Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to provide morphometric data, obtained from macerated mandibles, which might facilitate the topographic location of the mandibular foramen, considering aspects such as gender, age and ethnicity.
Materials and methods
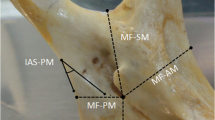
One hundred and eighty-five macerated mandibles of adult black and white individuals of both sexes were analyzed. Initially, 5 points were established: MF, the lowest point of the mandibular foramen; S, greatest concavity of the mandibular notch; A, anterior margin of the ramus of mandible; P, posterior margin of the ramus of mandible; and Go, gonion. Then the following measurements were performed bilaterally: MF-S, MF-A, MF-P and MF-Go.
Results
The following mean values were found: MF-S: 21.02 mm for white females (WF) and 22.00 mm for black females (BF); 24.40 mm for white males (WM) and 24.35 mm for black males (BM); MF-A: 17.05 mm for WF and 18.09 mm for BF; 17.18 mm for WM and 18.11 mm for BM; MF-P: 11.11 mm for WF and 12.24 mm for BF; 13.10 mm for WM and 14.15 mm for BM; MF-Go: 19.00 mm for WF and 19.44 mm for BF; 23.13 mm for WM and 22.12 mm for BM.
Conclusions
The values found in this study, considering gender, age and ethnic group, can be used as a parameter to carry out the sagittal split ramus osteotomy technique, making it more predictable and with less risk of complications.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afsar A, Haas DA, Rossouw PE, Wood RE (1998) Radiographic localization of mandibular anesthesia landmarks. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 86:234–241
Alves N, Cândido PL (2013) Anatomia para o cirurgião-dentista. Gen-Santos, São Paulo
Chávez-Lomeli ME, Mansilla Lory J, Pompa JA, Kjaer I (1996) The human mandibular canal arises from three separate canals innervating different tooth groups. J Dent Res 75:1540–1544
Chrcanovic BR, Abreu MHNG, Custódio ALN (2011) Morphological variation in dentate and edentulous human mandibles. Surg Radiol Anat 33:203–213
Cvetko E (2013) Bilateral anomalous high position of the mandibular foramen: a case report. Surg Radiol Anat. doi:10.1007/s00276-013-1209-y
da Fontoura RA, Vasconcellos HA, Campos AES (2002) Morphologic basis for the intraoral vertical ramus osteotomy: anatomic and radiographic localization of the mandibular foramen. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 60:660–665
Dal Pont G (1961) Retromolar osteotomy for the correction of prognathism. J Oral Surg Anesth Hosp Dent Serv 19:42–47
Daw JL Jr, de la Paz MG, Han H, Aitken ME, Patel PK (1999) The mandibular foramen: an anatomic study and its relevance to the sagittal ramus osteotomy. J Craniofac Surg 10:475–479
Ennes JP, Medeiros RM (2009) Localization of mandibular foramen and clinical implications. Int J Morphol 27:1305–1311
Freire AR, Rossi AC, Prado FB, Caria PHF, Botacin PR (2012) Incidence of the mandibular accessory foramina in brazilian population. Braz J Morphol Sci 29:171–173
Gutierrez-Ventura F, Tataje-Vivanco Y (2012) Posición del agujero dentario inferior en la rama ascendente en huesos mandibulares secos de adultos. Rev Estomatol Hered 22:152–157
Kaffe I, Ardekian L, Gelerenter I, Taicher S (1994) Location of the mandibular foramen in panoramic radiographs. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 78:662–669
Kilarkaje N, Nayak SR, Narayan P, Prabhu LV (2005) The location of the mandibular foramen maintains absolute bilateral symmetry in mandibles of different age groups. Hong Kong Dent J 2:35–37
Kjaer I, Keeling JW, Hansen BF (1999) The prenatal human cranium: normal and pathologic development. Munksgaard, Copenhagen
Lima DSC, Figuerêdo AA, Rocha EA, Costa VHMV, Castro MP, Silva RCP, Chagas GL, Araújo LP, Mendonça VRR, Gravina PR, Meneses JVL (2011) Estudo anatômico do forame mandibular e suas relações com pontos de referência do ramo da mandíbula. Rev Bras Cir Craniomaxilofac 14:91–96
Muto T, Shigeo K, Yamamoto K, Kawakami J (2003) Computed tomography morphology of the mandibular ramus in prognathism: effect on the medial osteotomy of the sagittal split ramus osteotomy. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 61:89–93
Oguz O, Bozkir MG (2002) Evaluation of location of mandibular and mental foramina in dry, young, adult human male, dentulous mandibles. West Indian Med J 51:14–16
Prado FB, Groppo FC, Volpato MC, Caria PHF (2010) Morphological changes in the position of the mandibular foramen in dentate and edentate brazilian subjects. Clin Anat 23:394–398
Rajchel J, Ellis E 3rd, Fonseca RJ (1986) The anatomical location of the mandibular canal: its relationship to the sagittal ramus osteotomy. Int J Adult Orthodon Orthognath Surg 1:37–47
Reitzik M, Griffths RR, Mirels H (1976) Surgical anatomy of the ascending ramus of the mandible. Br J Oral Surg 14:150–155
Salgado AG, Inzunza HO, Cantín M, Fuentes R, Inostroza V, Errázuriz MJ, Pavez C (2012) Evaluación de la anatomía mandibular relacionada con la osteotomía sagital de la rama. Int J Morphol 30:30–39
Sekerci AE, Sisman Y (2013) Cone-beam computed tomography analysis of the shape, height, and location of the mandibular lingula. Surg Radiol Anat. doi:10.1007/s00276-013-1150-0
Shenoy V, Vijayalakshmi S, Saraswathi P (2012) Osteometric analysis of the mandibular foramen in dry human mandibles. J Clin Diagn Res 6:557–560
Strini PJSA, Silva Júnior W, Rodrigues DA, Strini PJSA, Guimarães EC, Bernardino Júnior R (2006) Avaliação topográfica do forame mandibular em peças anatômicas maceradas parcialmente dentadas e edêntulas. Rev Fac Odontol Univ Passo Fundo 11:11–15
Thangavelu K, Kannan R, Senthil Kumar N, Rethish E, Sabitha S, SayeeGanesh N (2012) Significance of localization of mandibular foramen in an inferior alveolar nerve block. J Nat Sci Biol Med 3:156–160
Trauner R, Obwegeser H (1957) The surgical correction of mandibular prognathism and retrognathia with consideration of genioplasty. I. Surgical procedures to correct mandibular prognathism and reshaping of the chin. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 10:677–689
Trost O, Salignon V, Cheynel N, Malka G, Trouilloud P (2010) A simple method to locate mandibular foramen: preliminary radiological study. Surg Radiol Anat 32:927–931
Valente VB, Arita WM, Gonçalves PCG, Campos JADB, Capote TSO (2012) Location of the mandibular foramen according to the amount of dental alveoli. Int J Morphol 30:77–81
Yoshida T, Nagamine T, Kobayashi T, Michimi N, Nakajima T, Sasakura H, Hanada K (1989) Impairment of the inferior alveolar nerve after sagittal split osteotomy. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 17:271–277
Yu IH, Wong YK (2008) Evaluation of mandibular anatomy related to sagittal split ramus osteotomy using 3-dimensional computed tomography scan images. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 37:521–528
Conflict of interest
There was no financial support for this research. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standard
The authors declare that all procedures adopted for this research are in agreement with the Brazilian laws.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alves, N., Deana, N.F. Morphometric study of mandibular foramen in macerated skulls to contribute to the development of sagittal split ramus osteotomy (SSRO) technique. Surg Radiol Anat 36, 839–845 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-014-1279-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-014-1279-5