Abstract
Objective and design
Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species are involved in the pathogenesis of sepsis syndrome with peritonitis and the septic shock. The aim of this study was to determine whether ozone oxidative preconditioning (OOP) may exert beneficial effects in the prevention and treatment of sepsis syndrome in rats inoculated by the intraperitoneal route (i.p.) with fecal material and also to determine if antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) may exert protective effects against this systemic inflammatory disorder.
Materials and methods
Male Wistar rats were used. SOD and GPx activities were determined in erythrocytes. Thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) content as biomarkers of oxidative stress, alanine amino transferase (ALT), aspartate amino transferase (AST) and creatinine (CRE) were measured in blood serum and myeloperoxidase (MPO) in lung tissue as markers of organs damage.
Results
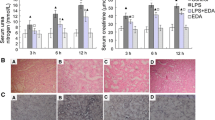
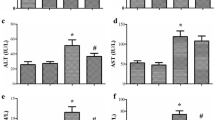
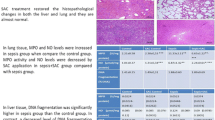
In rats submitted to OOP, SOD and GPx activities were significantly increased and it was accompanied by significant decrease of TBARS content in blood serum. OOP also significantly reduced levels of ALT, AST and CRE in blood serum as well as MPO in rat lung.
Conclusion
The results support the important role of SOD and GPx in the protective effects of OOP against organ damage induced by fecal peritonitis in rats.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Perdue PW, Kazarian KK, Nevola J, Low WR, Williams T. The use of local and systemic antibiotics in rats with faecal peritonitis. J Surg Res. 1994;57:360–5.
Cohen J. The inmunopathogenesis of sepsis. Nature. 2003;420:885–91.
Zanotti S, Kumar A. Cytokine modulation in sepsis and septic shock. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2002;11:1–15.
Annane D, Bellisant E, Cavaillon JM. Septic shock. Lancet. 2005;365:63–78.
Flowers F, Zimmerman J. Reactive oxygen species in the cellular pathophysiology of shock. New Horiz. 1998;6:169–80.
Cauwels A. Nitric oxide in shock. Kidney Int. 2007;72:557–65.
Khinev S, Dafinovak KG. The induction of lipid peroxidation in the serum of patients with acute peritonitis. Khirurgia. 1996;49:27–9.
Cowley HC, Bacon PJ, Goode hF, Webster NR, Jones JG, Menon DK. Plasma antioxidant potential in severe sepsis: a comparison of survivors and nonsurvivors. Crit Care Med. 1996;24:1179–83.
Goode HF, Webster NR. Free radicals and antioxidants in sepsis. Crit Care Med. 1993;21:1770–6.
Ghisellz R, Giacometti A, Cirioni O, Mocchegiani F, Viticchi C, Scalise G, et al. Cationic peptides combined with betalactams reduce mortality from peritonitis in experimental rat model. J Surg Res. 2002;108:107–11.
Wu CC. Possible therapies of septic shock: Based on animal studies and clinical trials. Curr Pharm Des. 2006;12:3535–41.
Schulz S, Zamora Z, Mutters R, Menendez S, Bette M. Repetitive pneumoperitoneum with ozonized oxygen as a preventive in lethal polymicrobial sepsis in rats. Eur Surg Res. 2003;35:26–34.
Bette M, Nuesing RM, Mutters R, Zamora ZB, Menendez S, Schulz S. Efficiency of tazobactam/piperacillin in lethal peritonitis is enhanced after preconditioning of rats with O3/O2—Pneumoperitoneum. Shock. 2006;1:26–9.
Zamora ZB, Borrego A, Lopez OY, Delgado R, Gonzalez R, Menendez S, et al. Effects of ozone oxidative preconditioning on TNF-α release and antioxidant-prooxidant intracellular balance in mice during endotoxic shock. Mediators Inflamm. 2005;1:16–22.
Knight AJ, Smith ES, Kinder EV, Anstall BH. Reference Intervals for plasma lipoperoxides: age, sex and specimen-related variations. Clin Chem. 1987;33:2289–91.
Minami M, Yoshikawa H. A simplified assay method of superoxide dismutase activity for clinical use. Clin Chim Acta. 1979;192:337–42.
Faraji B, Kang HK, Valentine JL. Methods compared for determining glutathione peroxidase activity in blood. Clin Chem. 1987;33:539–43.
Bradley PP, Priebat DA, Christensen RD, Rothtein G. Measurement of cutaneous inflammation. Estimation of neutrophil content with an enzyme marker. J Invest Dermatol. 1982;78:206–9.
Leon OS, Menendez S, Merino N, Castillo R, Sam S, Perez L, et al. Ozone oxidative preconditioning: a protection against cellular damage by free radicals. Mediators Inflamm. 1998;7:289–94.
Peralta C, Leon OS, Xaus C, Prats N, Jalil EC, Sala Planell E. Protective effect of ozone treatment on the injury associated with hepatic ischemia-reperfusion: antioxidant-prooxidant balance. Free Rad Res. 1999;31:191–6.
Candelario-Jalil E, Mohammed S, Leon OS, Menendez S, Merino N. Oxidative preconditioning affords protection against carbon tetrachloride-induced glycogen depletion and oxidative stress in rats. J Appl Toxicol. 2001;21:297–301.
Ajamieh HH, Berlanga J, Merino N, Sanchez G, Menendez S, Leon OS. Role of protein synthesis in the protection conferred by ozone-oxidative preconditioning in hepatic ischaemic/reperfusion. Trasplant Int. 2005;18:604–12.
Murry CE, Jennings RB, Reimer KA. Preconditioning with ischemia: a delay of lethal cell injury in ischaemic myocardium. Circulation. 1986;74:1124–36.
Neschis DG, Safford SD, Raghunath PN, Langer DJ, David ML, Hanna AK, et al. Thermal preconditioning before rat arterial balloon injury: limitation of injury and surtained reduction of intimal thickening. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1998;18:120–6.
Riepe MW, Ludolph AC. Chemical preconditioning: a cytoprotective strategy. Mol Cell Biochem. 1997;174:249–54.
Madej P, Pleuka JA, Nowak M, Plewka D, Franck G, Golka D. Ozonetherapy in an induced septic shock. 1. Effect of ozonetherapy on rat organ in evaluation of free radical reactions and selected enzymatic system. Inflammation. 2007;30:52–8.
Jacobs S, Sobki S, Morais C, Tariq M. Effect of pentaglobin and piperacillin on survival in a rat model of faecal peritonitis: importance of intervention timings. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2000;44:88–95.
Cuzzocrea S, Riley DP, Capute AP, Salvemin D. Antioxidant therapy; a new pharmacological approach in shock, inflammation, and ischemia/reperfusion injury. Pharmacol Rev. 2001;53:135–59.
Matés JM. Effects of antioxidant enzymes in the molecular control of reactive oxygen species in toxicology. Biog Amines. 2000;16:53–62.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: A. Bauhofer.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodríguez, Z.Z., Guanche, D., Álvarez, R.G. et al. Preconditioning with ozone/oxygen mixture induces reversion of some indicators of oxidative stress and prevents organic damage in rats with fecal peritonitis. Inflamm. Res. 58, 371–375 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-009-0001-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-009-0001-2