Abstract.
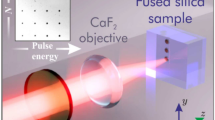
Atomic-scale structural changes have been observed in the glass network of fused silica after modification by tightly focused 800-nm, 130-fs laser pulses at fluences between 5 and 200 J cm-2. Raman spectroscopy of the modified glass shows an increase in the 490 and 605-cm-1 peaks, indicating an increase in the number of 4- and 3-membered ring structures in the silica network. These results provide evidence that densification of the glass occurs after exposure to fs pulses. Fluorescence spectroscopy of the modified glass shows a broad fluorescence band at 630 nm, indicating the formation of non-bridging oxygen hole centers (NBOHC) by fs pulses. Waveguides that support the fundamental mode at 633 nm have been fabricated inside fused silica by scanning the glass along the fs laser beam axis. The index changes are estimated to be approximately 0.07×10-3.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 17 December 2001 / Accepted: 9 July 2002 / Published online: 25 October 2002
RID="*"
ID="*"Corresponding author. Fax: +1-925/423-2463, E-mail: dmkrol@ucdavis.edu
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chan, J., Huser, T., Risbud, S. et al. Modification of the fused silica glass network associated with waveguide fabrication using femtosecond laser pulses . Appl Phys A 76, 367–372 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-002-1822-9
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-002-1822-9