Abstract
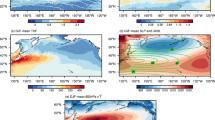
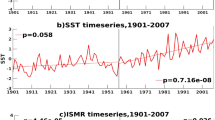
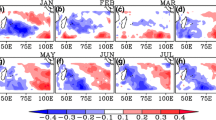
This study investigated the ocean-atmosphere interaction effect on the winter surface air temperature in Taiwan. Temperature fluctuations in Taiwan and marine East Asia correlated better with a SST dipole in the western North Pacific than the SST in the central/eastern equatorial Pacific. During the warm (cold) winters, a positive (negative) SST anomaly appears in marine East Asia and a negative (positive) SST anomaly appears in the Philippine Sea. The corresponding low-level atmospheric circulation is a cyclonic (anticyclonic) anomaly over the East Asian continent and an anticyclonic (cyclonic) circulation in the Philippine Sea during the warm (cold) winters. Based on the results of both numerical and empirical studies, it is proposed that a vigorous ocean-atmosphere interaction occurring in the western North Pacific modulates the strength of the East Asian winter monsoon and the winter temperature in marine East Asia. The mechanism is described as follows. The near-surface circulation anomalies, which are forced by the local SST anomaly, strengthen (weaken) the northeasterly trade winds in the Philippine Sea and weaken (strengthen) the northeasterly winter monsoon in East Asia during warm (cold) winters. The anomalous circulation causes the SST to fluctuate by modulating the heat flux at the ocean surface. The SST anomaly in turn enhances the anomalous circulation. Such an ocean-atmosphere interaction results in the rapid development of the anomalous circulation in the western North Pacific and the anomalous winter temperature in marine East Asia. This interaction is phase-locked with the seasonal cycle and occurs most efficiently in the boreal winters.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 22 October 1999 / Accepted: 5 June 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hsu, HH., Chen, YL. & Kau, WS. Effects of atmosphere-ocean interaction on the interannual variability of winter temperature in Taiwan and East Asia. Climate Dynamics 17, 305–316 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003820000116
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003820000116