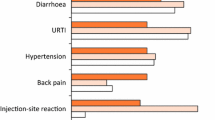
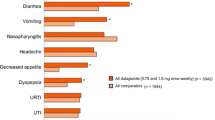
Abstract
Albiglutide (Eperzan® [EU]; Tanzeum™ [US]), a glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist, has been developed by GlaxoSmithKline for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Albiglutide has received its first global approval in this indication in the EU, for use in combination with other antihyperglycaemic agents, including basal insulin, when these drugs and diet and exercise do not provide adequate glycaemic control, and as monotherapy in patients unable to take metformin due to contraindications or intolerance when diet and exercise alone do not provide adequate glycaemic control. Albiglutide has subsequently been approved for the second-line or later treatment of T2DM as an adjunct to diet and exercise in the US. This article summarizes the milestones in the development of albiglutide leading to this first approval for the treatment of T2DM.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meier JJ, Nauck MA. Is the diminished incretin effect in type 2 diabetes just an epi-phenomenon of impaired beta-cell function? Diabetes. 2010;59(5):1117–25.
Berlie H, Hurren KM, Pinelli NR. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists as add-on therapy to basal insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2012;5:165–74.
Lorenz M, Evers A, Wagner M. Recent progress and future options in the development of GLP-1 receptor agonists for the treatment of diabesity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2013;23(14):4011–8.
European Medicines Agency. EPAR summary for the public: Eperzan albiglutide. http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Product_Information/human/002735/WC500165117.pdf. Accessed 10 April 201.
GlaxoSmithKline. GSK receives European authorisation for once-weekly type 2 diabetes treatment, Eperzan(Rm) (albiglutide) [media release]. 26 Mar 2014. URL.
European Medicines Agency. Eperzan: EPAR - Product Information. http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Product_Information/human/002735/WC500165117.pdf. Accessed 10 April 2014.
European Medicines Agency. Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Eperzan (albiglutide). http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Risk-management-plan_summary/human/002735/WC50016258pdf. Accessed 10 April 2014.
US Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves Tanzeum to treat type 2 diabetes [media release]. 15 April 2014. http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm393289.htm.
GlaxoSmithKline. TANZEUM Prescribing Information. https://www.gsksource.com/gskprm/htdocs/documents/TANZEUM-PI-MG-IFU-COMBINED.PDF. Accessed 8 May 2014.
US Food and Drug Administration. BLA STN-125431 TANZEUM™ (Albiglutide). Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Receptor Agonist, GlaxoSmithKline LLC. RISK EVALUATION AND MITIGATION STRATEGY (REMS). http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/DrugSafety/PostmarketDrugSafetyInformationforPatientsandProviders/UCM393986.pdf. Accessed 8 May 2014.
Human Genome Sciences. Human Genome Sciences Announces Agreement With GlaxoSmithKline for Development and Commercialization of Novel Drug to Treat Diabetes [media release]. 26 Oct 2004. http://www.hgsi.com.
GlaxoSmithKline. GSK Completes Acquisition of Human Genome Sciences [media release]. 3 Aug 20 http://www.gsk.com.
Novozymes. Novozymes technology enables GlaxoSmithKline’s new once-weekly diabetes treatment [media release]. 31 March 2014. http://novozymes.com/en/news/news-archive/Pages/Novozymes-technology-enables-GlaxoSmithKline’s-new-once-weekly-diabetes-treatment.aspx.
Bush MA, Matthews JE, De Boever EH, et al. Safety, tolerability, pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of albiglutide, a long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 mimetic, in healthy subjects. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2009;11(5):498–505.
Baggio LL, Huang Q, Brown TJ, et al. A recombinant human glucagon-like peptide (GLP)-1-albumin protein (albugon) mimics peptidergic activation of GLP-1 receptor-dependent pathways coupled with satiety, gastrointestinal motility, and glucose homeostasis. Diabetes. 2004;53(9):2492–500.
Bao W, Aravindhan K, Alsaid H, et al. Albiglutide, a long lasting glucagon-like peptide-1 analog, protects the rat heart against ischemia/reperfusion injury: evidence for improving cardiac metabolic efficiency. PLoS ONE [Electronic Resource]. 2011;6(8):e23570.
Hompesch M, Leone-Jones A, Carr MC, et al. Albiglutide does not impact the counter regulatory hormone response or recovery time from hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2DM): A randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled, stepped automated glucose clamp study. Diabetes. 2013;62:A260.
Stewart MW, Matthews J, De Boever EH, et al. Pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability of albiglutide (Syncria Rm), a long-acting GLP-1 mimetic, in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2008;57(Suppl. 1):154 (plus poster) abstr. 519-P.
Seino Y, Nakajima H, Miyahara H, et al. Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of albiglutide, a long-acting GLP-1-receptor agonist, in Japanese subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Curr Med Res Opin. 2009;25(12):3049–57.
Darpo B, Zhou M, Matthews J, et al. Albiglutide does not prolong the QTc interval in healthy subjects: A thorough QT/QTc study. Diabetes. 2013;62:A269.
Stewart MW, Matthews J, De Boever EH, et al. Albiglutide, a long-acting GLP-1 mimetic: pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, safety and tolerability in subjects with type 2 diabetes. In: 44th Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. 2008:abstr. 870.
Seino Y, Nakajima H, Miyahara H, et al. Safety and tolerability, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of albiglutide in japanese subjects with type 2 diabetes: A comparison with an ethnically mixed population. Can J Diabetes. 2009;33(3):291–2.
Bush MA, Smith C, Watanalumlerd P, et al. Population pharmacokinetic (PK) analysis of albiglutide in a phase iib study in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2012;61:A261–2.
Bush M, Scott R, Watanalumlerd P, et al. Effects of multiple doses of albiglutide on the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and safety of digoxin, warfarin, or a low-dose oral contraceptive. Postgrad Med. 2012;124(6):55–72.
GlaxoSmithKline. An Open-label, Sequential Study to Evaluate the Pharmacokinetics of Simvastatin When Coadministered With Albiglutide in Healthy Adult Subjects. 2011. http://www.gsk-clinicalstudyregister.com/study/108366#ps. Accessed 2014.
Reusch J, Stewart M, Perkins C, et al. HARMONY 1 results at week 52 primary endpoint: once-weekly albiglutide vs placebo in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus not controlled on pioglitazone ± metformin. In: 49th Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. 2013:abstr. 902.
Reusch J, Stewart M, Perkins C, et al. HARMONY 1 week 52 results: albiglutide vs. placebo in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus not controlled onpioglitazone ± metformin. In: 73rd Annual Scientific Sessions of the American Diabetes Association. 2013:abstr. 57-LB.
Nauck M, Stewart M, Perkins C, et al. HARMONY 2 Wk 52 Results: Albiglutide Monotherapy in Drug Naive Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. In: 73rd Annual Scientific Sessions of the American Diabetes Association. 2013:abstr. 55-LB.
Reinhardt R, Nauck MA, Stewart M, et al. HARMONY 2 results at week 52 primary endpoint: once-weekly albiglutide monotherapy for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled with diet and exercise. In: 49th Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. 2013:abstr. 903.
Ahren B, Stewart M, Cirkel D, et al. HARMONY 3: 104 Week (Wk) Efficacy of Albiglutide (Albi) Compared to Sitagliptin (Sita) and Glimepiride (SU) in Patients (pts) with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) on Metformin (Met). In: 73rd Annual Scientific Sessions of the American Diabetes Association. 2013:abstr. 52-LB.
Johnson S, Ahren B, Stewart M, et al. HARMONY 3: 104 week efficacy of albiglutide compared to sitagliptin and glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus on metformin. In: 49th Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. 2013:abstr. 5.
Pratley R, Stewart M, Cirkel D, et al. HARMONY 4: 52-week efficacy of albiglutide vs insulin glargine in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. In: 49th Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. 2013:abstr. 904.
Home P, Stewart M, Yang F. 52-week efficacy of albiglutide vs placebo and vs pioglitazone in triple therapy (background metformin and glimepiride) in people with type 2 diabetes: HARMONY5 Study. In: 73rd Annual Scientific Sessions of the American Diabetes Association. 2013:abstr. 58-LB.
Fonseca VL, Ahren B, Chow F, et al. Once weekly GLP-1 receptor agonist albiglutide vs prandial lispro added to basal glargine in type 2 diabetes: similar glycaemic control with weight loss and less hypoglycaemia. Diabetologia. 2012;55:S241.
Rosenstock J, Ahren B, Chow F, et al. Once-weekly GLP-1 receptor agonist Albiglutide vs. Titrated prandial lispro added on to titrated basal insulin glargine in Type 2 Diabetes (T2D) uncontrolled on glargine plus oral agents: Similar glycemic control with weight loss and less hypoglycemia. Diabetes. 2012;61:A15–6.
Pratley RE, Barnett A, Feinglos MM, et al. Efficacy and safety of once-weekly (QW) albiglutide vs. once-daily (QD) liraglutide in type 2 diabetes (T2D) inadequately controlled on oral agents: Harmony 7 trial. Diabetes. 2012;61:A240–1.
Leiter LA, Carr MC, Stewart M, et al. Harmony 8: Once weekly (QW) GLP1 Agonist Albiglutide (Albi) vs. Sitagliptin (Sita) in Type 2 Diabetes (T2D) Pts With Renal Impairment (RI): Week 26 Results. Diabetes. 2013;62:A17.
Martin AA, Johnson SL, Ye J, et al. Improved treatment satisfaction with weekly abiglutide vs. Thrice daily prandial insulin added to insulin glargine in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2013;62:A659.
Pratley RE, Nauck MA, Barnett AH, et al. Once-weekly albiglutide versus once-daily liraglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on oral drugs (HARMONY 7): a randomised, open-label, multicentre, non-inferiority phase 3 study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014;2(4):289–97.
Martin AA, Johnson SL, Ye J, et al. Treatment satisfaction with albiglutide and liraglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes uncontrolled with oral therapy. Diabetes. 2013;62:A259–60.
GlaxoSmithKline. A randomized, double-blind, active-controlled, parallel-group, multicenter study to determine the efficacy and safety of albiglutide as compared with sitagliptin in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus with renal impairment. http://www.gsk-clinicalstudyregister.com/study/114130#rs. Accessed 08 May 2014.
Rosenstock J, Reusch J, Bush M, et al. Potential of albiglutide, a long-acting GLP-1 receptor agonist, in type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial exploring weekly, biweekly, and monthly dosing. Diabetes Care. 2009;32:1880–6.
Seino Y, Inagaki N, Miyahara H, et al. Albiglutide significantly lowers glycemia in japanese patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D). Diabetes. 2012;61:A248.
GlaxoSmithKline. A monotherapy study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of 2 dose levels of albiglutide in japanese subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) [ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT01733758] US National Institutes of Health, ClinicalTrials.gov. http://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01733758?term=NCT01733758&rank=1. Accessed 15 April 2014.
GlaxoSmithKline. A Study to Determine the Long Term Safety and Efficacy of Albiglutide in Combination With Oral Monotherapy Antihyperglycemic Medications in Japanese Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus [ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT01777282] US National Institutes of Health, ClinicalTrials.gov. http://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01777282?term=NCT01777282&rank=1. Accessed 15 April 2014.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This report has been extracted and modified from the Adis R&D Insight drug pipeline database. Adis R&D Insight tracks drug development worldwide through the entire development process, from discovery, through pre-clinical and clinical studies to market launch.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poole, R.M., Nowlan, M.L. Albiglutide: First Global Approval. Drugs 74, 929–938 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-014-0228-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-014-0228-2