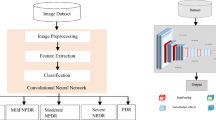
Abstract
Diabetic eye disease is a collection of ocular problems that affect patients with diabetes. Thus, timely screening enhances the chances of timely treatment and prevents permanent vision impairment. Retinal fundus images are a useful resource to diagnose retinal complications for ophthalmologists. However, manual detection can be laborious and time-consuming. Therefore, developing an automated diagnose system reduces the time and workload for ophthalmologists. Recently, the image classification using Deep Learning (DL) in between healthy or diseased retinal fundus image classification already achieved a state of the art performance. While the classification of mild and multi-class diseases remains an open challenge, therefore, this research aimed to build an automated classification system considering two scenarios: (i) mild multi-class diabetic eye disease (DED), and (ii) multi-class DED. Our model tested on various datasets, annotated by an opthalmologist. The experiment conducted employing the top two pretrained convolutional neural network (CNN) models on ImageNet. Furthermore, various performance improvement techniques were employed, i.e., fine-tune, optimization, and contrast enhancement. Maximum accuracy of 88.3% obtained on the VGG16 model for multi-class classification and 85.95% for mild multi-class classification.





Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
References
Abràmoff MD, Reinhardt JM, Russell SR, Folk JC, Mahajan VB, Niemeijer M, Quellec G. Automated early detection of diabetic retinopathy. Ophthalmology. 2010;117(6):1147–54.
Arunkumar R, Karthigaikumar P. Multi-retinal disease classification by reduced deep learning features. Neural Comput Appl. 2017;28(2):329–34.
Asaoka R, Murata H, Iwase A, Araie M. Detecting preperimetric glaucoma with standard automated perimetry using a deep learning classifier. Ophthalmology. 2016;123(9):1974–80.
Association BD, et al. Retinal photography screening for diabetic eye disease. London: BDA; 1997.
Bargshady G, Zhou X, Deo RC, Soar J, Whittaker F, Wang H. Enhanced deep learning algorithm development to detect pain intensity from facial expression images. Expert Syst Appl. 2020;149:113305.
Burlina P, Freund DE, Joshi N, Wolfson Y, Bressler NM. Detection of age-related macular degeneration via deep learning. In: 2016 IEEE 13th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), p. 184–88. IEEE 2016..
Caixinha M, Nunes S. Machine learning techniques in clinical vision sciences. Curr Eye Res. 2017;42(1):1–15.
Chen X, Xu Y, Wong DWK, Wong TY, Liu J. Glaucoma detection based on deep convolutional neural network. In: 2015 37th annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society (EMBC); 2015, p. 715–18. IEEE.
Choi JY, Yoo TK, Seo JG, Kwak J, Um TT, Rim TH. Multi-categorical deep learning neural network to classify retinal images: a pilot study employing small database. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(11):e0187336.
Congdon NG, Friedman DS, Lietman T. Important causes of visual impairment in the world today. Jama. 2003;290(15):2057–60.
De Fauw J, Keane P, Tomasev N, Visentin D, van den Driessche G, Johnson M, Hughes CO, Chu C, Ledsam J, Back T et al. Automated analysis of retinal imaging using machine learning techniques for computer vision. F1000Research. 2016;5.
De Fauw J, Ledsam JR, Romera-Paredes B, Nikolov S, Tomasev N, Blackwell S, Askham H, Glorot X, O’Donoghue B, Visentin D, et al. Clinically applicable deep learning for diagnosis and referral in retinal disease. Nat Med. 2018;24(9):1342–50.
Deng, J., Berg, A.C., Li, K., Fei-Fei, L.: What does classifying more than 10,000 image categories tell us? In: European conference on computer vision, p. 71–84. Springer; 2010.
Esteva A, Kuprel B, Novoa RA, Ko J, Swetter SM, Blau HM, Thrun S. Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks. Nature. 2017;542(7639):115–8.
Gao X, Lin S, Wong TY. Automatic feature learning to grade nuclear cataracts based on deep learning. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2015;62(11):2693–701.
Gargeya R, Leng T. Automated identification of diabetic retinopathy using deep learning. Ophthalmology. 2017;124(7):962–9.
Goceri, E., Goceri, N. Deep learning in medical image analysis: recent advances and future trends; 2017.
Gulshan V, Peng L, Coram M, Stumpe MC, Wu D, Narayanaswamy A, Venugopalan S, Widner K, Madams T, Cuadros J, et al. Development and validation of a deep learning algorithm for detection of diabetic retinopathy in retinal fundus photographs. Jama. 2016;316(22):2402–10.
He, J., Rong, J., Sun, L., Wang, H., Zhang, Y., Ma, J. A framework for cardiac arrhythmia detection from IoT-based ECGS. World Wide Web, p. 1–16; 2020.
Karri SPK, Chakraborty D, Chatterjee J. Transfer learning based classification of optical coherence tomography images with diabetic macular edema and dry age-related macular degeneration. Biomed Opt Express. 2017;8(2):579–92.
Kwasigroch, A., Jarzembinski, B., Grochowski, M. Deep CNN based decision support system for detection and assessing the stage of diabetic retinopathy. In: 2018 International Interdisciplinary PhD Workshop (IIPhDW), p. 111–16. IEEE; 2018
Lam C, Yi D, Guo M, Lindsey T. Automated detection of diabetic retinopathy using deep learning. AMIA Summits Transl Sci Proc. 2018;2018:147.
LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G. Deep learning. Nature. 2015;521(7553):436–44.
Lee CS, Baughman DM, Lee AY. Deep learning is effective for classifying normal versus age-related macular degeneration oct images. Ophthalmol Retina. 2017;1(4):322–7.
Li H, Wang Y, Wang H, Zhou B. Multi-window based ensemble learning for classification of imbalanced streaming data. World Wide Web. 2017;20(6):1507–25.
Li, X., Pang, T., Xiong, B., Liu, W., Liang, P., Wang, T. Convolutional neural networks based transfer learning for diabetic retinopathy fundus image classification. In: 2017 10th international congress on image and signal processing, biomedical engineering and informatics (CISP-BMEI), p. 1–11. IEEE; 2017.
Ma J, Sun L, Wang H, Zhang Y, Aickelin U. Supervised anomaly detection in uncertain pseudoperiodic data streams. ACM Trans Internet Technol. 2016;16(1):1–20.
Mateen M, Wen J, Song S, Huang Z, et al. Fundus image classification using VGG-19 architecture with PCA and SVD. Symmetry. 2019;11(1):1.
Mookiah MRK, Acharya UR, Chua CK, Lim CM, Ng E, Laude A. Computer-aided diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy: a review. Comput Biol Med. 2013;43(12):2136–55.
Pandey D, Yin X, Wang H, Zhang Y. Accurate vessel segmentation using maximum entropy incorporating line detection and phase-preserving denoising. Comput Vis Image Unders. 2017;155:162–72.
Pandey D, Yin X, Wang H, Su MY, Chen JH, Wu J, Zhang Y. Automatic and fast segmentation of breast region-of-interest (ROI) and density in MRIS. Heliyon. 2018;4(12):e01042.
Pratt H, Coenen F, Broadbent DM, Harding SP, Zheng Y. Convolutional neural networks for diabetic retinopathy. Procedia Comput Sci. 2016;90:200–5.
Sarki R, Ahmed K, Zhang Y. Early detection of diabetic eye disease through deep learning using fundus images. EAI Endors Trans Pervasive Health Technol. 2020;6(22).
Shin HC, Roth HR, Gao M, Lu L, Xu Z, Nogues I, Yao J, Mollura D, Summers RM. Deep convolutional neural networks for computer-aided detection: CNN architectures, dataset characteristics and transfer learning. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2016;35(5):1285–98.
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556; 2014.
Sokolova M, Lapalme G. A systematic analysis of performance measures for classification tasks. Inf Process Manag. 2009;45(4):427–37.
Thapar, S., Garg, S. Study and implementation of various morphology based image contrast enhancement techniques. Int J Comput Bus Res. 2012;2229–6166.
Torrey, L., Shavlik, J. Transfer learning. In: Handbook of research on machine learning applications and trends: algorithms, methods, and techniques, p. 242–64. IGI Global; 2010.
Wan S, Liang Y, Zhang Y. Deep convolutional neural networks for diabetic retinopathy detection by image classification. Comput Electr Eng. 2018;72:274–82.
Wang Y, Zhang Y, Yao Z, Zhao R, Zhou F. Machine learning based detection of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and diabetic macular edema (DME) from optical coherence tomography (OCT) images. Biomed Opt Express. 2016;7(12):4928–40.
Yamashita R, Nishio M, Do RKG, Togashi K. Convolutional neural networks: an overview and application in radiology. Insights Imaging. 2018;9(4):611–29.
Yin X, Ng BW, He J, Zhang Y, Abbott D. Accurate image analysis of the retina using hessian matrix and binarisation of thresholded entropy with application of texture mapping. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(4):e95943.
Yoo TK, Hong S. Artificial neural network approach for differentiating open-angle glaucoma from glaucoma suspect without a visual field test. Investig Ophthalmol Visual Sci. 2015;56(6):3957–66.
Yoo TK, Park EC. Diabetic retinopathy risk prediction for fundus examination using sparse learning: a cross-sectional study. BMC Med Inform Decis Making. 2013;13(1):106.
Zhang W, Zhong J, Yang S, Gao Z, Hu J, Chen Y, Yi Z. Automated identification and grading system of diabetic retinopathy using deep neural networks. Knowl-Based Syst. 2019;175:12–25.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarki, R., Ahmed, K., Wang, H. et al. Automated detection of mild and multi-class diabetic eye diseases using deep learning. Health Inf Sci Syst 8, 32 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13755-020-00125-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13755-020-00125-5