Abstract
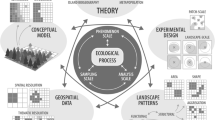
A variety of ecological questions now require the study of large regions and the understanding of spatial heterogeneity. Methods for spatial-temporal analyses are becoming increasingly important for ecological studies. A grid cell based spatial analysis program (SPAN) is described and results of landscape pattern analysis using SPAN are presentedd. Several ecological topics in which geographic information systems (GIS) can play an important role (landscape pattern analysis, neutral models of pattern and process, and extrapolation across spatial scales) are reviewed. To study the relationship between observed landscape patterns and ecological processes, a neutral model approach is recommended. For example, the expected pattern (i.e., neutral model) of the spread of disturbance across a landscape can be generated and then tested using actual landscape data that are stored in a GIS. Observed spatial or temporal patterns in ecological data may also be influenced by scale. Creating a spatial data base frequently requires integrating data at different scales. Spatial is shown to influence landscape pattern analyses, but extrapolation of data across spatial scales may be possible if the grain and extent of the data are specified. The continued development and testing of new methods for spatial-temporal analysis will contribute to a general understanding of landscape dynamics.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Addicott, J.F., Aho, J.M., Antolin, M.F., Padilla, D.K., Richardson, J.S. and Soluk, D.A. 1987. Ecological neighborhoods: scaling environmental patterns. Oikos 49: 340–346.
Allen, T.F.H. and Starr, T.B. 1992. Hierarchy. University of Chicago Press, Chicago.
Allen, T.F.H., O’Neill, R.V. and Hoekstra, T.W. 1987. Interlevel relations in ecological research and management: some working principles from hierarchy theory. Journal of Applied Systems Analysis 14: 63–79.
Burgess, R.L. and Sharpe, D.M., eds. 1981. Forest island dynamics in man-dominated landscapes, Springer-Verlag, New York.
Burrough, P.A. 1986. Principles of geographic information systems for land resources assessment. Clarendon Press, Oxford.
Caswell, H. 1976. Community structure: a neutral model analysis. Ecol. Monogr. 46: 327–354.
Caswell, H. 1988. Theory and models in ecology: a different perspective. Bull. Ecol. Soc. Amer. 69: 102–109.
Delcourt, H.R., Delcourt, P.A. and Webb, T., III. 1983. Dynamic plant ecology: The spectrum of vegetation change in space and time. Quaternary Science Review 1: 153–175.
Fahrig, L. and Paloheimo, J. 1988. Effect of spatial arrangement of habitat patches on local population size. Ecology 69: 468–475.
Forman, R.T.T. and Godron, M. 1981. Patches and structural components for a landscape ecology. BioScience 31: 733–740.
Forman, R.T.T. and Gordon, M. 1986. Landscape Ecology. John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Franklin, J.F. and Forman, R.T.T. 1987. Creating landscape patterns by forest cutting: ecological consequences and principles. Landscape Ecology 1: 5–18.
Gardner, R.H., Milne, B.T., Turner, M.G. and O’Neill, R.V. 1987. Neutral models for the analysis of broad-scale landscape pattern. Landscape Ecology 1: 19–28.
Getis, A. and Franklin, J. 1987. Second-order neighborhood analysis of mapped point patterns. Ecology
Henderson-Sellers, A., Wilson, M.F. and Thomas, G. 1985. The effect of spatial resolution on archives of land cover type. Climatic Change 7: 391–402.
Krummel, J.R., Gardner, R.H., Sugihara, G., O’Neill, R.V. and Coleman, P.R. 1987. Landscape patterns in a disturbed environment. Oikos 48: 321–324.
Mandelbrot, B.B. 1988. The fractal geometry of nature. W.H. Freeman and Co., San Francisco, CA.
Meentemeyer, V. and Box, E.O. 1987. Scale effects in landscape studies.In: Landscape heterogeneity and disturbance. pp. 15–34. Edited by M.G. Turner. Springer-Verlag, New York.
Milne, B.T. 1988. Measuring the fractal dimension of landscapes. Appl. Math. Comp. 27: 67–79.
Morris, D.W. 1987. Ecological scale and habitat use. Ecology 68: 362–369.
O’Neill, R.V., DeAngelis, D.L., Waide, J.B. and Allen, T.F.H. 1986. A hierarchical concept of ecosystems. Princeton University Press, New Jersey.
O’Neill, R.V., Krummel, J.R., Gardner, R.H., Sugihara, G., Jackson, B., DeAngelis, D.L., Milne, B.T., Turner, M.G., Zygmunt, B., Christensen, S.W., Dale, V.H. and Graham, R.L. 1988. Indices of landscape pattern. Landscape Ecology 1: 153–162.
Orbach, R. 1986. Dynamics of fractal networks. Science 231: 814–819.
Palmeirim, J.M. 1988. Automatic mapping of avian species habitat using satellite imagery. Oikos 52: 59–68.
Peterjohn, W.T. and Correll, D.L. 1984. Nutrient dynamics in an agricultural watershed: observations on the role of a riparian forest. Ecology 65: 1466–1475.
Romme, W. and Knight, D.H. 1982. Landscape diversity: the concept applied to Yellowstone Park. BioScience 32: 664–670.
Ryszkowski, L. and Kedziora, A. 1987. Impact of agricultural landscape structure on energy flow and water cycling. Landscape Ecology 1: 85–94.
Sala, O.E., Parton, W.J., Joyce, L.A. and Lauenroth, W.K. 1988. Primary production of the central grassland region of the United States. Ecology 69: 40–45.
SAS Institute. 1982. User’s guide: statistics. SAS Institute, Cary, North Carolina.
Schonewald-Cox, C. 1988. Boundaries in the protection of nature reserves. BioScience 38: 480–486.
Senft, R.L., Coughenour, M.B., Bailey, D.W., Rittenhouse, L.R., Sala, O.E., and Swift, D.M. 1987. Large herbivore foraging and ecological hierarchies. BioScience 37: 789–799.
Shannon, C.E. and Weaver, W. 1962. The mathematical theory of communication. University of Illinois Press, Urbana.
Sharpe, D.M., Guntenspergen, G.R., Dunn, C.P., Leitner, L.A. and Stearns, F. 1987. Vegetation dynamics in a southern Wisconsin agricultural landscape.In: Landscape heterogeneity and disturbance. pp. 139–158. Edited by M.G. Turner. Springer-Verlag, New York.
Stauffer, D. 1985. Introduction to percolation theory. Taylor and Francis, London.
Swanson, F.J., Kratz, T.K., Caine, N. and Woodmansee, R.G. 1988. Landform effects on ecosystem patterns and processes. BioScience 38: 92–98.
Turner, M.G., ed. 1987a. Landscape heterogeneity and disturbance. Springer-Verlag, New York.
Turner, M.G. 1987b. Land use changes and net primary production in the Georgia landscape: 1935 to 1982. Environ. Manage. 11: 237–247.
Turner, M.G. 1987c. Spatial simulation of landscape changes in Georgia: a comparison of 3 transition models. Landscape Ecology 1: 29–36.
Turner, M.G. 1988. A spatial simulation model of land use changes in Georgia. Appl. Math. Comp. 27: 39–51.
Turner, M.G. and Ruscher, C.L. 1988. Changes in the spatial patterns of land use in Georgia. Landscape Ecology 1: 241–251.
Turner, M.G., Gardner, R.H., Dale, V.H., and O’Neill, R.V. 1988. Landscape pattern and the spread of disturbance.In: Proc. VIIIth Intl. Symp. Probs. Landsc. Ecol. Res., Vol. 1. pp. 373–382. Edited by M. Ruzicka, T. Hrnciarova, and L. Miklos. Institute of Experimental Biology and Ecology, CBES SAS, Bratislava, Czechoslovakia.
Turner, M.G., Gardner, R.H., Dale, V.H. and O’Neill, R.V. 1989a. Predicting the spread of disturbance in heterogeneous landscapes. Oikos. 55: 121–129.
Turner, M.G., O’Neill, R.V., Gardner, R.H. and Milne, B.T. 1989b. Effects of changing spatial scale on the analysis of landscape pattern. Landscape Ecology 3(3/4): 153–163.
Urban, D.L., O’Neill, R.V. and Shugart, H.H. 1987. Landscape ecology. BioScience 37: 119–127.
Van Dorp, D. and Opdam, P.F.M. 1987. Effects of patch size, isolation and regional abundance on forest bird communities. Landscape Ecology 1: 59–73.
Whitney, G.T. and Somerlot, W.J. 1985. A case study of woodland continuity and change in the American midwest. Biol. Conserv. 31: 265–287.
Wiens, J.A., Crawford, C.S. and Gosz, J.R. 1985. Boundary dynamics: a conceptual framework for studying landscape ecosystems. Oikos 45: 421–427.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Turner, M.G. Spatial and temporal analysis of landscape patterns. Landscape Ecol 4, 21–30 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02573948
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02573948