Abstract
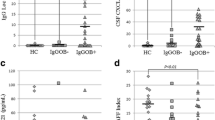
In this study the aim was to evaluate the intrathecal sICAM-1 production in multiple sclerosis (MS) patients during relapse and remission. In addition to this, we assessed whether there is a correlation between intrathecal sICAM-1 production and other disease activity markers such as IgG index and gadolinium enhancement in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Twenty four relapsing- remitting MS patients were included in the study. Serum and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) samples were obtained both during relapse and remission. The soluble form of ICAM (sICAM) was measured by the ELISA method in serum and CSF. Cranial MRI with triple dose gadolinium injection was performed for each patient both during relapse and remission. Serum levels of sICAM-1 (245.23±92.88 ng/ml) were higher during relapse than those in remission (219.90±110.94 ng/ml), but the difference was not statistically significant. In relapse periods CSF levels of sICAM-1 (1.304±0.92 ng/ml) were higher than those in remission (1.06±0.86 ng/ml), but this was not significant. However, during relapse periods patients had significantly higher sICAM-1 index values (1.76±0.60) than those found during remission periods (1.01±0.44) (p<0.05). The IgG index values were higher in relapse periods than in remission (0.88±0.37 vs. 0.67±0.28) (p<0.005). On T1 weighted images following triple dose Gd injection, at least two or more enhancing lesions were present in 22/24 of the patients (91 %) in relapse and 4/24 of the patients (19 %) in remission. There was strong correlation both between the sICAM-1 index and Gd enhancement (r=0.72 p<0.05) and sICAM-1 index and IgG index in relapse (r=0.69 p<0.05). In conclusion, there is association between high sICAM-1 and IgG indices, as well as between high sICAM-1 index and Gd enhancing MRI lesions in relapsing MS patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bevilacqua MP (1993) Endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecules. Annu Rev Immunol 11:767–804
Dore-Duffy P, Newman W, Balabanov R, et al. (1995) Circulating soluble adhesion proteins in cerebrospinal fluid and serum of the patients with multiple sclerosis: correlation with clinical activity. Ann Neurol 37:55–62
Droogan AG, McMillan SA, Douglas JP, Hawkins SA (1996) Serum and cerebrospinal fluid levels of soluble adhesion molecules in multiple sclerosis: predominant intrathecal release of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1. J Neuroimmunol 64:185–191
Gearing JH, Newman W (1993) Circulating adhesion molecules in disease. Immunol Today 14:506–507
Giovannoni G, Lai M, Thorpe J, Kidd D, Chamoun V, Thompson AJ, Miller DH, Feldmann M, Thompson EJ (1997) Longitudinal study of soluble adhesion molecules in multiple sclerosis: correlation with gadolinium enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Neurology 48:1557–1565
Hartung HP, Michels M, Reiners K, Seeldrayers P, Archelos JJ, Toyka KV (1993) Soluble ICAM-1 serum levels in multiple sclerosis and viral encephalitis. Neurology 43:2331–2335
Hartung HP, Reiners K, Archelos JJ, Michels M, Seeldrayers P, Heidenreich F, Pflughaupt KW, Toyka KV (1995) Circulating adhesion molecules and tumor necrosis factor receptor in multiple sclerosis: correlation with magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol 38(2):186–193
Jander S, Heidenreich F, Stoll G (1993) Serum and CSF levels of soluble Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in inflammatory neurologic diseases. Neurology 43:1809–1813
Kurtzke JF (1983) Rating neurological impairment in multiple sclerosis: An expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology 33:1444–1452
McDonald WI, Combston A, Edan G, Goodkin D,Hartung HP, Lublin FD, McFarland HF, Paty DW, Polman CH, Reingold SC, Sandberg-Wollheim M, Sibley W, Thompson A, van den Noort S, Weinshenker BY, Wolinsky JS (2001) Recommended diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: Guidelines from the international panel on the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 50:121–127
McDonnell GV, McMillan SA, Douglas JP, Droogan AG, Hawkins SA (1998) Raised CSF levels of soluble adhesion molecules across the clinical spectrum of multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 85:186–192
Petersen AA, Sellebjerg F, Freeriksen J, Olesen J, Vejlsgaard GL (1998) Soluble ICAM-1, demyelination and inflammation in multiple sclerosis and acute optic neuritis. J Neuroimmunol 88:120–127
Rieckmann P, Altenhofen B, Riegel A, Baudewig J, Felgenhauer K (1997) Soluble adhesion molecules (sVCAM-1 and sICAM-1) in cerebrospinal fluid and serum correlate with MRI activity in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 41:326–333
Rieckmann P, Martin S, Weichselbraun I, Albrecht M, Kitze B, Weber T, Tumani H, Broocks A, Luer W, Helwig A (1994) Serial analysis of circulating adhesion molecule and the TNF receptor in serum of patients with multiple sclerosis: cICAM-1 is an indicator for relapse. Neurology 44:2367–2372
Sharief MK, Noori MA, Ciardi M, Cirelli A, Thompson EJ (1993) Increased levels of circulating ICAM-1 in serum and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with active multiple sclerosis: correlation with TNF-α and blood brain barrier damage. J Neuroimmunol 43:15–22
Trojano M, Avolio C, Simone IL, Defazio G, Manzari C, de Robertis F, Calo A, Livrea P (1996) Soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in serum and cerebrospinal fluid of clinically active relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: correlation with Gd-DTPA magnetic resonance imaging enhancement and cerebrospinal fluid findings. Neurology 47:1535–1541
Tsukada N, Miyagi K, Matsuda M, Yanagisawa N (1993) Increased levels of circulating intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in multiple sclerosis and human T-lymphotropic virus type-1 associated myelopathy. Ann Neurol 33:646–649
Vachula M, Van Epps DE (1992) In vitro models of lymphocyte transendothelial migration. Invasion Metastasis 12:66–81
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Acar, G., İdiman, F., Kirkali, G. et al. Intrathecal sICAM-1 production in multiple sclerosis Correlation with triple dose Gd-DTPA MRI enhancement and IgG index. J Neurol 252, 146–150 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-005-0618-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-005-0618-1