Abstract
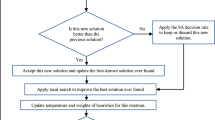
This paper proposed a novel quantum differential evolutionary algorithm (QDEA) based on the basic quantum-inspired evolutionary algorithm (QEA) for permutation flow shop scheduling problem (PFSP). In this QDEA, the quantum chromosomes are encoded and decoded by using the quantum rotating angle and a simple strategy named largest rotating angle value rule to determine job sequence based on job’s quantum information is proposed for the representation of PFSP, firstly. Then, we merge the advantages of differential evolution strategy, variable neighborhood search and QEA by adopting the differential evolution to perform the updating of quantum gate and variable neighborhood search to raise the performance of the local search. We adopted QDEA to minimize the makespan, total flowtime and the maximum lateness of jobs and make the simulations. The results and comparisons with other algorithms based on famous benchmarks demonstrated the effectiveness of the proposed QDEA. Another contribution of this paper is to report new absolute values of total flowtime and maximum lateness for various benchmark problem sets.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garey M, Johnson D, Sethi R (1976) The complexity of flowshop and jobshop scheduling. Math Oper Res 24(1):117–129
Nawaz M, Enscore E Jr, Ham I (1983) A heuristic algorithm for the m-machine, n-job flow-shop sequencing problem. OMEGA 11:91–95
Kalczynski PJ, Kaznburowski J (2007) On the NEH heuristic for minimizing the makespan in permutation flow shops. OMEGA 35:53–60
Murata T, Ishibuchi H, Tanaka H (1996) Genetic algorithms for flowshop scheduling problems. Comput Ind Eng 30(4):1061–1071
Reeves CR, Yamada T (1998) Genetic algorithms, path relinking and the flowshop sequencing problem. Evol Comput 6:45–60
Iyer SK, Saxena B (2004) Improved genetic algorithm for the permutation flowshop scheduling problem. Comput Oper Res 34(4):593–606
Doyen A, Engin O, Ozkan C (2003) A new artificial immune system approach to solve permutation flow shop scheduling problems. Tukish Symposium on Artificial Immune System and Neural Networks TAINN’03.
Nowicki E, Smutnicki C (1996) A fast tabu search algorithm for the permutation flow-shop problem. Eur J Oper Res 91:160–175
Grabowski J, Wodecki M (2004) A very fast tabu search algorithm for the permutation flow shop problem with makespan criterion. Comput Oper Res 31:1891–1909
Osman IH, Potts CN (1989) Simulated annealing for permutation flow-shop scheduling. OMEGA 17:551–557
Ishibuchi H, Misaki S, Tanaka H (1995) Modified simulated annealing algorithms for the flow shop sequencing problem. Eur J Oper Res 81(2):388–398
Merkle D, Middendorf M (2001) A new approach to solve permutation scheduling problems with ant colony optimization. Lect Notes Comput Sci 2037:484–494
Yinga K-C, Liao C-J (2004) An ant colony system for permutation flow-shop sequencing. Comput Oper Res 31(5):791–801
Rameshkumar K, Suresh RK, Mohanasundaram KM (2005) Discrete particle swarm optimization (DPSO) algorithm for permutation flowshop scheduling to minimize makespan. Adv Nat Comp 3612:572–581
Jarboui B, Ibrahim S, Siarry P, Rebai A (2008) A combinatorial particle swarm optimisation for solving permutation flowshop problems. Comput Ind Eng 54(3):526–538
Stützle T (1998) Applying iterated local search to the permutation flow shop problem. Technical report, AIDA-98-04, FG Intellektik, TU Darmstadt
Ruiz R, Stützle T (2007) A simple and effective iterated greedy algorithm for the permutation flowshop scheduling problem. Eur J Oper Res 177(3):2033–2049
Wolpert DH, Macready WG (1997) No free lunch theorems for optimization. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 1(1):67–82
Zheng D, Wang L (2003) An effective hybrid heuristic for flow shop scheduling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 21(1):38–44
Wang L, Zhang L, Zheng Da-Zhong (2006) An effective hybrid genetic algorithm for flow shop scheduling with limited buffers. Comput Oper Res 33(10):2960–2971
Liu Z, Wang S (2006) Hybrid Particle Swarm Optimization for Permutation Flow Shop Scheduling. Intelligent Control and Automation, 2006. WCICA 2006. The Sixth World Congress on. 1, pp. 3245–3249
Chandrasekaran, S. Ponnambalam, S.G..Suresh, R.K. Vijayakumar (2006) A Hybrid Discrete Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm to Solve Flow Shop Scheduling Problems. Cybernetics and Intelligent Systems, 2006 IEEE Conference on, pp.1–6.
Tavakkoli-Moghaddama R, Rahimi-Vaheda A, Mirzaei AH (2007) A hybrid multi-objective immune algorithm for a flow shop scheduling problem with bi-objectives: weighted mean completion time and weighted mean tardiness. Inf Sci 177(22):5072–5090
Andreas AC, Nearchou C (2004) A novel metaheuristic approach for the flow shop scheduling problem. Eng Appl Artif Intell 17(3):289–300
Talbi E-G, Rahoual M, Mabed MH, Dhaenens C (2001) A hybrid evolutionary approach for multicriteria optimization problems: application to the flow shop. Lect Notes Comput Sci 1993:416–428
Ponnambalam SG, Jagannathan H, Kataria M, Gadicherla A (2009) A TSP-GA multi-objective algorithm for flow-shop scheduling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 23(11–12):909–915
Han K-H (2000) Genetic quantum algorithm and its application to combinatorial optimization problem. In: IEEE Proc. Of the 2000 Congress on Evolutionary Computation, San Diego, USA IEEE Press
KH Han, KH Park, CH Lee, JH Kim Parallel quantum-inspired genetic algorithm for combinatorial optimization problem。Evolutionary Computation, 2001. Proceedings of the 2001.
KH Han, JH Kim, On setting the parameters of quantum-inspired evolutionary algorithm for practical application Evolutionary Computation, 2003. CEC’03. The 2003 Congress on 2003.
Han K-H, Kim J-H. Quantum-inspired Evolutionary Algorithm for a Class of Combinatorial Optimization. IEEE Trans on Evolutionary Computation, 2002.
Han K-H, Kim J-H. Quantum-inspired Evolutionary Algorithms with a New Termination Criterion H,Gate and Two-Phase Scheme. IEEE Trans on Evolutionary Computation 2004.
Wang Ling, Wu Hao, and Zheng Da-Zhong (2005) A quantum-inspired genetic algorithm for scheduling problems. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, v 3612, n PART III. Advances in Natural Computation: First International Conference, ICNC 2005. Proceedings, pp. 417–423.
Wang L, Wu H, Tang F, Zheng DZ (2005) A hybrid quantum-inspired genetic algorithm for flow shop scheduling. Lect Notes Comput Sci 3645:636–644
Li Bin-Bin and Wang Ling (2006) A hybrid quantum-inspired genetic algorithm for multi-objective scheduling. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, v 4113 LNCS—I, International Conference on Intelligent Computing, ICIC 2006, Proceedings, pp. 511–522.
Bean JC (1994) Genetics and random keys for sequencing and optimization. ORSA J Comput 6(2):154–160
Storn R, Price K (1999) Differential Evolution - A simple and efficient adaptive scheme for global optimization over continuous spaces. Technical Report TR-95-012, ICSI.
Storn R, Price K (1997) Differential evolution—a simple evolution strategy for fast optimization. Dr. Dobb’s J 78:18–24
Pan QK, Tasgetiren MF, Liang YC (2008) A discrete differential evolution algorithm for the permutation flowshop scheduling problem. Comput Ind Eng 55(4):795–816
Qian B, Wang L, Rong Hu, Wang W-L, Huang De-Xian, Wang X (2008) A hybrid differential evolution method for permutation flow-shop scheduling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 38(5–6):757–777
Hansen P, Mladenovic N (2003) A tutorial on variable neighborhood search. GERAD and Mathematical Institute, SANU
Ong YS, Lim MH, Zhu N (2006) Classification of adaptive memetic algorithms: a comparative study. IEEE Transact Sys, Man and Cyb-B: Cyb 36:141–152
Hart W E, Krasnogor N, Smith J E. ( 2004) Recent advances in memetic algorithms. Springer: Heidelberg.
Carlier J (1978) Ordonnancements a contraintes disjonctives. Rech Opér 12(4):333–350
Reeves CR (1995) A genetic algorithm for flowshop sequencing. Comp Ope Res 22(1):5–13
Heller J (1960) Some numerical experiments for an MxJ flow shop and its decision-theoretical aspects. Oper Res 8:178–184
Taillard E (1993) Benchmarks for basic scheduling problems. Eur J Oper Res 64(2):278–285
Demirkol E, Mehta S, Uzsoy R (1998) Benchmarks for shop scheduling problems. Eur J Oper Res 109:137–141
Tasgetiren MF, Liang YC, Sevkli M, Gencyilmaz G. (2004) Particle swarm optimization algorithm for makespan and maximum lateness minimization in permutation flowshop sequencing problem. In: Proceedings of the fourth international symposium on intelligent manufacturing systems. Turkey: Sakarya. pp. 431–41.
Liao C-J, Tseng C-T, Luarn P (2007) A discrete version of particle swarm optimization for flowshop scheduling problems. Comput Oper Res 34(10):3099–3111
Liu J, Reeves CR (2001) Constructive and composite heuristic solutions to the scheduling P//ΣCi problem. Eur J Oper Res 132:439–452
Rajendran C, Ziegler H (2004) Ant-colony algorithms for permutation flowshop scheduling to minimize makespan/total flowtime of jobs. Eur J Oper Res 155:426–438
Rajendran C, Ziegler H (2005) Two ant-colony algorithms for minimizing total flowtime in permutation flowshops. Comput Ind Eng 48(4):789–797
Rajendran C, Chaudhuri D (1991) A flowshop scheduling algorithm to minimize maximum lateness. J Oper Res Soc Jpn 34:28–45
Laha D, Sarin SC (2009) A heuristic to minimize total flow time in permutation flow shop. Omega 37(3):734–739
Framinan JM, Leisten R (2003) An efficient constructive heuristic for flowtime minimisation in permutation flow shops. Omega 31(4):311–317
Rad SF, Ruiz R, Boroojerdian N (2009) New high performing heuristics for minimizing makespan in permutation flowshops. Omega 37(2):331–345
Zhang C, Sun J (2009) An alternate two phases particle swarm optimization algorithm for flow shop scheduling problem. Expert Systems Appl 36(3):5162–5167
Changsheng Zhang, Jiaxu Ning and Dantong Ouyang (2009) A hybrid alternate two phases particle swarm optimization algorithm for flow shop scheduling problem. Comp Ind Eng (in press)
Rajkumar R, Shahabudeen P (2009) Scheduling jobs on flowshop environment applying simulated annealing algorithm. Int Jour Serv Op Info 4(3):212–231
Rajkumar R, Shahabudeen P (2009) An improved genetic algorithm for the flowshop scheduling problem. Int J Prod Res 47(1):233–249
Zobolas GI, Tarantilisa CD, Ioannoua G (2009) Minimizing makespan in permutation flow shop scheduling problems using a hybrid metaheuristic algorithm. Comput Oper Res 36(4):1249–1267
Qian B, Wang L, Huang DX, Wang X (2009) An effective hybrid DE-based algorithm for flow shop scheduling with limited buffers. Int J Prod Res 47(1):1–24
Tseng L-Y, Lin Y-T (2009) A hybrid genetic local search algorithm for the permutation flowshop scheduling problem. Eur J Oper Res 198(1):84–92
Laha D, Chakraborty UK (2009) An efficient hybrid heuristic for makespan minimization in permutation flow shop scheduling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 44(5–6):559–569
Kuo I-Hong, Horng S-J, Kao T-W, Lin T-L, Lee C-L, Terano T, Pan Y (2009) An efficient flow-shop scheduling algorithm based on a hybrid particle swarm optimization model. Expert Systems Appl 36(2):7027–7032
Lian Z, Gu X, Jiao B (2008) A novel particle swarm optimization algorithm for permutation flow-shop scheduling to minimize makespan. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 35:851–861
Zhang Y, Li X, Wang Q (2009) Hybrid genetic algorithm for permutation flowshop scheduling problems with total flowtime minimization. Eur J Oper Res 196(3):869–876
PC Chang, WH Huang, CJ Ting, LC Wu, CM Lai (2009) A Hybrid Genetic-Immune Algorithm with Improved Offsprings and Elitist Antigen for Flow-shop Scheduling Problems. 11th IEEE International Conference on High Performance Computing and Communications.
Bożejko W (2009) Solving the flow shop problem by parallel programming. J Parallel Distrib Comput 69(5):470–481
Vallada E, Ruiz R (2009) Cooperative metaheuristics for the permutation flowshop scheduling problem. Eur J Oper Res 193(2):365–376
Bai D, Tang L (2009) New heuristics for flow shop problem to minimize makespan. J Oper Res Soc (in press)
Naderi B, Tavakkoli-Moghaddam R, Khalili M (2009) Electromagnetism-like mechanism and simulated annealing algorithms for flowshop scheduling problems minimizing the total weighted tardiness and makespan. Knowledge-Based Systems (in press).
Li X, Wang Q, Cheng Wu (2009) Efficient composite heuristics for total flowtime minimization in permutation flow shops. Omega 37(1):155–164
Sheibani K (2009) A fuzzy greedy heuristic for permutation flow-shop scheduling. J Oper Res Soc (in press)
Chin-Chia Wu and Wen-Chiung Lee (2009) A note on the total completion time problem in a permutation flowshop with a learning effect. Eur J Oper Res 192(1):343–347
Rahimi-Vahed A, Dangchi M, Rafiei H, Salimi E (2009) A novel hybrid multi-objective shuffled frog-leaping algorithm for a bi-criteria permutation flow shop scheduling problem. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 41(11–12):1227–1239
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, T., Yamashiro, M. Solving flow shop scheduling problems by quantum differential evolutionary algorithm. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 49, 643–662 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-009-2438-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-009-2438-4