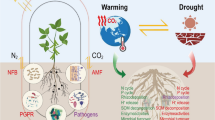
Abstract
Soils around the world are degraded due to inappropriate management practices. There is thus the necessity to find more conservationist agricultural systems. Agroforestry system is an alternative system that helps prevent land degradation while allowing continuing use of land to produce crops and livestock on a sustainable basis. Agroforestry system is a form of sustainable land use that combines trees and shrubs with crops and livestock in ways that increase and diversify farm and forest production while also conserving natural resources. This system enhances organic carbon accumulation in soils by the inclusion of cover crops and permanent vegetation, which is expected to increase the soil microbial biomass. The use of microorganisms aims at improving nutrient availability for plants. Currently, there is an emerging demand to decrease the dependence on chemical fertilizers and achieve sustainable agriculture and agroforestry. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria, and the association of rhizobia with leguminous plants are mutualistic symbioses of high economic importance for increasing agricultural production. The biological nitrogen fixation (BNF) process is an economically attractive and ecologically sound method to reduce external nitrogen input and improve the quality and quantity of internal resources. BNF by associative diazotrophic bacteria is a spontaneous process where soil nitrogen is limited and adequate carbon sources are available. However, the ability of these bacteria to contribute to increased crop yields is only partly a result of BNF. The successful use of legumes is dependent upon appropriate attention to the formation of effective symbioses with root nodule bacteria. An essential component for increasing the use of legumes is the integration of plant breeding and cultivar development, with appropriate research leading to the selection of elite strains of root nodule bacteria. An expansion of the utility of inoculants is also necessary to develop a broad conceptual framework and methodology that is supported by scientific arguments; it is destined to impact assessment of the use of new biological products in agriculture.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilar OM, López MV, Riccillo PM (2001) The diversity of rhizobia nodulating beans in Northwest Argentina as a source of more efficient inoculant strains. J Biotech 91:181–188
Albareda M, Rodriguez-Navarro DN, Camacho M, Temprano FJ (2008) Alternatives to peat as a carrier for rhizobia inoculants: solid and liquid formulations. Soil Biol Biochem 40:2771–2779
Alberton O, Kaschuk G, Hungria M (2006) Sampling effects on the assessment of genetic diversity of rhizobia associated with soybean and common bean. Soil Biol Biochem 38:1298–1307
Albrecht A, Kandji ST (2003) Carbon sequestration in tropical agroforestry systems. Agric Ecosyst Environ 99:15–27
Alexandre A, Laranjo M, Oliveira S (2006) Natural populations of chickpea rhizobia evaluated by antibiotic resistance profiles and molecular methods. Microb Ecol 51:128–136
Alexandre A., Brígido C., Laranjo M., Rodrigues S., Oliveira S. (2009) Survey of Chickpea Rhizobia Diversity in Portugal Reveals the Predominance of Species Distinct from Mesorhizobium ciceri and Mesorhizobium mediterraneum. Microb Ecol 1–12. doi:10.1007/s00248-009-9536-6.
Almeida EF, Polizel RPH, Gomes LC, Xavier FA, Mendonça ES (1997) Biomassa microbiana em sistemas agroflorestais na zona da mata mineira. Rev Bras Agroecol 2:739–742
Andrade G, Mihara KL, Linderman RG, Bethlenfalvay GJ (1998) Soil aggregation status and rhizobacteria in the mycorrhizosphere. Plant Soil 202:89–96
Andronov EE, Roumyantseva ML, Sagoulenko VV, Simarov BV (1999) Effect of the host plant on the genetic diversity of a natural population of Sinorhizobium meliloti. Russian J Genet 35:1169–1176
Anyango B, Wilson KJ, Beynon JL, Giller KE (1995) Diversity of rhizobia nodulating Phaseolus vulgaris L. in two Kenyan soils with contrasting pHs. App Env Microb 61:4016–4021
Araújo ASF, Monteiro RTR (2006) Microbial biomass and activity in a Brazilian soil plus untreated and composted textile sludge. Chemosphere 64:1043–1046
Araújo ASF, Monteiro RTR, Abarkeli RB (2003) Effect of glyphosate on the microbial activity of two Brazilian soils. Chemosphere 52:799–804
Araújo FB, Hungria M (1999) Nodulação e rendimento de soja co-infectada com Bacillus subtilis e Bradyrhizobium japonicum/Bradyrhizobium elkanii. Pesq Agropec Bras 34:1633–1643
Aysan E, Demir S (2009) Using arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and Rhizobium leguminosarum, Biovar Phaseoli Against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum (Lib.) de bary in the common bean Phaseolus vulgaris L. Plant Pathol J 8:74–78
Bai YM, Zhou XM, Smith DL (2003) Enhanced soybean plant growth resulting from coinoculation of Bacillus strains with Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Crop Sci 43:1774–1781
Bala A, Giller KE (2006) Relationships between rhizobial diversity and host legume nodulation and nitrogen fixation in tropical ecosystems. Nut Cycl Agroecosys 76:319–330
Bala A, Murphy P, Giller KE (2002) Occurrence and genetic diversity of rhizobia nodulating Sesbania sesban in African soils. Soil Biol Biochem 34:1759–1768
Bala A, Murphy P, Giller KE (2003a) Distribution and diversity of rhizobia nodulating agroforestry legumes in soils from three continents in the tropics. Mol Ecol 12:917–929
Bala A, Murphy PJ, Osunde AO, Giller KE (2003b) Nodulation of tree legumes and the ecology of their native rhizobial populations in tropical soils. App Soil Ecol 22:211–223
Balachandar D, Raja P, Kumar K, Sundaram SP (2007) Non-rhizobial nodulation in legumes. Biotech Mol Biol Rev 2:49–57
Barea JM, Azcon R, Azcon-Aguilar C (1992) Vesicular–arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in nitrogen-fixing systems. In: Norris JR, Read DJ, Varma AK (eds) Methods in microbiology. Academic, London, pp 391–416
Barea JM, Azcon R, Azcon-Aguilar C (2002) Mycorrhizosphere interactions to improve plant fitness and soil quality. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek Inter J Gen Mol Microbiol 81:343–351
Barea JM, Azcon R, Azcon-Aguilar C (2004) Mycorrhizal fungi and plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. In: Varma A, Abbott L, Werner D, Hampp R (eds) Plant surface microbiology. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 351–371
Barea JM, Werner D, Azcon-Aguilar C, Azcon R (2005) Interactions of arbuscular mycorrhiza and nitrogen fixing simbiosis in sustainable agriculture. In: Werner D, Newton WE (eds) Agriculture, forestry, ecology and the environment. Kluwer, The Netherlands
Barreto PAB, Gama-Rodrigues EF, Gama-Rodrigues AC, Fontes AG, Polidoro JC, Moço MKS, Machado RCR, Baligar VC (2010) Distribution of oxidizable organic C fractions in soils under cacao agroforestry systems in Southern Bahia, Brazil. Agrofor Sys doi:10.1007/s10457-010-9300-4
Barrett CF, Parke MA (2005) Prevalence of Burkholderia sp. nodule symbionts on four mimosoid legumes from Barro Colorado Island. Panama Syst App Microbiol 28:57–65
Barrett CF, Parke MA (2006) Coexistence of Burkholderia, Cupriavidus, and Rhizobium sp. nodule bacteria on two Mimosa spp. in Costa Rica. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:1198–1206
Bashan Y, Salazar B, Puente ME (2009) Responses of native legume desert trees used for reforestation in the Sonoran Desert to plant growth-promoting microorganisms in screen house. Biol Fert Soils 45:655–662
Belsky AJ, Amundson RG, Duxbury JM (1989) The effects of trees on their physical, chemical and biological environments in a semi-arid savanna in Kenya. J App Ecol 26:1005–1024
Ben RF, Prévost D, Yezza A, Tyagi RD (2007) Agro-industrial waste materials and wastewater sludge for rhizobium inoculant production: a review. Biores Tech 98:3535–3546
Benata H, Mohammed O, Noureddine B, Abdelbasset B, Abdelmoumen H, Muresu R, Squartini A, Idrissi MME (2008) Diversity of bacteria that nodulate Prosopis juliflora in the eastern area of Morocco. Syst App Microbiol 31:378–386
Benhizia Y, Benhizia H, Benguedouar A, Muresu R, Giacomini A, Squartir A (2004) Gamma proteobacteria can nodulate legumes of the genus Hedysarum. Syst Appl Microbiol 27:462–468
Bontemps C, Elliott GN, Simon MF, Reis Júnior FB, Gross E, Lawton RC, Elias NN, Loureiro MF, De Faria SM, Sprent JI, James EK, Young JPW (2009) Burkholderia species are ancient symbionts of legumes. Mol Ecol 19:44–52
Bowen GD, Rovira AD (1991) The rhizosphere. The hidden half of the hidden half. In: Waisel Y, Eshel A, Kafkafi U (eds) Plant roots: the hidden half. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 641–669
Bressiani JA (2001). Seleção sequencial em cana-de-açúcar Agronomy—Plant Breed. Genet. USP, Piracicaba, pp 159
Brockman FJ, Bezdicek DF (1989) Diversity within serogroups of Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viceae in the Palouse region of eastern Washington as indicated by plasmid profiles, intrinsic antibiotic resistance, and topography. App Env Microb 55:109–115
Brookes PC (2001) The soil microbial biomass: concept, measurement and applications in soil ecosystem research. Microbes Environ 16:131–140
Browaldh M (1997) Change in soil mineral nitrogen and respiration following tree harvesting from an agrisilvicultural system in Sweden. Agrofor Sys 35:131–138
Caballero-Mellado J, Martinez-Romero E (1999) Soil fertilization limits the genetic diversity of Rhizobium in bean nodules. Symbiosis 26:111–121
Cacho O (2001) An analysis of externalities in agroforestry systems in the presence of land degradation. Ecol Econ 39:131–143
Cardoso MI, Kuyper TW (2006) Mycorrhizas and tropical soil fertility. Agric Ecosys Environ 116:72–84
Catroux G, Hartmann A, Revellin C (2001) Trends in rhizobial inoculant production and use. Plant Soil 230:21–30
Ceccon E (2008) Production of bioenergy on small farms: a two-year agroforestry experiment using Eucalyptus urophylla intercropped with rice and beans in Minas Gerais, Brazil. New For 35:285–298
Chander K, Goyal S, Nandal DP, Kapoor KK (1998) Soil organic matter, microbial biomass and enzyme activities in a tropical agroforestry system. Biol Fertil Soils 27:168–172
Chebotar VK, Asis CA, Akao S (2001) Production of growthpromoting substances and high colonization ability of rhizobacteria enhance the nitrogen fixation of soybean when inoculated with Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Biol Fert Soils 34:427–432
Chen W, De Faria SM, Straliotto R, Pitard RM, Simões-Araújo JL, Chou J, Chou Y, Barrios E, Prescott AR, Elliott GN, Sprent JI, Young PW, James EK (2005) Proof that Burkholderia strains form effective symbioses with legumes: a study of novel mimosa-nodulating strains from South America. App Environ Microbiol 71:7461–7471
Chen W-M, Laevens S, Lee TM, Coenye T, de Vos P, Mergeay M, Vandamme P (2001) Ralstonia taiwanensis sp. nov., isolated from root nodules of Mimosa species and sputum of a cystic fibrosis patient. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:1729–1735
Chen WM, Moulin L, Bontemps C, Vandamme P, Béna G, Boivin-Masson C (2003) Legume symbiotic nitrogen fixation by β-Proteobacteria is widespread in nature. J Bacteriol 185:7266–7272
Chen WM, Faria SM, Chou JH, James EK, Elliott GN, Sprent JI, Bontemps C, Young JPW, Vandamme P (2008) Burkholderia sabiae sp nov., isolated from root nodules of Mimosa caesalpiniifolia. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:2174–2179
Chesney P (2008) Nitrogen and fine root length dynamics in a tropical agroforestry system with periodically pruned Erythrina poeppigiana. Agrofor Sys 72:149–159
Chikowo R, Mapfumo P, Leffelaar PA, Giller KE (2006) Integrating legumes to improve N cycling on smallholder farms in sub-humid Zimbabwe: resource quality, biophysical and environmental limitations. Nut Cycl Agroecosys 76:219–231
Collins MT, Thies JE, Abbott LK (2002) Diversity and symbiotic effectiveness of Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii isolates from pasture soils in south-western Australia. Austr J Soil Res 40:1319–1329
Daba S, Haile M (2000) Effects of rhizobial inoculant and nitrogen fertilizer on yield and nodulation of common bean. J Pl Nut 23:581–591
Dashti N, Zhang F, Hynes R, Smith DL (1998) Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria accelerate nodulation and increase nitrogen fixation activity by field grown soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.] under short season conditions. Plant Soil 2:205–213
Date RA (1997) The contribution of R&D on root-nodule bacteria to future cultivars of tropical forage legumes. Trop Grass 31:350–354
Date RA (2000) Inoculated legumes in cropping systems of the tropics. Field Crops Res 65:123–136
Daudin D, Sierra J (2008) Spatial and temporal variation of below-ground N transfer from a leguminous tree to an associated grass in an agroforestry system. Agric Ecosys Environ 126:275–280
De Boer W, Folman LB, Summerbell RC, Boddy L (2005) Living in a fungal world: impact of fungi on soil bacterial niche development. FEMS Microbiol Rev 29:795–811
Deaker R, Roughley RJ, Kennedy IR (2004) Legume seed inoculation technology—a review. Soil Biol Biochem 36:1275–1288
Demir S, Akkopru A (2007) Using of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) for biocontrol of soil-borne fungal plant pathogens. In: Chincholkar SB, Mukerji KG (eds) Biological control of plant diseases. Haworth Press, USA, pp 17–37
Diabate M, Munive A, Faria SM, Ba A, Dreyfus B, Galiana A (2005) Occurrence of nodulation in unexplored leguminous trees native to the West African tropical rainforest and inoculation response of native species useful in reforestation. New Phytol 166:231–239
Dick RP (1997) Soil enzymes activities as integrative indicator of soil health. In: Pankhurst C, Doube BM, Gupta VVSR (eds) Biological indicators of soil health. CAB International, Cambridge, pp 121–156
Diouf D, Samba-Mbaye R, Lesueur D, Ba AT, Dreyfus B, De Lajudie P, Neyra M (2007) Genetic diversity of Acacia seyal Del. rhizobial populations indigenous to senegalese soils in relation to salinity and pH of the sampling sites. Micro Ecol 54:553–566
Dobbelaere S, Vanderleyden J, Okon Y (2003) Plant growth promoting effects of diazotrophs in the rhizosphere. Crit Rev Plant Sci 22:107–149
Doignon-Bourcier F, Sy A, Willems A, Torck U, Dreyfus B, Gillis M, De Lajudie P (1999) Diversity of Bradyrhizobia from 27 tropical Leguminosae species native of Senegal. Syst App Microbiol 22:647–661
Doyle JJ, Doyle J (1998) Phylogenetic perspectives on nodulation: evolving views of plants and symbiotic bacteria. Trends Plant Sci 3:473–478
Duodu S, Nsiah EK, Bhuvaneswari TV, Svenning MM (2006) Genetic diversity of a natural population of Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar trifolii analysed from field nodules and by a plant infection technique. Soil Biol Biochem 38:1162–1165
Duodu S, Carlsson G, Huss-Danell K, Svenning MM (2007) Large genotypic variation but small variation in N2 fixation among rhizobia nodulating red clover in soils of northern Scandinavia. J App Microbiol 102:1625–1635
Elliott GN, Chou J-H, Chen W-M, Bloemberg GV, Bontemps C, Martinez-Romero E, Velazquez E, Young JPW, Sprent JI, James EK (2009) Burkholderia spp. are the most competitive symbionts of Mimosa, particularly under N-limited conditions. Environ Microbiol 11:762–778
Fagerli IL, Svenning MM (2005) Arctic and subarctic soil populations of Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar trifolii nodulating three different clover species: characterisation by diversity at chromosomal and symbiosis loci. Pl Soil 275:371–381
FAO (2005) The importance of soil organic matter. Key to drought-resistant soil and sustained food and production. Rome, p 78
Faria S.M. (1997) Obtenção de Estirpes de Rizóbio Eficientes na Fixação Biológica de Nitrogênio para Espécies Florestais. (Aproximação 1997). Embrapa Agrobiologia, Serop‚dica, p 4
Faria SM (2000) Obtenção de estirpes de rizóbio eficientes na fixação de nitrogênio para espécies florestais (aproximação 2000). Embrapa Agrobiologia, Seropédica, p 10
Faria SM (2002) Obtenção de estirpes de rizóbio eficientes na fixação de nitrogênio para espécies florestais (aproximação 2001). Embrapa Agrobiologia, Seropédica, p 16
Faria SM, Lima HC (1998) Additional studies of the nodulation status of legume species in Brazil. Plant Soil 200:185–192
Faria SM, Franco AA (2002) Identificação de bactérias eficientes na fixação biológica de nitrogênio para espécies leguminosas arbóreas. EMBRAPA-Agrobiologia, Seropédica, p 16
Faria SM, Moreira VCG, Franco AA (1984) Seleção de estirpes de Rhizobium para espécies leguminosas florestais. Pesq Agropec Bras 19:175–179
Faria, S.M. Ocurrence and rhizobial selection for legume trees adapted to acid soils (1995). In: Evans DO, Szott T (eds) Nitrogen fixing trees for acid soil. Nitrogen Fixing Tree Association. Morrilton, USA, pp 295–300
Ferguson BJ, Mathesius U (2003) Signaling interactions during nodule development. J Plant Growth Regul 22:47–72
Fernandes Júnior PI, Rohr TG, Oliveira PJ, Xavier GR, Rumjanek NG (2009) Polymers as carriers for rhizobial inoculant formulations. Pesq Agropec Bras 44:184–1190
Figueiredo MVB, Martinez CR, Burity HA, Chanway CP (2008) Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria for improving nodulation and nitrogen fixation in the common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). World J. Microbiol Biotechnol 24:1187–1193
Fisher RF (1995) Amelioration of degraded rain forest soils by plantations of native trees. Soil Sci Soc Am J 59:544–549
Fontes SJ, Barrios E, Six J (2010) Earthworms, soil fertility and aggregate-associated soil organic matter dynamics in the Quesungual agroforestry system. Geoderma 155:320–328
Freitas ADS, Sampaio EVSB, Santos CERS, Fernandes AR (2010) Biological nitrogen fixation in tree legumes of the Brazilian semi-arid caatinga. J Arid Environ 74:344–349
Frey-Klett P, Garbaye J, Tarkka M (2007) The mycorrhiza helper bacteria revisited. New Phytol 176:22–36
Galli-Terasawa LV, Glienke-Blanco C, Hungria M (2003) Diversity of a soybean rhizobial population adapted to a Cerrados soil. World J Microb Biotech 19:933–939
Garbaye J (1994) Helper bacteria: a new dimension to the mycorrhizal symbiosis. New Phytol 128:197–210
García-Fraile P, Velázquez E, Mateos PF, Martínez-Molina E, Rivas R (2008) Cohnella phaseoli sp. nov., isolated from root nodules of Phaseolus coccineus in Spain, and emended description of the genus Cohnella. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:1855–1859
Gomez E, Bisaro V, Conti M (2000) Potential C-source utilization patterns of bacterial communities as influenced by clearing and land use in a vertic soil of Argentina. Appl Soil Ecol 15:273–281
Grange L, Hungria M (2004) Genetic diversity of indigenous common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) rhizobia in two Brazilian ecosystems. Soil Biol Biochem 36:1389–1398
Handley BA, Hedges AJ, Beringer JE (1998) Importance of host plants for detecting the population diversity of Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar Viciae in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 30:241–249
Haney RL, Senseman SA, Krutz LJ, Hons FM (2003) Soil carbon and nitrogen mineralization as affected by atrazine and glyphosate. Biol Fert Soils 35:35–40
Heuvelop J, Fassbender HW, Alpizar L, Enriquez G, Falster H (1988) Modelling agroforestry systems of cacao (Theobroma cacao) in Costa Rica. II. Cacao and wood production, litter production and decomposition. Agrofor Syst 6:37–48
Hirsch AM, Lum MR, Downie JA (2001) What makes the rhizobia-legume symbiosis so special? Plant Physiol 127:1484–1492
Howieson J, Ballard R (2004) Optimising the legume symbiosis in stressful and competitive environments within southern Australia—some contemporary thoughts. Soil Biol Biochem 36:1261–1273
Hubbell DH, Kidder G (2003) Biological nitrogen fixation. SL-16, soil and water science department, Florida cooperative extension service, institute of food and agricultural sciences. University of Florida, USA, pp 1–4
Hungria M, Vargas MAT (2000) Environmental factors affecting N2 fixation in grain legumes in the tropics, with an emphasis on Brazil. Field Crops Res 65:151–164
Jaftha JB, Strijdom BW, Steyn PL (2002) Characterization of pigmented methylotrophic bacteria which nodulate Lotononis bainesii. Syst Appl Microbiol 25:440–449
Jalonen R, Nygren P, Sierra J (2009) Transfer of nitrogen from a tropical legume tree to an associated fodder grass via root exudation and common mycelial networks. Plant Cell Environ 32:1366–1376
Jenkinson DS, Ladd JN (1981) Microbial biomass in soil: measurement and turnover. In: Paul EA, Ladd JN (eds) Soil biochemistry. Dekker, New York, pp 415–471
Jesus EC, Moreira FMS, Florentino LA, Rodrigues MID, Oliveira MS (2005) Diversidade de bactérias que nodulam siratro em três sistemas de uso da terra da Amazônia Ocidental. Pesq Agropec Bras 40:769–776
Kaur B, Gupta SR, Singh G (2000) Soil carbon, microbial activity and nitrogen availability in agroforestry systems on moderately alkaline soils in northern India. App Soil Ecol 15:283–294
Kirby KR, Potvin C (2007) Variation in carbon storage among tree species: implications for the management of a small-scale carbon sink project. For Ecol Manage 246:208–221
Kuklinsky-Sobral J, Araujo WL, Mendes R, Geraldi IO, Pizzirani-Kleiner AA, Azevedo JL (2004) Isolation and characterization of soybean-associated bacteria and their potential for plant growth promotion. Environ Microbiol 6:1244–1251
Langer H, Nandasena KG, Howieson JG, Jorquera M, Borie F (2008) Genetic diversity of Sinorhizobium meliloti associated with alfalfa in Chilean volcanic soils and their symbiotic effectiveness under acidic conditions. World J Microb Biot 24:301–308
Law IJ, Botha WF, Majaule UC, Phalane FL (2007) Symbiotic and genomic diversity of ‘cowpea’ bradyrhizobia from soils in Botswana and South Africa. Biol Fert Soils 43:653–663
Lesueur D, Ingleby K, Odee D, Chamberlain J, Wilson J, Manga TT, Sarrailh JM, Pottinger A (2001) Improvement of forage production in Calliandra calothyrsus: methodology for the identification of an effective inoculum containing Rhizobium strains and arbuscular mycorrhizal isolates. J Biotech 91:269–282
Loveall ST, Sullivan WC (2006) Environmental benefits of conservation buffers in the United States: evidence, promise, and open questions. Agric Ecosyst Environ 112:249–260
Lowrance R, Dabney S, Schultz R (2002) Improving water and soil quality with conservation buffers. J Soil Water Conserv 57:36–43
Lucas-Garcia JA, Probanza A, Ramos B, Colon-Flores JJ, Gutierrez-Mañero FJ (2004) Effects of plant growth promoting rhizobateria (PGPRs) on the biological nitrogen fixation, nodulation and growth of Lupinus albus I. cv. Multolupa. Eng Life Sci 4:71–77
Ma W, Penrose DM, Glick BR (2002) Strategies used by rhizobia to lower plant ethylene levels and increase nodulation. Can J Microbiol 48:947–954
Macdicken KG, Vergara NT (1990) Agroforestry: classification and management. Wiley, New York, p 382
Makatiani ET, Odee DW (2007) Response of Sesbania sesban (L.) Merr. to rhizobial inoculation in an N-deficient soil containing low numbers of effective indigenous rhizobia. Agrofor Sys 70:211–216
Manassila M, Nuntagij A, Kotepong S, Boonkerd N, Teaumroong N (2007) Characterization and monitoring of selected rhizobial strains isolated from tree legumes in Thailand. African J Biotech 6:1393–1402
Manley R, Feller C, Swift MJ (2007) Historical evolution of soil organic matter concepts and their relationships with the fertility and sustainability of cropping systems. Agric Ecosys Environ 119:217–233
Martinez-Romero E, Segovia L, Mercante FM, Franco AA, Graham P, Pardo MA (1991) Rhizobium tropici, a novel species nodulating Phaseolus vulgaris L. beans and Leucaena sp. trees. Int J Sys Bacteriol 41:417–426
Martins LMV, Xavier GR, Rangel FW, Ribeiro JRA, Neves MCP, Morgado LB, Rumjanek NG (2003) Contribution of biological nitrogen fixation to cowpea: a strategy for improving grain yield in the semi-arid region of Brazil. Biol Fert Soils 38:333–339
Masson-Boivin C, Giraud E, Perret X, Batut J (2009) Establishing nitrogen-fixing symbiosis with legumes: how many Rhizobium recipes? Trends Microbiol 17:458–466
Mayak S, Tirosh T, Glick BR (1999) Effect of wild type and mutant plant growth promoting rhizobacteriaon the rooting of mung bean cuttings. J Plant Growth Regul 18:49–53
Mendonça ES, Leite LFC, Ferreira Neto PS (2001) Cultivo do café em sistema agroflorestal: uma opção para recuperação de solos degradados. Rev Arvore 25:375–383
Miralles I, Ortega R, Alemandros G, SancheZ-Maranon M, Soriano M (2009) Soil quality and organic carbon ratios in mountain agroecosystems of South-east Spain. Geoderma 150:32–40
Mnasri B, Mrabet M, Laguerre G, Aouani ME, Mhamdi R (2007) Salt-tolerant rhizobia isolated from a Tunisian oasis that are highly effective for symbiotic N 2 -fixation with Phaseolus vulgaris constitute a novel biovar (bv. mediterranense) of Sinorhizobium meliloti. Arch Microbiol 187:79–85
Moonen AC, Bàrberi P (2008) Functional biodiversity: an agroecosystem approach. Agric Ecosys Environ 127:7–21
Mostasso L, Mostasso FL, Dias BG, Vargas MAT, Hungria M (2002) Selection of bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) rhizobial strains for the Brazilian Cerrados. Field Crops Res 73:121–132
Moulin L, Munive A, Dreyfus B, Boivin-Masson C (2001) Nodulation of legumes by members of the β-subclass of Proteobacteria. Nature 411:948–950
Moulin L, Chen W-M, Béna G, Dreyfus B, Boivin-Masson C (2002) Rhizobia: the family is expanding. In: Finan T, O’Brian M, Layzell D, Vessey K, Newton W (eds) Nitrogen fixation: global perspectives. CAB International, Wallingford, pp 61–65
Mungai NW, Motavalli PP, Kremer RJ, Nelson KA (2005) Spatial variation of soil enzyme activities and microbial functional diversity in temperate alley cropping systems. Biol Fertil Soils 42:129–136
Muresu R, Polone E, Sulas L, Baldan B, Tondello A, Delogu G, Cappuccinelli P, Alberghini S, Benhizia Y, Benhizia H, Benguedouar A, Mori B, Calamassi R, Dazzo FB, Squartini A (2008) Coexistence of predominantly nonculturable rhizobia with diverse, endophytic bacterial taxa within nodules of wild legumes. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 63:383–400
Myers RT, Zak DR, White DC, Peacock A (2001) Landscape-level patterns of microbial community composition and substrate use in upland forest ecosystems. Soil Sci Soc Am J 65:359–367
Nair PKR, Gordone AM, Mosquera-Losadac, MR (2008) Agroforestry. Elsevier, Netherland, pp. 101–110
Nair PKR, Kumar BM, Nair VD (2009) Agroforestry as a strategy for carbon sequestration. J Pl Nutrit Soil Sci 172:10–23
Nygren P, Leblanc HA (2009) Natural abundance of 15N in two cacao plantations with legume and non-legume shade trees. Agrofor Sys 76:303–315
Odee DW, Haukka K, McInroy SG, Sprent JI, Sutherland JM, Young JPW (2002) Genetic and symbiotic characterization of rhizobia isolated from tree and herbaceous legumes grown in soils from ecologically diverse sites in Kenya. Soil Biol Biochem 34:801–811
Okasaki S, Sugawara M, Yuhashi KI, Minamisawa K (2007) Rhizobitoxine-induced chlorosis occurs in coincidence with methionine deficiency in soybeans. Ann Botany 100:55–59
Palma JHN, Graves AR, Bunce RGH, Burgess PJ, Filippi R, Keesman K, van Keulen H, Liagre F, Mayus M, Moreno G, Reisner Y, Herzog F (2007) Modeling environmental benefits of silvoarable agroforestry in Europe. Agric Ecosyst Environ 119:320–334
Porcel R, Barea JM, Ruiz-Lozano JM (2003) Antioxidant activities in mycorrhizal soybean plants under drought stress and their possible relationship to the process of nodule senescence. New Phytol 157:135–143
Powlson DS, Brookes PC, Christensen BT (1987) Measurement of soil microbial biomass provides an early indication of changes in total organic matter due to straw incorporation. Soil Biol Biochem 19:159–164
Pueppke SG, Broughton WJ (1999) Rhizobium sp. strain NGR234 and R. fredii USDA257 share exceptionally broad, nested host ranges. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 12:293–318
Rao DLN, Pathak H (1996) Ameliorative influence of organic matter on biological activity of salt affected soils. Arid Soil Res Rehab 10:311–319
Remans R, Croonenborghs A, Gutierrez RT, Michiels J, Vanderleyden J (2007) Effects of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria on nodulation of Phaseolus vulgaris [L.] are dependent on plant P nutrition. Euro J Plant Pathol 119:341–351
Rhamani HA, Saleh-Rastin N, Khavazi K, Asgharzadeh A, Fewer D, Kiani S, Lindstrm K (2009) Selection of thermotolerant bradyrhizobial strains for nodulation of soybean (Glycine max L.) in semi-arid regions of Iran. World J Microb Biotech 25:591–600
Rivas R, Velázquez E, Willems A, Vizcaíno N, Subba-Rao NS, Mateos PF, Gillis M, Dazzo FB, Martínez-Molina E (2002) A new species of Devosia that forms a unique nitrogen-fixing rootnodule symbiosis with the aquatic legume Neptunia natans. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:5217–5222
Roshetko JM, Lasco RD, Delos Angeles MD (2007) Smallholder agroforestry systems for carbon storage. Mitigation Adapt Strategies Global Change 12:219–242
Ruiz-Díez B, Fajardo S, Puertas-Mejía MA, De Felipe MDR, Fernández-Pascual M (2009) Stress tolerance, genetic analysis and symbiotic properties of root-nodulating bacteria isolated from Mediterranean leguminous shrubs in Central Spain. Arch Microbiol 191:35–46
Ruiz-Lozano JM, Collados C, Barea JM, Azcon R (2001) Arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis can alleviate droughtinduced nodule senescence in soybean plants. New Phytol 151:493–502
Salati E, Santos AA, Klabin I (2006) Relevant environmental issues. Estudos Avançados 20:107–127
Saravana-Kumar D, Samiyappan R (2007) ACC deaminase from Pseudomonas fluorescens mediated saline resistance in groundnut (Arachis hypogea) plants. J Appl Microbial 102:1283–1292
Scheublin TR, Van der Heijden MGA (2006) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi colonize nonfixing root nodules of several legume species. New Phytol 172:732–738
Serraj R (2004) Symbiotic nitrogen fixation: prospects for enhanced application in tropical agriculture. IBH, New Delhi, p 367
Sharrow SH, Ismail S (2004) Carbon and nitrogen storage in agroforests, tree plantations, and pastures in western Oregon, USA. Agroforest Syst 60:123–130
Silva MF, Oliveira PJ, Xavier GR, Rumjanek NG, Reis VM (2009) Inoculantes formulados com polímeros e bactérias endofíticas para a cultura da cana-de-açúcar. Pesq Agropec Bras 44:1437–1443
Silva VN, Silva LESF, Figueiredo MVB (2006) Atuação de rizóbios com rizobactérias promotora de crescimento em plantas na cultura do caupi (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp). Acta Sci Agron 28:407–412
Silva VN, Silva LESF, Figueiredo MVB, Carvalho FG, Silva MLRB, Silva AJN (2007) Caracterização e seleção de populações nativas de rizóbios de solo da região semi-árida de Pernambuco. Pesq Agropec Trop 37:16–21
Sørensen J, Sessitsch A (2007) Plant-associated bacterial-lifestyle and molecular interactions. In: Van Elsas JD, Jansson JK, Trevors JT (eds) Modern soil microbiology. CRC, New York, pp 221–236
Sprent JI (2001) Nodulation in legumes. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, London
Steenhoudt O, Vanderleyden J (2000) Azospirillum, a free-living nitrogen-fixing bacterium closely associated with grasses: genetic, biochemical and ecological aspects. FEMS Microbiol Rev 24:487–506
Sun Y, Cheng Z, Glick BR (2009) The presence of a 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate (ACC) deaminase deletion mutation alters the physiology of the endophytic plant growth-promoting bacterium Burkholderia phytofirmans PsJN. FEMS Microbiol Let 296:131–136
Sy A, Giraud E, Jourand P, Garcia N, Willems A, de Lajudie P, Prin Y, Neyra M, Gillis M, Boivin-Masson C, Dreyfus B (2001) Methylotrophic Methylobacterium bacteria nodulate and fix nitrogen in symbiosis with legumes. J Bacteriol 183:214–220
Sziderics AH, Rasche F, Trognitz F, Sessitsch A, Wilhelm E (2007) Bacterial endophytes contribute to abiotic stress adaptation in pepper plants (Capsicum annuum L.). Can J Microbiol 53:1195–1202
Tangjang S, Arunachalam K, Arunachalam A, Shukla AK (2009) Microbial population dynamics of soil under traditional agroforestry systems in Northeast India. Res J Soil Biol 1:1–7
Tilak KVBR, Rauganayaki N, Manoharachari C (2006) Synergistic effects of plant-growth promoting rhizobacteria and Rhizobium on nodulation and nitrogen fixation by pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan). Europ J Soil Sci 57:67–71
Tornquist CG, Hons FM, Feagley SE, Haggar J (1999) Agroforestry system effects on soil characteristics of the Sarapiquí region of Costa Rica. Agric Ecosys Environ 73:19–28
Udawatta RP, Kremer RJ, Adamson BW, Anderson SH (2008) Variations in soil aggregate stability and enzyme activities in a temperate agroforestry practice. App Soil Ecol 39:153–160
Van Berkum P, Eardly BD (2002) The aquatic budding bacterium Blastobacter denitrificans is a nitrogen-fixing symbiont of Aeschynomene indica. In: Finan TM, O’Brian MR, Layzell DB, Vessey JK, Newton WE (eds) Nitrogen fixation: global perspectives. CAB International, New York, p 520
Vandamme P, Goris J, Chen WM, Vos P, Willems A (2002) Burkholderia tuberum sp. nov. and Burkholderia phymatum sp. nov., nodulate the roots of tropical legumes. Syst App Microbiol 25:507–512
Vessey JK, Buss TJ (2002) Bacillus cereus UW85 inoculation effects on growth, nodulation, and N accumulation in grain legumes. Controlled-environment studies. Can J Plant Sci 82:282–290
Vivas A, Marulanda A, Ruiz-Lozano JM, Barea JM, Azcon R (2003a) Influence of a Bacillus sp. on physiological activities of two arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and on plant responses to PEG-induced drought stress. Mycorrhiza 13:249–256
Vivas A, Azcon R, Biro B, Barea JM, Ruiz-Lozano JM (2003b) Influence of bacterial strains isolated from lead-polluted soil and their interactions with arbuscular mycorrhizae on the growth of Trifolium pretense L. under lead toxicity. Can J Microbiol 49:577–588
Watanabe K, Hamamura N (2003) Molecular and physiological approaches to understanding the ecology of pollutant degradation. App Soil Ecol 31:120–135
Willems A (2006) The taxonomy of rhizobia: an overview. Plant Soil 287:3–14
Wolde-Meskel E, Terefework Z, Lindström K, Frostegard A (2004) Rhizobia nodulating African Acacia spp. and Sesbania sesban trees in southern Ethiopian soils are metabolically and genomically diverse. Soil Biol Biochem 36:2013–2025
Xavier GR, Correia MEF, Aquino AM, Zilli JÉ, Rumjanek NG (2010) The structural and functional biodiversity of soil: an interdisciplinary vision for conservation agriculture in Brazil. In: Dion P (ed) Soil biol agric trop. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 65–80
Yadav RS, Yadav BL, Chhipa BR, Dhyani SK, Ram M (2010) Soil biological properties under different tree based traditional agroforestry systems in a semi-arid region of Rajasthan, India. Agroforest Syst 81:195–202
Yan F, McBratney AB, Copeland L (2000) Functional substrate biodiversity of cultivated and uncultivated a horizons of vertisols in NW New South Wales. Geoderma 96:321–343
Yates RJ, Howieson JG, Real D, Reeve WG, Vivas-Marfisi A, O’Hara GW (2005a) Evidence of selection for effective nodulation in the Trifolium spp. symbiosis with Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar trifolii. Aust J Experim Agric 45:189–198
Yates RJ, Howieson JG, Nandasena KG, O’Hara GW (2005b) Root-nodule bacteria from indigenous legumes in the north-west of Western Australia and their interaction with exotic legumes. Soil Biol Biochem 36:1319–1329
Zafar-ul-Hye M (2008) Improving nodulation in lentil through co-inoculation with rhizobia and ACC-deaminase containing plant growth promoting rhizobacteria, PhD Thesis, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, Pakistan, p 198
Zhang F, Dashti N, Hynes RK, Smith DL (1996) Plant-growth promoting rhizobacteria and soybean (Glycine max [L.] Merr.) nodulation and nitrogen fixation at suboptimal root zone temperatures. Ann Botany 77:453–459
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Araujo, A.S.F., Leite, L.F.C., Iwata, B.F. et al. Microbiological process in agroforestry systems. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 32, 215–226 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13593-011-0026-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13593-011-0026-0