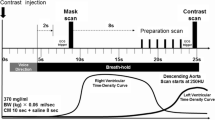
Abstract
The purpose of this study was to assess the ability of 16-slice computed tomography (CT) to detect in-stent restenosis of proximal coronary arteries. From November 2002 to April 2004, 134 consecutive patients with proximal stents (3.25 ± 0.47 mm) were prospectively studied. Multidetector CT (MDCT) was performed 24 h (baseline) and 6 months after angioplasty and analysed by two radiologists blinded to the results of the coronary angiography. Sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values for in-stent restenosis were compared with conventional quantitative coronary angiography (QCA). Stenosis with a diameter ≥50% was considered diagnostic of in-stent restenosis. The CT analysis was performed in 131 and 114 patients at baseline and 6 months, respectively. The in-stent lumen was evaluable in 111 (121 stents) and 99 patients (108 stents) at baseline and 6 months, respectively. The prevalence of in-stent restenosis was 22.5%. Restenoses were correctly identified in 91.7 and 87.5% by the two radiologists. The sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values for the assessment of significant in-stent restenosis were 92, 67, 43, 97% and 87, 66, 41, 95% for the radiologists, respectively. MDCT is a potential non-invasive technique for the screening of in-stent restenosis of proximal coronary arteries that needs further improvements.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Takagi T, Stankovic G, Finci L et al (2002) Results and long-term predictors of adverse clinical events after elective percutaneous interventions on unprotected left main coronary artery. Circulation 106:698–702
Schoepf UJ, Becker CR, Ohnesorge BM, Yucel EK (2004) CT of coronary artery disease. Radiology 232:18–37
Hong C, Chrysant GS, Woodard PK, Bae KT (2004) Coronary artery stent patency assessed with in-stent contrast enhancement measured at multi-detector row CT angiography: initial experience. Radiology 233:286–291
Schuijf JD, Bax JJ, Jukema JW, Lamb HJ, Warda HMA, Vliegen HW, de Roos A, Van der Wall EE (2004) Feasibility of assessment of coronary stent patency using 16-slice computed tomography. Am J Cardiol 94:427–430
Ligabue G, Rossi R, Ratti C, Favali M, Modena MG, Romagnoli R (2004) Noninvasive evaluation of coronary artery stents patency after PTCA: role of multislice computed tomography. Radiol Med (Torino) 108(1–2):128–137
Maintz D, Grude M, Fallenberg EM, Heindel W, Fischbach R (2003) Assessment of coronary arterial stents by multislice-CT angiography. Acta Radiol 44:597–603
Gilard M, Cornily JC, Rioufol G, Finet G, Pennec PY, Mansourati J, Blanc JJ, Boschat J (2005) Noninvasive assessment of left main coronary stent patency with 16-slice computed tomography. Am J Cardiol 95:110–112
Cademartiri F, Marano R, Runza G, Mollet N, Nieman K, Luccichenti G, Gualerzi M, Brambilla L, Coruzzi P, Galia M, Midiri M (2005) Non-invasive assessment of coronary stent patency with multislice CT: preliminary experience. Radiol Med (Torino) 109(5–6):500–507
Mahnken AH, Buecker A, Wildberger JE, Ruebben A, Stanzel S, Vogt F, Günther RW, Blindt R (2003) Coronary artery stents in multislice computed tomography: in vitro artefact evaluation. Invest Radiol 39(1):27–33
Nieman K, Cademartiri F, Raaijmakers R, Pattynama P, De Feyter P (2003) Noninvasive angiographic evaluation of coronary stents with multi-slice spiral computed tomography. Herz 28:136–142
Maintz D, Seifarth H, Raupach R, Flohr T, Rink M, Sommer T, Ozgün M, Heindel W, Fischbach R (2006) 64-slice multidetector coronary CT angiography: in vitro evaluation of 68 different stents. Eur Radiol 16:818–826
Mahnken AH, Muhlenbruck G, Seyfarth H, Flohr T, Stanzel S, Wildberger JE, Gunther KW, Kuettner A (2006) 64-slice computed tomography assessment of coronary artery stents: a phantom study. Acta Radiol 47(1):36–42
Maintz D, Juergens KU, Wichter T, Grude M, Heindel W, Fischbach R (2003) Imaging artery stents using multislice computed tomography: in vitro evaluation. Eur Radiol 13:830–835
Mahnken AH, Seyfarth T, Flohr T, Herzog C, Stahl J, Stanzel S, Kuettner A, Wildberger JE, Gunther RW (2005) Flat-panel detector computed tomography for the assessment of coronary artery stents: phantom study in comparison with 16-slice spiral computed tomography. Invest Radiol 40(1):8–13
Maintz D, Seifarth H, Flohr T, Krämer S, Wichter T, Heindel W, Fischbach R (2003) Improved coronary artery stent visualization and in-stent stenosis detection using 16-slice computed-tomography and dedicated image reconstruction technique. Invest Radiol 38:790–795
Seifarth H, Raupach R, Schaller S et al (2005) Assessment of coronary artery stents using 16-slice MDCT angiography: evaluation of a dedicated reconstruction kernel and a noise reduction filter. Eur Radiol 15(4):721–726
Gaspart T, Halon DA, Lewis BS, Adawi S, Schliamser JE, Rubinshtein R, Flugelman MY, Peled N (2005) Diagnosis of coronary in-stent restenosis with multidetector row spiral computed tomography. J Am Coll Cardiol 46(8):1573–1579
Martuscelli E, Romagnoli A, D’Eliseo A, Razzini C, Tomassini M, Massimiliano S, Simonetti G, Romeo F (2004) Accuracy of thin-slice computed tomography in the detection of coronary stenoses. Eur Heart J 25:1043–1048
Giesler T, Baum U, Ropers D, Ulzheimer S, Wenkel E, Mennicke M, Bautz W, Kalender WA, Daniel WG, Achenbach S (2002) Noninvasive visualization of coronary arteries using contrast-enhanced multidetector CT: Influence of heart rate on image quality and stenosis detection. AJR Am J Roentgenol 179:911–916
Acknowledgments
To Dr. A. Gozlan for the drawings.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chabbert, V., Carrie, D., Bennaceur, M. et al. Evaluation of in-stent restenosis in proximal coronary arteries with multidetector computed tomography (MDCT). Eur Radiol 17, 1452–1463 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-006-0510-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-006-0510-0