muscle electrolytes in man. Scand J Clin Lab Invest [Suppl] 68:11–13
Borghouts LB, Keizer HA (2000) Exercise and insulin sensitivity: a review. Int J Sports Med 21:1–12
Brooke MH, Kaiser KK (1970) Three ‘myosin ATPase’ systems; the nature of their pH liability and sulfhydryl dependence. J Histochem Cytochem 18:670–672
Bruce CR, Kriketos AD, Cooney GJ, Hawley JA (2004) Disassociation of muscle triglyceride content and insulin sensitivity after exercise training in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 47:23–30
Ebeling P, Essén-Gustavsson B, Tuominen JA, Koivisto VA (1998) Intramuscular triglyceride content is increased in IDDM. Diabetologia 41:111–115
Gaster M, Poulsen P, Handberg A, Schroder HD, Beck-Nielsen H (2000) Direct evidence of fiber type dependent GLUT-4 expression in human skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol 278:E910–916
Gaster M, Poulsen P, Handberg A, Scholder HD, Beck-Nilsen H, Schroder HD (2003) GLUT-4 expression in human muscle fiber is not correlated with intracellular triglyceride (TG) content. Is TG a marker or a marker of insulin resistance? APMIS 111:338–348
Goodpaster BH, Thriault SC, Wakins SC, Kelly DE (2000) Intramuscular lipid content is increased in obesity and decreased by weight loss. Metabolism 49:467–472
Haffner SM, Miettinen H, Gaskill SP, Stern MP (1996) Decreased insulin action and insulin secretion predict the development of impaired glucose tolerance. Diabetologia 39:1201–1207
Horton E (1991) Exercise and decreased risk of NIDDM. N Engl J Med 325:196–199
Ivy JL (1997) Role of exercise training in the prevention and treatment of insulin resistance and non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Sports Med 24:321–336
Karvonen M, Kentala K, Musta O (1957) The effect of training on heart rate: a longitudinal study. Annu Med Exp Biol Fenn 35:307–315
Kelly DE, Mandarino LJ (2000) Fuel selection in human skeletal muscle in insulin resistance: a reexamination. Diabetes 49:677–683
Kirwan JP, Jing M (2001) Modulation of insulin signaling in human skeletal muscle in response to exercise. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 30:85–90
Kirwan JP, del Aguila LF, Hernandez JM, Williamson DL, O’Gorman DJ, Lewis R, Krishnan RK (2000) Regular exercise enhances insulin activation of IRS-I associated PI3 kinase in human skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 8:797–803
Krssak M, Petersen KF, Drenser A, DiPietro L, Vogel SM, Rothman, DL, Shulman, GI Roden M (1999) Intramyocellular lipid concentrations are correlated with insulin sensitivity in humans: a 1H NMR spectroscopy study. Diabetologia 42:113–116
Larsson H, Richter EA, Daugaard JR, Ahrén B, Kiens B (1999) Muscle fiber characteristics in postmenopausal women with normal or impaired glucose tolerance. Diabetes Care 22:1330–1338
Leturque A, Loizeau M, Baulont S, Salminen M, Girard J (1996) Improvement of insulin action in diabetic transgenic mice selectively overexpressing GLUT4 in skeletal muscle. Diabetes 45:23–27
Lillie RD, Ashburn LL (1943) Super-saturated solutions of fat stains in dilute isopropanol for demonstration of acute fatty degenerations not shown by the Herxheimer technique. Arch Pathol 36:432–440
Lowry OH, Passonneau JV (1972) A flexible system of enzymatic analysis. Academic, New York, pp 189–193
Malenfant P, Joanisse DR, Theriault R, Goodpaster BH, Kelly DE, Simoneau JA (2001) Fat content in individual muscle fibers of lean and obese subjects. Int J Obesity 25:1316–1321
Oakes ND, Cooney GJ, Camilleri S, Chisholm DJ, Kraegen EW (1997) Mechanisms of liver and muscle insulin resistance induced by chronic high-fat feeding. Diabetes 46:1768–1774
Pan DA, Lillioja S, Kriketos AD, Milner MR, Baur LA, Bogardus C, Jenkins AB, Storlien LH (1997) Skeletal muscle triglyceride levels are inversely related to insulin action. Diabetes 46:983–988
Ren JM, Marshall BA, Muecker M, McCaleb M, Amatruda JM, Shulman GI (1995) Overexpression of GLUT4 protein in muscle increases basal and insulin-stimulated whole body glucose disposal in conscious mice. J Clin Invest 1:429–432
Shimabukuro M, Koyama K, Chen G, Wang MY, Trieu F, Lee Y, Newgard CB, Unger RH (1997) Direct antidiabetic effect of leptin through triglyceride depletion of tissues. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 94:4637–4641
Simoneau J-A, Veerkamp JH, Turcotte LP, Kelly DE (1999) Markers of capacity to utilize fatty acids in human skeletal muscle. Relation to insulin resistance and obesity and effects of weight loss. FASEB J 13:2051–2060
Srere PA (1969) Citrate synthase. In: Methods in enzymology. Academic, New York, pp 3–11
The Korean Nutrition Society (2001) Recommended dietary allowances for Koreans, 7th edn, 2001
Wojtaszewski JFP, Richter EA (1998) Glucose utilization during exercise: influence of endurance training. Acta Physiol Scand 162:351–358
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant from the Korea Research Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, H.J., Lee, J.S. & Kim, C.K. Effect of exercise training on muscle glucose transporter 4 protein and intramuscular lipid content in elderly men with impaired glucose tolerance. Eur J Appl Physiol 93, 353–358 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-004-1214-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-004-1214-2