Abstract
Background and aims
Aspirin is associated with a reduced risk of colorectal cancer (CRC), and it showed inhibited effects on interleukin 6 (IL-6)/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) signaling pathway which is thought to play an important role in intestinal inflammation and the tumorigenesis of CRC.
Methods
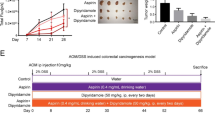
Mouse model for inflammation-related CRC was induced by a combined treatment with azoxymethane (AOM) and dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) in BALB/c mice. Effects of aspirin on tumor number and size and apoptosis of CRC cells were investigated. Key molecules of IL-6–STAT3 pathway, such as IL-6, sIL-6R, phosphorylated STAT3, and their downstream anti-apoptotic genes Bcl-2 and Bcl-xl, were assessed by ELISA and Western blot.
Results
Treatment with aspirin significantly promoted CRC cell apoptosis in AOM/DSS-induced CRC mice in vivo. The expression level of IL-6, which is an upstream molecule of STAT3 and capable of activating STAT3, was reduced in aspirin-treated mice. Furthermore, the phosphorylated form of STAT3 and the levels of STAT3’s target gene products such as Bcl-xl and Bcl-2, which are essential for cell growth and survival, were also decreased in aspirin-treated mice.
Conclusions
Our data suggested that the protective mechanisms of aspirin in CRC may be associated with its effects on induction of CRC cell apoptosis and suppression of IL-6–STAT3 signaling pathway, which implied that aspirin has a potential therapeutic activity in CRC.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cole BF, Logan RF, Halabi S, Benamouzig R, Sandler RS, Grainge MJ et al (2009) Aspirin for the chemoprevention of colorectal adenomas: meta-analysis of the randomized trials. J Natl Cancer Inst 101:256–266
Jana NR (2008) NSAIDs and apoptosis. Cell Mol Life Sci 65:1295–1301
Bollrath J, Phesse TJ, von Burstin VA, Putoczki T, Bennecke M, Bateman T et al (2009) gp130-mediated Stat3 activation in enterocytes regulates cell survival and cell-cycle progression during colitis-associated tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 15:91–102
Grivennikov S, Karin E, Terzic J, Mucida D, Yu GY, Vallabhapurapu S et al (2009) IL-6 and Stat3 are required for survival of intestinal epithelial cells and development of colitis-associated cancer. Cancer Cell 15:103–113
Scheller J, Ohnesorge N, Rose-John S (2006) Interleukin-6 trans-signalling in chronic inflammation and cancer. Scand J Immunol 63:321–329
Corvinus FM, Orth C, Moriggl R, Tsareva SA, Wagner S, Pfitzner EB et al (2005) Persistent STAT3 activation in colon cancer is associated with enhanced cell proliferation and tumor growth. Neoplasia 7:545–555
Kusaba T, Nakayama T, Yamazumi K, Yakata Y, Yoshizaki A, Inoue K et al (2006) Activation of STAT3 is a marker of poor prognosis in human colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep 15:1445–1451
Kusaba T, Nakayama T, Yamazumi K, Yakata Y, Yoshizaki A, Nagayasu T et al (2005) Expression of p-STAT3 in human colorectal adenocarcinoma and adenoma; correlation with clinicopathological factors. J Clin Pathol 58:833–838
Lassmann S, Schuster I, Walch A, Gobel H, Jutting U, Makowiec F et al (2007) STAT3 mRNA and protein expression in colorectal cancer: effects on STAT3-inducible targets linked to cell survival and proliferation. J Clin Pathol 60:173–179
Ma XT, Wang S, Ye YJ, Du RY, Cui ZR, Somsouk M (2004) Constitutive activation of Stat3 signaling pathway in human colorectal carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 10:1569–1573
Rose-John S, Mitsuyama K, Matsumoto S, Thaiss WM, Scheller J (2009) Interleukin-6 trans-signaling and colonic cancer associated with inflammatory bowel disease. Curr Pharm Des 15:2095–2103
Xiong H, Zhang ZG, Tian XQ, Sun DF, Liang QC, Zhang YJ et al (2008) Inhibition of JAK1, 2/STAT3 signaling induces apoptosis, cell cycle arrest, and reduces tumor cell invasion in colorectal cancer cells. Neoplasia 10:287–297
Atreya R, Neurath MF (2008) Signaling molecules: the pathogenic role of the IL-6/STAT-3 trans signaling pathway in intestinal inflammation and in colonic cancer. Curr Drug Targets 9:369–374
Becker C, Fantini MC, Schramm C, Lehr HA, Wirtz S, Nikolaev A et al (2004) TGF-beta suppresses tumor progression in colon cancer by inhibition of IL-6 trans-signaling. Immunity 21:491–501
Nishimoto N, Kishimoto T (2008) Humanized antihuman IL-6 receptor antibody, tocilizumab. Handb Exp Pharmacol 181:151–160
Kim SR, Bae MK, Kim JY, Wee HJ, Yoo MA, Bae SK (2009) Aspirin induces apoptosis through the blockade of IL-6–STAT3 signaling pathway in human glioblastoma A172 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 387:342–347
Mahmoud NN, Dannenberg AJ, Mestre J, Bilinski RT, Churchill MR, Martucci C et al (1998) Aspirin prevents tumors in a murine model of familial adenomatous polyposis. Surgery 124:225–231
Chiu CH, McEntee MF, Whelan J (2000) Discordant effect of aspirin and indomethacin on intestinal tumor burden in Apc(Min/+)mice. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 62:269–275
Cooper HS, Murthy SN, Shah RS, Sedergran DJ (1993) Clinicopathologic study of dextran sulfate sodium experimental murine colitis. Lab Invest 69:238–249
Sinicrope FA, Ruan SB, Cleary KR, Stephens LC, Lee JJ, Levin B (1995) Bcl-2 and p53 oncoprotein expression during colorectal tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 55:237–241
Fukata M, Chen A, Klepper A, Krishnareddy S, Vamadevan AS, Thomas LS et al (2006) Cox-2 is regulated by Toll-like receptor-4 (TLR4) signaling: role in proliferation and apoptosis in the intestine. Gastroenterology 131:862–877
Capuano G, Rigamonti N, Grioni M, Freschi M, Bellone M (2009) Modulators of arginine metabolism support cancer immunosurveillance. BMC Immunol 10:1
Baral R, Bose A, Ray C, Paul S, Pal S, Haque E et al (2009) Association of early phase of colorectal carcinogenesis with STAT3 activation and its relevance in apoptosis regulation. Exp Mol Pathol 87:36–41
Boivin GP, Washington K, Yang K, Ward JM, Pretlow TP, Russell R et al (2003) Pathology of mouse models of intestinal cancer: consensus report and recommendations. Gastroenterology 124:762–777
Okayasu I, Ohkusa T, Kajiura K, Kanno J, Sakamoto S (1996) Promotion of colorectal neoplasia in experimental murine ulcerative colitis. Gut 39:87–92
Suzuki R, Kohno H, Sugie S, Nakagama H, Tanaka T (2006) Strain differences in the susceptibility to azoxymethane and dextran sodium sulfate-induced colon carcinogenesis in mice. Carcinogenesis 27:162–169
Friis S, Poulsen AH, Sorensen HT, Tjonneland A, Overvad K, Vogel U et al (2009) Aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and risk of colorectal cancer: a Danish cohort study. Cancer Causes Control 20:731–740
Kankuri E, Vaali K, Korpela R, Paakkari I, Vapaatalo H, Moilanen E (2001) Effects of a COX-2 preferential agent nimesulide on TNBS-induced acute inflammation in the gut. Inflammation 25:301–310
Bengmark S (2007) Bioecological control of inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Nutr 26:169–181
Kabashima K, Saji T, Murata T, Nagamachi M, Matsuoka T, Segi E et al (2002) The prostaglandin receptor EP4 suppresses colitis, mucosal damage and CD4 cell activation in the gut. J Clin Invest 109:883–893
Kraus S, Arber N (2009) Inflammation and colorectal cancer. Curr Opin Pharmacol 9:405–410
Slattery ML, Wolff RK, Herrick JS, Caan BJ, Potter JD (2007) IL6 genotypes and colon and rectal cancer. Cancer Causes Control 18:1095–1105
Rose-John S, Scheller J, Elson G, Jones SA (2006) Interleukin-6 biology is coordinated by membrane-bound and soluble receptors: role in inflammation and cancer. J Leukoc Biol 80:227–236
Scheller J, Rose-John S (2006) Interleukin-6 and its receptor: from bench to bedside. Med Microbiol Immunol 195:173–183
Dymicka-Piekarska V, Matowicka-Karna J, Gryko M, Kemona-Chetnik I, Kemona H (2007) Relationship between soluble P-selectin and inflammatory factors (interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein) in colorectal cancer. Thromb Res 120:585–590
Yu HG, Yu LL, Yang Y, Luo HS, Yu JP, Meier JJ et al (2003) Increased expression of RelA/nuclear factor-kappa B protein correlates with colorectal tumorigenesis. Oncology 65:37–45
McEntee MF, Chiu CH, Whelan J (1999) Relationship of beta-catenin and Bcl-2 expression to sulindac-induced regression of intestinal tumors in Min mice. Carcinogenesis 20:635–640
Miyaki M, Iijima T, Kimura J, Yasuno M, Mori T, Hayashi Y et al (1999) Frequent mutation of beta-catenin and APC genes in primary colorectal tumors from patients with hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer. Cancer Res 59:4506–4509
Kishimoto T (2005) Interleukin-6: from basic science to medicine—40 years in immunology. Annu Rev Immunol 23:1–21
Becker C, Fantini MC, Wirtz S, Nikolaev A, Lehr HA, Galle PR et al (2005) IL-6 signaling promotes tumor growth in colorectal cancer. Cell Cycle 4:217–220
Klampfer L (2008) The role of signal transducers and activators of transcription in colon cancer. Front Biosci 13:2888–2899
Acknowledgment
The authors thank Dr. Bing Guan (Jinling Hospital of Nanjing, China) for the excellent technical assistance in histologic assay.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, Y., Ye, Y., Gao, W. et al. Aspirin promotes apoptosis in a murine model of colorectal cancer by mechanisms involving downregulation of IL-6–STAT3 signaling pathway. Int J Colorectal Dis 26, 13–22 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-010-1060-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-010-1060-0