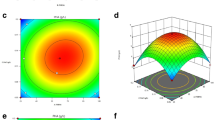
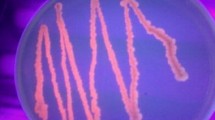
Abstract
Substituting petroleum-derived polymers with biodegradable and biocompatible polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) is a challenge to sustain the environmental system. This study intends to optimize the cultural conditions for PHB production by nonpathogenic Bacillus subtilis isolated from Jatropha field. Various agricultural and industrial wastes such as corn bran, corncob, wheat bran, rice bran, dairy waste, and sugarcane molasses were utilized for PHB production. Among these wastes, rice bran was the best carbon source for PHB production (0.31 g/l) with 30.4% of the dry cell weight (DCW). Cultural parameters influencing PHB production were studied employing Plackett–Burman and Box–Behnken designs. Accordingly, pH, incubation time, and inoculum size were found to be the most influential factors on PHB production. Using optimized conditions, sixfold augment in PHB content (0.81 g/l, 62.6% DCW) was attained using rice bran. PHBs obtained from glucose and rice bran were characterized using 1H NMR, FT-IR, TGA, and DSC analysis. Structures of PHBs were comparable, whereas the findings of thermal studies revealed that rice bran-derived PHB showed higher thermal stability with lower melting temperature than glucose-derived PHB. These results substantiate the potential use of this safe isolate utilizing inexpensive substrates for PHB production that could be adopted in medical applications.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abol Fotouh DM, Bayoumi RA, Hassan MA (2016) Production of thermoalkaliphilic lipase from geobacillus thermoleovorans DA2 and application in leather industry. Enzyme Res 2016:9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/9034364
Aramvash A, Akbari Shahabi Z, Dashti Aghjeh S, Ghafari MD (2015) Statistical physical and nutrient optimization of bioplastic polyhydroxybutyrate production by Cupriavidus necator. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12:2307–2316. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-015-0768-3
Cavalheiro JMBT, de Almeida MCMD, Grandfils C, da Fonseca MMR (2009) Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) production by Cupriavidus necator using waste glycerol. Process Biochem 44:509–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2009.01.008
Choi GG, Kim HW, Rhee YH (2004) Enzymatic and non-enzymatic degradation of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) copolyesters produced by Alcaligenes sp. MT-16. J Microbiol 42:346–352
Dhangdhariya JH, Dubey S, Trivedi HB, Pancha I, Bhatt JK, Dave BP, Mishra S (2015) Polyhydroxyalkanoate from marine Bacillus megaterium using CSMCRI’s Dry Sea Mix as a novel growth medium. Int J Biol Macromol 76:254–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.02.009
Du G, Yu J (2002) Green technology for conversion of food scraps to biodegradable thermoplastic polyhydroxyalkanoates. Environ Sci Technol 36:5511–5516. https://doi.org/10.1021/es011110o
El-Fakharany E, Hassan M, Taha T (2016) Production and application of extracellular laccase produced by Fusarium oxysporum EMT. Int J Agric Biol 18:939–947
El Fawal GF, Abu-Serie MM, Hassan MA, Elnouby MS (2018) Hydroxyethyl cellulose hydrogel for wound dressing: Fabrication, characterization and in vitro evaluation. Int J Biol Macromol 111:649–659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.01.040
Gao X, Chen J-C, Wu Q, Chen G-Q (2011) Polyhydroxyalkanoates as a source of chemicals, polymers, and biofuels. Curr Opin Biotechnol 22:768–774. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2011.06.005
Hablot E, Bordes P, Pollet E, Avérous L (2008) Thermal and thermo-mechanical degradation of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate)-based multiphase systems. Polym Degrad Stab 93:413–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2007.11.018
Hassan MA, Amara AA, Abuelhamd AT, Haroun BM (2010) Leucocytes show improvement growth on PHA polymer surface. Pak J Pharm Sci 23:332–336
Hassan MA, Haroun BM, Amara AA, Serour EA (2013) Production and characterization of keratinolytic protease from new wool-degrading Bacillus species isolated from Egyptian ecosystem. Biomed Res Int 2013:14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/175012
Hassan MA, Bakhiet EK, Ali SG, Hussien HR (2016) Production and characterization of polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) produced by Bacillus sp. isolated from Egypt. J Appl Pharm Sci 6:046–051
Holt JG, Krieg NR, Sneath PHA, Staley JT, Williams ST (1994) Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology, 9th edn. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore
Jiang Y, Song X, Gong L, Li P, Dai C, Shao W (2008) High poly(β-hydroxybutyrate) production by Pseudomonas fluorescens A2a5 from inexpensive substrates. Enzyme Microb Technol 42:167–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2007.09.003
Kavitha G, Kurinjimalar C, Sivakumar K, Palani P, Rengasamy R (2016) Biosynthesis, purification and characterization of polyhydroxybutyrate from Botryococcus braunii kütz. Int J Biol Macromol 89:700–706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.04.086
Keshavarz T, Roy I (2010) Polyhydroxyalkanoates: bioplastics with a green agenda. Curr Opin Microbiol 13:321–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2010.02.006
Khanna S, Srivastava AK (2005) Recent advances in microbial polyhydroxyalkanoates. Process Biochem 40:607–619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2004.01.053
Liu Y, Huang S, Zhang Y, Xu F (2014) Isolation and characterization of a thermophilic Bacillus shackletonii K5 from a biotrickling filter for the production of polyhydroxybutyrate. J Environ Sci 26:1453–1462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2014.05.011
Lutke-Eversloh T et al (2002) Biosynthesis of novel thermoplastic polythioesters by engineered Escherichia coli. Nat Mater 1:236–240. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat773
Mizuno K, Ohta A, Hyakutake M, Ichinomiya Y, Tsuge T (2010) Isolation of polyhydroxyalkanoate-producing bacteria from a polluted soil and characterization of the isolated strain Bacillus cereus YB-4. Polym Degrad Stab 95:1335–1339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2010.01.033
Nikel PI, Pettinari MJ, Mendez BS, Galvagno MA (2005) Statistical optimization of a culture medium for biomass and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) production by a recombinant Escherichia coli strain using agroindustrial byproducts. Int Microbiol 8:243–250
Pandian SR, Deepak V, Kalishwaralal K, Rameshkumar N, Jeyaraj M, Gurunathan S (2010) Optimization and fed-batch production of PHB utilizing dairy waste and sea water as nutrient sources by Bacillus megaterium SRKP-3. Biores Technol 101:705–711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.08.040
Park S-B, Lih E, Park K-S, Joung YK, Han DK (2017) Biopolymer-based functional composites for medical applications. Prog Polym Sci 68:77–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2016.12.003
Prabisha TP, Sindhu R, Binod P, Sankar V, Raghu KG, Pandey A (2015) Production and characterization of PHB from a novel isolate Comamonas sp. from a dairy effluent sample and its application in cell culture. Biochem Eng J 101:150–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2015.05.012
Pradhan S, Borah AJ, Poddar MK, Dikshit PK, Rohidas L, Moholkar VS (2017) Microbial production, ultrasound-assisted extraction and characterization of biopolymer polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) from terrestrial (P. hysterophorus) and aquatic (E. crassipes) invasive weeds. Biores Technol 242:304–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.03.117
Rehm BHA (2010) Bacterial polymers: biosynthesis, modifications and applications. Nat Rev Microbiol 8:578. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2354
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR (1977) DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:5463–5467
Sathiyanarayanan G, Saibaba G, Seghal Kiran G, Selvin J (2013) A statistical approach for optimization of polyhydroxybutyrate production by marine Bacillus subtilis MSBN17. Int J Biol Macromol 59:170–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2013.04.040
Schlegel HG, Kaltwasser H, Gottschalk G (1961) A submersion method for culture of hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria: growth physiological studies. Archiv fur Mikrobiologie 38:209–222
Sharma L, Kumar Singh A, Panda B, Mallick N (2007) Process optimization for poly-β-hydroxybutyrate production in a nitrogen fixing cyanobacterium, Nostoc muscorum using response surface methodology. Bioresour Technol 98:987–993. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2006.04.016
Sharma V, Misra S, Kumar Srivastava A (2017) Developing a green and sustainable process for enhanced PHB production by Azohydromonas australica. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 10:122–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2017.02.014
Spiekermann P, Rehm BH, Kalscheuer R, Baumeister D, Steinbuchel A (1999) A sensitive, viable-colony staining method using Nile red for direct screening of bacteria that accumulate polyhydroxyalkanoic acids and other lipid storage compounds. Arch Microbiol 171:73–80
Steinbuchel A (1991) Polyhydroxyalkanoic acids. In: Byrom D (ed) Biomaterials: novel materials from biological sources. Macmillan, New York
Suriyamongkol P, Weselake R, Narine S, Moloney M, Shah S (2007) Biotechnological approaches for the production of polyhydroxyalkanoates in microorganisms and plants—a review. Biotechnol Adv 25:148–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2006.11.007
Tamer TM, Omer AM, Hassan MA, Hassan ME, Sabet MM, Eldin MSM (2015) Development of thermo-sensitive poly N-isopropyl acrylamide grafted chitosan derivatives. J Appl Pharm Sci 5:001–006
Tamer TM, Hassan MA, Omer AM, Baset WMA, Hassan ME, El-Shafeey MEA, Eldin MSM (2016) Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial evaluation of two aromatic chitosan Schiff base derivatives. Process Biochem 51:1721–1730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2016.08.002
Tamer TM, Hassan MA, Omer AM, Valachová K, Eldin MSM, Collins MN, Šoltés L (2017) Antibacterial and antioxidative activity of O-amine functionalized chitosan. Carbohyd Polym 169:441–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.04.027
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msr121
Tripathi AD, Srivastava SK, Singh RP (2013) Statistical optimization of physical process variables for bio-plastic (PHB) production by Alcaligenes sp. Biomass Bioenergy 55:243–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2013.02.017
Yousuf RG, Winterburn JB (2016) Date seed characterisation, substrate extraction and process modelling for the production of polyhydroxybutyrate by Cupriavidus necator. Biores Technol 222:242–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.09.107
Yüksekdağ ZN, Beyatli Y, Aslim B (2003) Determination of poly-β-hydroxybutyrate (PHB) production by some mesophilic and thermophilic lactic acid bacteria. Turk J Biol 27:37–42
Zinn M, Witholt B, Egli T (2001) Occurrence, synthesis and medical application of bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoate. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 53:5–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-409X(01)00218-6
Zuriani R, Vigneswari S, Azizan MNM, Majid MIA, Amirul AA (2013) A high throughput Nile red fluorescence method for rapid quantification of intracellular bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoates. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 18:472–478. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-012-0607-z
Acknowledgment
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology Research Institute (GEBRI), The City of Scientific Research and Technological Applications (SRTA-City), New Borg El-Arab City, Alexandria, Egypt.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: M. Abbaspour.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hassan, M.A., Bakhiet, E.K., Hussein, H.R. et al. Statistical optimization studies for polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) production by novel Bacillus subtilis using agricultural and industrial wastes. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 16, 3497–3512 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1900-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1900-y