Abstract
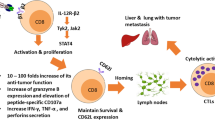
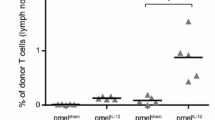
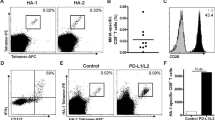
During the antigen-dependant activation process several subsets CD8+ T cells appear with different phenotypic and functional characteristics. Recent studies indicate that the state of T cell differentiation radically affects their ability to effectively respond to tumor challenge, with early effector CD8+ T (CD62Lhigh) cells having better anti-tumor activity. Thus strategies aimed at optimizing the generation of such subpopulations could significantly enhance the effectiveness of adoptive cell therapy (ACT) for cancer. In this study, we show that priming of naïve CD8+ T cells in the presence of IL-12 selectively rescued early CD8+ CD62Lhi from activation induced cell death and resulted in the increased accumulation of this subset of CD8+ T cells. Furthermore, we demonstrated that IL-12 directly modulated the expression of CD62L on activated CD8+ T cells. When used for ACT, naïve CD8+ T cells primed in vitro in the presence of IL-12 showed superior anti-tumor activity toward B16 melanoma. Importantly, using the Pmel-1 model, priming pmel-1 cells in vitro with IL-12 reduced the state of functional tolerance associated with the non-mutated “self” tumor antigen gp100, as demonstrated by significant tumor responses in the absence of vaccination. Together, our results suggest that in vitro conditioning of naïve CD8+ T cells with IL-12 prior to ACT could significantly enhance their anti-tumor activity.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Airoldi I, Gri G, Marshall JD, Corcione A, Facchetti P, Guglielmino R, Trinchieri G, Pistoia V (2000) Expression and function of IL-12 and IL-18 receptors on human tonsillar B cells. J Immunol 165:6880
Bachmann MF, Wolint P, Schwarz K, Jager P, Oxenius A (2005) Functional properties and lineage relationship of CD8+ T cell subsets identified by expression of IL-7 receptor alpha and CD62L. J Immunol 175:4686
Car BD, Eng VM, Lipman JM, Anderson TD (1999) The toxicology of interleukin-12: a review. Toxicol Pathol 27:58
Chang J, Cho JH, Lee SW, Choi SY, Ha SJ, Sung YC (2004) IL-12 priming during in vitro antigenic stimulation changes properties of CD8 T cells and increases generation of effector and memory cells. J Immunol 172:2818
Cohen J (1995) IL-12 deaths: explanation and a puzzle. Science 270:908
Curtsinger JM, Johnson CM, Mescher MF (2003) CD8 T cell clonal expansion and development of effector function require prolonged exposure to antigen, costimulation, and signal 3 cytokine. J Immunol 171:5165
Curtsinger JM, Lins DC, Mescher MF (2003) Signal 3 determines tolerance versus full activation of naive CD8 T cells: dissociating proliferation and development of effector function. J Exp Med 197:1141
Emtage PC, Clarke D, Gonzalo-Daganzo R, Junghans RP (2003) Generating potent Th1/Tc1 T cell adoptive immunotherapy doses using human IL-12: harnessing the immunomodulatory potential of IL-12 without the in vivo-associated toxicity. J Immunother 26:97
Gately MK, Renzetti LM, Magram J, Stern AS, Adorini L, Gubler U, Presky DH (1998) The interleukin-12/interleukin-12-receptor system: role in normal and pathologic immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol 16:495
Gattinoni L, Klebanoff CA, Palmer DC, Wrzesinski C, Kerstann K, Yu Z, Finkelstein SE, Theoret MR, Rosenberg SA, Restifo NP (2005) Acquisition of full effector function in vitro paradoxically impairs the in vivo antitumor efficacy of adoptively transferred CD8+ T cells. J Clin Invest 115:1616
Gattinoni L, Powell DJ Jr, Rosenberg SA, Restifo NP (2006) Adoptive immunotherapy for cancer: building on success. Nat Rev 6:383
Grohmann U, Belladonna ML, Bianchi R, Orabona C, Ayroldi E, Fioretti MC, Puccetti P (1998) IL-12 acts directly on DC to promote nuclear localization of NF-kappaB and primes DC for IL-12 production. Immunity 9:315
Hinrichs CS, Gattinoni L, Restifo NP (2006) Programming CD8+ T cells for effective immunotherapy. Curr Opin Immunol 18:363
Jung TM, Gallatin WM, Weissman IL, Dailey MO (1988) Down-regulation of homing receptors after T cell activation. J Immunol 141:4110
Kieper WC, Prlic M, Schmidt CS, Mescher MF, Jameson SC (2001) Il-12 enhances CD8 T cell homeostatic expansion. J Immunol 166:5515
Klebanoff CA, Finkelstein SE, Surman DR, Lichtman MK, Gattinoni L, Theoret MR, Grewal N, Spiess PJ, Antony PA, Palmer DC, et al (2004) IL-15 enhances the in vivo antitumor activity of tumor-reactive CD8+ T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:1969
Klebanoff CA, Gattinoni L, Torabi-Parizi P, Kerstann K, Cardones AR, Finkelstein SE, Palmer DC, Antony PA, Hwang ST, Rosenberg SA, et al (2005) Central memory self/tumor-reactive CD8+ T cells confer superior antitumor immunity compared with effector memory T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:9571
Macgregor JN, Li Q, Chang AE, Braun TM, Hughes DP, McDonagh KT (2006) Ex vivo culture with interleukin (IL)-12 improves CD8(+) T-cell adoptive immunotherapy for murine leukemia independent of IL-18 or IFN-gamma but requires perforin. Cancer Res 66:4913
Mescher MF, Curtsinger JM, Agarwal P, Casey KA, Gerner M, Hammerbeck CD, Popescu F, Xiao Z (2006) Signals required for programming effector and memory development by CD8+ T cells. Immunol Rev 211:81
Overwijk WW, Theoret MR, Finkelstein SE, Surman DR, de Jong LA, Vyth-Dreese FA, Dellemijn TA, Antony PA, Spiess PJ, Palmer DC, et al (2003) Tumor regression and autoimmunity after reversal of a functionally tolerant state of self-reactive CD8+ T cells. J Exp Med 198:569
Overwijk WW, Tsung A, Irvine KR, Parkhurst MR, Goletz TJ, Tsung K, Carroll MW, Liu C, Moss B, Rosenberg SA, et al (1998) gp100/pmel 17 is a murine tumor rejection antigen: induction of “self”-reactive, tumoricidal T cells using high-affinity, altered peptide ligand. J Exp Med 188:277
Portielje JE, Gratama JW, van Ojik HH, Stoter G, Kruit WH (2003) IL-12: a promising adjuvant for cancer vaccination. Cancer Immunol Immunother 52:133
Rogge L, Barberis-Maino L, Biffi M, Passini N, Presky DH, Gubler U, Sinigaglia F (1997) Selective expression of an interleukin-12 receptor component by human T helper 1 cells. J Exp Med 185:825
Salem ML, Gillanders WE, Kadima AN, El-Naggar S, Rubinstein MP, Demcheva M, Vournakis JN, Cole DJ (2006) Review: novel nonviral delivery approaches for interleukin-12 protein and gene systems: curbing toxicity and enhancing adjuvant activity. J Interferon Cytokine Res 26:593
Salem ML, Kadima AN, Zhou Y, Nguyen CL, Rubinstein MP, Demcheva M, Vournakis JN, Cole DJ, Gillanders WE (2004) Paracrine release of IL-12 stimulates IFN-gamma production and dramatically enhances the antigen-specific T cell response after vaccination with a novel peptide-based cancer vaccine. J Immunol 172:5159
Sallusto F, Lenig D, Forster R, Lipp M, Lanzavecchia A (1999) Two subsets of memory T lymphocytes with distinct homing potentials and effector functions. Nature 401:708
Schluns KS, Kieper WC, Jameson SC, Lefrancois L (2000) Interleukin-7 mediates the homeostasis of naive and memory CD8 T cells in vivo. Nat Immunol 1:426
Schluns KS, Lefrancois L (2003) Cytokine control of memory T-cell development and survival. Nat Rev 3:269
Schmidt CS, Mescher MF (1999) Adjuvant effect of IL-12: conversion of peptide antigen administration from tolerizing to immunizing for CD8+ T cells in vivo. J Immunol 163:2561
Schmidt CS, Mescher MF (2002) Peptide antigen priming of naive, but not memory, CD8 T cells requires a third signal that can be provided by IL-12. J Immunol 168:5521
Springer TA (1994) Traffic signals for lymphocyte recirculation and leukocyte emigration: the multistep paradigm. Cell 76:301
Szabo SJ, Dighe AS, Gubler U, Murphy KM (1997) Regulation of the interleukin (IL)-12R beta 2 subunit expression in developing T helper 1 (Th1) and Th2 cells. J Exp Med 185:817
Teague RM, Sather BD, Sacks JA, Huang MZ, Dossett ML, Morimoto J, Tan X, Sutton SE, Cooke MP, Ohlen C, et al (2006) Interleukin-15 rescues tolerant CD8+ T cells for use in adoptive immunotherapy of established tumors. Nat Med 12:335
Trinchieri G (2003) Interleukin-12 and the regulation of innate resistance and adaptive immunity. Nature Rev 3:133
Valenzuela J, Schmidt C, Mescher M (2002) The roles of IL-12 in providing a third signal for clonal expansion of naive CD8 T cells. J Immunol 169:6842
Valenzuela JO, Hammerbeck CD, Mescher MF (2005) Cutting edge: Bcl-3 up-regulation by signal 3 cytokine (IL-12) prolongs survival of antigen-activated CD8 T cells. J Immunol 174:600
van Wely CA, Beverley PC, Brett SJ, Britten CJ, Tite JP (1999) Expression of l-selectin on Th1 cells is regulated by IL-12. J Immunol 163:1214
Watford WT, Moriguchi M, Morinobu A, O’Shea JJ (2003) The biology of IL-12: coordinating innate and adaptive immune responses. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 14:361
Weninger W, Crowley MA, Manjunath N, von Andrian UH (2001) Migratory properties of naive, effector, and memory CD8(+) T cells. J Exp Med 194:953
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health Grant 1 R01 CA94856-01. We thank Dr. Yian Chen and Elizabeth Little for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Díaz-Montero, C.M., El Naggar, S., Al Khami, A. et al. Priming of naive CD8+ T cells in the presence of IL-12 selectively enhances the survival of CD8+CD62Lhi cells and results in superior anti-tumor activity in a tolerogenic murine model. Cancer Immunol Immunother 57, 563–572 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-007-0394-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-007-0394-0