Abstract
Background/Objectives
The determinants of plasma ghrelin concentrations including the effects of aging, gender, and body composition, are unclear. Appetite and energy intake decrease with advancing age, and there is a corresponding decline in total body lean tissue, and an increase in fat mass.
Methods
We measured fasting plasma ghrelin and insulin concentrations in 52 healthy subjects aged 22–82 years, and assessed body composition by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry. Energy intake was estimated from diet diaries.
Results
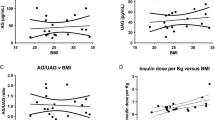
Fasting ghrelin concentrations were not significantly correlated with age and energy intake (R = 0.07, P = 0.62; and R = −0.14, P = 0.34 respectively) on univariate regression analysis, and ghrelin concentrations were higher in females than males (2886.8 ± 182.1 pg/ml vs 2082.5 ± 121.2 pg/ml; P = 0.001). Ghrelin was inversely related to body mass index (R = −0.328, P = 0.018), fat-free body mass (R = −0.428, P = 0.002), and total skeletal muscle mass (R = −0.439, P = 0.001), but not related to body fat mass (R = 0.177, P = 0.208). On multiple regression analysis, total skeletal muscle mass (corrected for height) was the only significant negative predictor (P < 0.0001) of fasting ghrelin concentrations.
Conclusions
In conclusion, in healthy adults, plasma ghrelin concentrations are not significantly influenced by age or energy intake per se, but relate to skeletal muscle mass.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arafat AM, Perschel FH, Otto B, Weickert MO, Rochlitz H, Schofl C, Spranger J, Mohlig M, Pfeiffer AF (2006) Glucagon suppression of ghrelin secretion is exerted at hypothalamus-pituitary level. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:3528–3533
Basiotis PP, Welsh SO, Cronin FJ, Kelsay JL, Mertz W (1987) Number of days of food intake records required to estimate individual and group nutrient intakes with defined confidence. J Nutr 117:1638–1641
Bauer JM, Wirth R, Troegner J, Erdmann J, Eberl T, Heppner HJ, Schusdziarra V, Sieber CC (2007) Ghrelin, anthropometry and nutritional assessment in geriatric hospital patients. Z Gerontol Geriatr 40:31–36
Baumgartner RN, Heymsfield SB, Roche AF (1995) Human body composition and the epidemiology of chronic disease. Obes Res 3:73–95
Bertoli S, Magni P, Krogh V, Ruscica M, Dozio E, Testolin G, Battezzati A (2006) Is ghrelin a signal of decreased fat-free mass in elderly subjects? Eur J Endocrinol 155:321–330
Bunt JC, Salbe AD, Tschop MH, DelParigi A, Daychild P, Tataranni PA (2003) Cross-sectional and prospective relationships of fasting plasma ghrelin concentrations with anthropometric measures in pima Indian children. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88:3756–3761
Caixas A, Bashore C, Nash W, Pi-Sunyer F, Laferrere B (2002) Insulin, unlike food intake, does not suppress ghrelin in human subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87:1902–1906
Chapman IM (2004) Endocrinology of anorexia of aging. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 18:437–452
Cummings DE, Purnell JQ, Frayo RS, Schmidova K, Wisse BE, Weigle DS (2001) A preprandial rise in plasma ghrelin levels suggests a role in meal initiation in humans. Diabetes 50:1714–1719
Cummings DE, Weigle DS, Frayo RS, Breen PA, Ma MK, Dellinger EP, Purnell JQ (2002) Plasma ghrelin levels after diet-induced weight loss or gastric bypass surgery. N Engl J Med 346:1623–1630
Di Francesco V, Fantin F, Residori L, Bissoli L, Micciolo R, Zivelonghi A, Zoico E, Omizzolo F, Bosello O, Zamboni M (2008) Effect of age on the dynamics of acylated ghrelin in fasting conditions and in response to a meal. J Am Geriatr Soc 56:1369–1370
Di Francesco V, Zamboni M, Zoico E, Mazzali G, Dioli A, Omizzolo F, Bissoli L, Fantin F, Rizzotti P, Solerte SB, Micciolo R, Bosello O (2006) Unbalanced serum leptin and ghrelin dynamics prolong postprandial satiety and inhibit hunger in healthy elderly: another reason for the “anorexia of aging”. Am J Clin Nutr 83:1149–1152
Druce MR, Small CJ, Bloom SR (2004) Minireview: gut peptides regulating satiety. Endocrinology 145:2660–2665
Espelund U, Hansen TK, Hojlund K, Beck-Nielsen H, Clausen JT, Hansen BS, Orskov H, Jorgensen JO, Frystyk J (2005) Fasting unmasks a strong inverse association between ghrelin and cortisol in serum: studies in obese and normal-weight subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90:741–746
Filigheddu N, Gnocchi VF, Coscia M, Cappelli M, Porporato PE, Taulli R, Traini S, Baldanzi G, Chianale F, Cutrupi S, Arnoletti E, Ghe C, Fubini A, Surico N, Sinigaglia F, Ponzetto C, Muccioli G, Crepaldi T, Graziani A (2007) Ghrelin and des-acyl ghrelin promote differentiation and fusion of C2C12 skeletal muscle cells. Mol Biol Cell 18:986–994
Foster-Schubert KE, McTiernan A, Frayo RS, Schwartz RS, Rajan KB, Yasui Y, Tworoger SS, Cummings DE (2005) Human plasma ghrelin levels increase during a one-year exercise program. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90:820–825
Fouladiun M, Korner U, Bosaeus I, Daneryd P, Hyltander A, Lundholm KG (2005) Body composition and time course changes in regional distribution of fat and lean tissue in unselected cancer patients on palliative care–correlations with food intake, metabolism, exercise capacity, and hormones. Cancer 103:2189–2198
Garcia JM, Iyer D, Poston WS, Marcelli M, Reeves R, Foreyt J, Balasubramanyam A (2006) Rise of plasma ghrelin with weight loss is not sustained during weight maintenance. Obesity (Silver Spring) 14:1716–1723
Gnanapavan S, Kola B, Bustin SA, Morris DG, McGee P, Fairclough P, Bhattacharya S, Carpenter R, Grossman AB, Korbonits M (2002) The tissue distribution of the mRNA of ghrelin and subtypes of its receptor, GHS-R, in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87:2988–2991
Gravholt CH, Hjerrild BE, Mosekilde L, Hansen TK, Rasmussen LM, Frystyk J, Flyvbjerg A, Christiansen JS (2006) Body composition is distinctly altered in Turner syndrome: relations to glucose metabolism, circulating adipokines, and endothelial adhesion molecules. Eur J Endocrinol 155:583–592
Hansen TK, Dall R, Hosoda H, Kojima M, Kangawa K, Christiansen JS, Jorgensen JO (2002) Weight loss increases circulating levels of ghrelin in human obesity. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 56:203–206
Kim J, Wang Z, Heymsfield SB, Baumgartner RN, Gallagher D (2002) Total-body skeletal muscle mass: estimation by a new dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry method. Am J Clin Nutr 76:378–383
Kojima M, Hosoda H, Date Y, Nakazato M, Matsuo H, Kangawa K (1999) Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature 402:656–660
Kraemer RR, Durand RJ, Hollander DB, Tryniecki JL, Hebert EP, Castracane VD (2004) Ghrelin and other glucoregulatory hormone responses to eccentric and concentric muscle contractions. Endocrine 24:93–98
Krsek M, Rosicka M, Papezova H, Krizova J, Kotrlikova E, Haluz’k M, Justova V, Lacinova Z, Jarkovska Z (2003) Plasma ghrelin levels and malnutrition: a comparison of two etiologies. Eat Weight Disord 8:207–211
Langenberg C, Bergstrom J, Laughlin GA, Barrett-Connor E (2005) Ghrelin and the metabolic syndrome in older adults. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90:6448–6453
Levine JA, Abboud L, Barry M, Reed JE, Sheedy PF, Jensen MD (2000) Measuring leg muscle and fat mass in humans: comparison of CT and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. J Appl Physiol 88:452–456
Makovey J, Naganathan V, Seibel M, Sambrook P (2007) Gender differences in plasma ghrelin and its relations to body composition and bone—an opposite-sex twin study. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 66:530–537
Marchesini G, Bianchi G, Lucidi P, Villanova N, Zoli M, De Feo P (2004) Plasma ghrelin concentrations, food intake, and anorexia in liver failure. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:2136–2141
Marzullo P, Verti B, Savia G, Walker GE, Guzzaloni G, Tagliaferri M, Di Blasio A, Liuzzi A (2004) The relationship between active ghrelin levels and human obesity involves alterations in resting energy expenditure. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:936–939
Moran LJ, Luscombe-Marsh ND, Noakes M, Wittert GA, Keogh JB, Clifton PM (2005) The satiating effect of dietary protein is unrelated to postprandial ghrelin secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90:5205–5211
Murdolo G, Lucidi P, Di Loreto C, Parlanti N, De Cicco A, Fatone C, Fanelli CG, Bolli GB, Santeusanio F, De Feo P (2003) Insulin is required for prandial ghrelin suppression in humans. Diabetes 52:2923–2927
Nagaya N, Moriya J, Yasumura Y, Uematsu M, Ono F, Shimizu W, Ueno K, Kitakaze M, Miyatake K, Kangawa K (2004) Effects of ghrelin administration on left ventricular function, exercise capacity, and muscle wasting in patients with chronic heart failure. Circulation 110:3674–3679
Natalucci G, Riedl S, Gleiss A, Zidek T, Frisch H (2005) Spontaneous 24-h ghrelin secretion pattern in fasting subjects: maintenance of a meal-related pattern. Eur J Endocrinol 152:845–850
Papotti M, Ghe C, Cassoni P, Catapano F, Deghenghi R, Ghigo E, Muccioli G (2000) Growth hormone secretagogue binding sites in peripheral human tissues. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85:3803–3807
Parker BA, Doran S, Wishart J, Horowitz M, Chapman IM (2005) Effects of small intestinal and gastric glucose administration on the suppression of plasma ghrelin concentrations in healthy older men and women. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 62:539–546
Purnell JQ, Weigle DS, Breen P, Cummings DE (2003) Ghrelin levels correlate with insulin levels, insulin resistance, and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, but not with gender, menopausal status, or cortisol levels in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88:5747–5752
Rigamonti AE, Pincelli AI, Corra B, Viarengo R, Bonomo SM, Galimberti D, Scacchi M, Scarpini E, Cavagnini F, Muller EE (2002) Plasma ghrelin concentrations in elderly subjects: comparison with anorexic and obese patients. J Endocrinol 175:R1–R5
Rossner S (2001) Obesity in the elderly—a future matter of concern? Obes Rev 2:183–188
Saad MF, Bernaba B, Hwu CM, Jinagouda S, Fahmi S, Kogosov E, Boyadjian R (2002) Insulin regulates plasma ghrelin concentration. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87:3997–4000
Schaller G, Schmidt A, Pleiner J, Woloszczuk W, Wolzt M, Luger A (2003) Plasma ghrelin concentrations are not regulated by glucose or insulin: a double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover clamp study. Diabetes 52:16–20
Schutte AE, Huisman HW, Schutte R, van Rooyen JM, Malan L, Malan NT (2007) Aging influences the level and functions of fasting plasma ghrelin levels: the POWIRS-study. Regul Pept 139:65–71
Sherwood NE, Jeffery RW, French SA, Hannan PJ, Murray DM (2000) Predictors of weight gain in the pound of prevention study. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 24:395–403
Shiiya T, Nakazato M, Mizuta M, Date Y, Mondal MS, Tanaka M, Nozoe S, Hosoda H, Kangawa K, Matsukura S (2002) Plasma ghrelin levels in lean and obese humans and the effect of glucose on ghrelin secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87:240–244
Soule S, Pemberton C, Hunt P, Cole D, Raudsepp S, Inder W (2005) Prandial regulation of ghrelin secretion in humans: does glucagon contribute to the preprandial increase in circulating ghrelin? Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 63:412–417
Sturm K, MacIntosh CG, Parker BA, Wishart J, Horowitz M, Chapman IM (2003) Appetite, food intake, and plasma concentrations of cholecystokinin, ghrelin, and other gastrointestinal hormones in undernourished older women and well-nourished young and older women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88:3747–3755
Takano H, Morita T, Iida H, Asada K, Kato M, Uno K, Hirose K, Matsumoto A, Takenaka K, Hirata Y, Eto F, Nagai R, Sato Y, Nakajima T (2005) Hemodynamic and hormonal responses to a short-term low-intensity resistance exercise with the reduction of muscle blood flow. Eur J Appl Physiol 95:65–73
Tschop M, Weyer C, Tataranni PA, Devanarayan V, Ravussin E, Heiman ML (2001) Circulating ghrelin levels are decreased in human obesity. Diabetes 50:707–709
VanItallie TB, Yang MU, Heymsfield SB, Funk RC, Boileau RA (1990) Height-normalized indices of the body’s fat-free mass and fat mass: potentially useful indicators of nutritional status. Am J Clin Nutr 52:953–959
Visser M, Fuerst T, Lang T, Salamone L, Harris TB (1999) Validity of fan-beam dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry for measuring fat-free mass and leg muscle mass. health, aging, and body composition study–dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry and Body Composition Working Group. J Appl Physiol 87:1513–1520
Yukawa M, Cummings DE, Matthys CC, Callahan HS, Frayo RS, Spiekerman CF, Weigle DS (2006) Effect of aging on the response of ghrelin to acute weight loss. J Am Geriatr Soc 54:648–653
Zhang W, Zhao L, Mulholland MW (2007) Ghrelin stimulates myocyte development. Cell Physiol Biochem 20:659–664
Acknowledgments
Associate Professor Ian Chapman was supported by a research grant from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia. Dr. Kamilia Tai was supported by a postgraduate scholarship from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tai, K., Visvanathan, R., Hammond, A.J. et al. Fasting ghrelin is related to skeletal muscle mass in healthy adults. Eur J Nutr 48, 176–183 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-009-0779-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-009-0779-2