Abstract
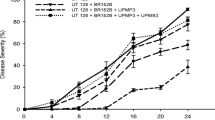
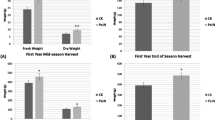
Brown patch disease, caused by Rhizoctonia solani, is one of the most serious diseases of turf grasses including bentgrass (Agrostis palustris). This disease is usually controlled by different formulations of synthetic fungicides. In this study, two pot trials were carried out to investigate the biocontrol potential of the antagonistic strain Paenibacillus ehimensis KWN38 against R. solani, and to examine the growth response of bentgrass to the inoculated strain. Bentgrass mats with root system in plastic boxes were treated with winter grass medium (W), W plus P. ehimensis KWN38 inoculation (WP), summer grass medium (S), S plus P. ehimensis KWN38 inoculation (SP), fertilizer (F), and F plus fungicide (FF) once every 10 days for three months. After the first month, all pots were infected with R. solani. Sixty days after infection, the leaves of bentgrass in all control treatments (W, S, and F) showed high levels of infection, with significantly higher values than those of WP, SP and FF. The leaf fresh and dry weights of bentgrass innoculated with P. ehimensis KWN38 were all greater than the control treatments W, S and F. Similarly, both fresh and dry weights of the roots and the chlorophyll contents of bentgrass in WP and SP were significantly higher than those of W, S, F and FF. Moreover, bentgrass innoculated with P. ehimensis KWN38 grew faster and showed greater growth performance as compared to the other treatments in the second pot trial with infected bentgrass. A butanol extract of the P. ehinmensis KWN38 culture supernatant significantly reduced the number of fungal colonies initiating from sclerotial fragments on potato dextrose agar. The growth of monilioid cells of R. solani was delayed by treatment with P. ehimensis KWN38 culture broth, while they elongated earlier into thinner structures in the control treatment. In conclusion, the antagonist P. ehimensis KWN38 can be considered as an effective biocontrol agent against brown patch disease, as well as a promising plant growth promoting bacteria of bentgrass.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Acuña, J.J., M.A. Jorquera, O.A. Martínez, D. Menezes-Blackburn, M.T. Fernández, P. Marschner, R. Greiner, and M.L. Mora. 2011. Indole acetic acid and phytase activity produced by rhizosphere bacilli as affected by pH and metals. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 11:1–12.
Adams, G.C. 1988. Thanatephorus cucumeris (Rhizoctonia solani) a species complex of wide host range, p 535–552. In: G.S. Sidhu (ed.) Advances in plant pathology vol. 6. Academic Press, New York, NY, USA.
Aliferis, K.A. and S. Jabaji. 2010. Metabolite composition and bioactivity of Rhizoctonia solani sclerotial exudates. J. Agric. Food Chem. 58:7604–7615.
Aoyagi, T., K. Kageyama, and M. Hyakumachi. 1998. Characterization and survival of Rhizoctonia solani AG-2-2LP associated with large patch disease of zoysiagrass. Plant Dis. 82:857–863.
Burpee, L.L. and B. Martin. 1992. Biology of Rhizoctonia species associated with turfgrasses. Plant Dis. 76:112–117.
Chai, B., S.B. Maqbool, R.K. Hajela, D. Green, J.M. Vargas Jr, D. Warkentin, R. Sabzikar, and M.B. Sticklen. 2002. Cloning of a chitinase-like cDNA (hs2), its transfer to creeping bentgrass (Agrostis palustris Huds.) and development of brown patch (Rhizoctonia solani) disease resistant transgenic lines. Plant Sci. 163:183–193.
Chang, T. and Y.S. Lee. 2013. Occurrence of brown patch on Kentucky Bluegrass caused by Rhizoctonia solani AG-1 IB. Weed Turf Sci. 2:88–94.
Coelho, M.R.R., I. von der Weid, V. Zahner, and L. Seldin. 2003. Characterization of nitrogen-fixing Paenibacillus species by polymerase chain reaction–restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of part of genes encoding 16S rRNA and 23S rRNA and by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis. FEMS Microbial. Lett. 222:243–250.
Couch, H.B. 1985. Turfgrass (several cultivated spp.). Plant Dis. 69:672–675.
Couch, H.B. 1995. Diseases of turfgrasses caused by fungi, p. 21–199. In: Diseases of turfgrass, 3rd ed. Krieger Publishing Co., Malabar, FL.
Cuppels, D.A., J. Higham, and J.A. Traquair. 2013. Efficacy of selected streptomycetes and a streptomycete + pseudomonad combination in the management of selected bacterial and fungal diseases of field tomatoes. Biol. Control 67:361–372.
Droby, S. 2006. Improving quality and safety of fresh fruit and vegetables after harvest by the use of biocontrol agents and natural materials. Acta Hortic. 709:45–51.
Giesler, L.J. and G.Y. Yuen. 1998. Evaluation of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia strain C3 for biocontrol of brown patch disease. Crop Prot. 17:509–513.
Guo, T. and M. Liao. 2014. Suppression of Rhizoctonia solani and induction of host plant resistance by Paenibacillus kribbensis PS04 towards controlling of rice sheath blight. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 12:116–121.
Haygood, R.A. and J.F. Walter. 1991. Biocontrol of brown patch of centipedegrass with Gliocladium virens in a growth chamber. Biol. Cult. Tests Cont. Plant Dis. 5:86.
Hsiang, T. and J.D. Dean. 2001. DNA sequencing for anastomosis grouping of rhizoctonia solani isolates from Poa annua. Int. Turfgrass Soc. Res. J. 9:674–678.
Ippolito, A. and F. Nigro. 2000. Impact of preharvest application of biological control agents on postharvest diseases of fresh fruits and vegetables. Crop Prot. 19:715–723.
Khan, N., A. Mishra, and C.S. Nautiyal. 2012. Paenibacillus lentimorbus B-30488r controls early blight disease in tomato by inducing host resistance associated gene expression and inhibiting Alternaria solani. Biol. Control 62:65–74.
Khan, Z., S.G. Kim, Y.H. Jeon, H.U. Khan, S.H. Son, and Y.H. Kim. 2008. A plant growth promoting rhizobacterium, Paenibacillus polymyxa strain GBR-1, suppresses root-knot nematode. Biores. Technol. 99:3016–3023.
Knievel, D.P. 1973. Procedures for estimating ratio of live or dead root dry matter in root core samples. Crop Sci. 13:124–126.
Kuckenberg, J., I. Tartachnyk, and G. Noga. 2009. Detection and differentiation of nitrogen-deficiency, powdery mildew and leaf rust at wheat leaf and canopy level by laser-induced chlorophyll fluorescence. Biosyst. Eng. 103:121–128.
Larsen, J., P. Cornejo, and J.M. Barea. 2009. Interactions between the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Glomus intraradices and the plant growth promoting rhizobacteria Paenibacillus polymyxa and P. macerans in the mycorrhizosphere of Cucumis sativus. Soil Biol. Biochem. 41:286–292.
Lo, C.T., E.B. Nelson, and G.E. Harman. 1996. Biological control of turfgrass diseases with a rhizosphere competent strain of Trichoderma huzianum. Plant Dis. 80:736–741.
Martin, S.B. and L.T. Lucas. 1984. Characterization and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia spp. and binucleate Rhizoctonia-like fungi from turfgrasses in North Carolina. Phytopathology 74:170–175.
Nadeem, M., A. Younis, A. Riaz, and M. Hameed. 2012. Growth response of some cultivars of Bermuda grass (Cyanodon dactylon L.) to salt stress. Pak. J. Bot. 44:1347–1350.
Naing, K.W., M. Anees, S.J. Kim, Y. Nam, Y.C. Kim, and K.Y. Kim. 2014a. Characterization of antifungal activity of Paenibacillus ehimensis KWN38 against soilborne phytopathgenic fungi belonging to various taxonomic groups. Ann. Microbiol. 64:55–63.
Naing, K.W., M. Anees, X.H. Nguyen, Y.S. Lee, S.W. Jeon, S.J. Kim, M.H. Kim, and K.Y. Kim. 2014b. Biocontrol of late blight disease (Phytophthora capsici) of pepper and the plant growth promotion by Paenibacillus ehimensis KWN38. J. Phytopathol. 162:367–376.
Raza, W., K. Makeen, Y. Wang, Y. Xu, and S. Qirong. 2011. Optimization, purification, characterization and antioxidant activity of an extracellular polysaccharide produced by Paenibacillus polymyxa SQR-21. Biores. Technol. 102:6095–6103.
Reuter, H.M., G.L. Schumann, M.L. Matheny, and R.T. Hatch. 1991. Suppression of dollar spot (Sclerotinia homoeocarpa) and brown patch (Rhizoctonia solani) on creeping bentgrass by an isolate of Streptomyces. Phytopathology 81:124.
SAS Institute Inc. 2008. SAS/STAT 9.2. User’s Guide. Cary, North Carolina, USA.
Shu, C., S. Sun, J. Chen, and E. Zhou. 2014. Comparison of different methods for total RNA extraction from sclerotia of Rhizoctonia solani. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 17:50–54.
Sneh, B., S. Jabaji-Hare, S. Neate, and G. Dijst. 1996. Rhizoctonia species: Taxonomy, molecular biology, ecology, pathology, and control. Kluwer Academic Publisher. Dordrecht. p. 578.
Sutker, E.M. and L.T. Lucus. 1987. Biocontrol of Rhizoctonia solani in tall fescue turfgrass. Phytopathology 77:1721.
Thompson, D.C., B.B. Clarke, and D.Y. Kobayashi. 1996. Evaluation of bacterial antagonists for reduction of summer patch symptoms in Kentucky bluegrass. Plant Dis. 80:856–862.
Timmusk, A., B. Nicander, U. Granhall, and E. Tillberg. 1999. Cytokinin production by Paenibacillus polymyxa. Soil Biol. Biochem. 31:1847–1852.
Vollmann, J., T. Sato, H. Walter, P. Schweiger, and H. Wagentrist. 2011. Soybean di-nitrogen fixation affecting photosynthesis and seed quality characters, p. 496–502. In: Soil, Plant and Food Interactions, Mendel University in Brno, Brno, Czech Republic.
Yang, D., N. Wang, X. Yan, J. Shi, M. Zhang, Z. Wang, and H. Yuan 2014. Microencapsulation of seed-coating tebuconazole and its effects on physiology and biochemistry of maize seedlings. Colloids Surf. B. Biointerfaces 114:241–246.
Younis, A., A. Riaz, S. Ikram, T. Nawaz, M. Hameed, S. Fatima, R. Batool, and F. Ahmad. 2013. Salinity-induced structural and functional changes in three cultivars of Alternanthra bettzikiana (Regel) G. Nicholson. Turk. J. Agric. For. 37:674–687.
Yuen, G.Y., M.L. Craig, and L.J. Giesler. 1994. Biological control of Rhizoctonia solani on tall fescue using fungal antagonists. Plant Dis. 78:118–123.
Zachow, C., R. Grosch, and G. Berg. 2011. Impact of biotic and a-biotic parameters on structure and function of microbial communities living on sclerotia of the soil-borne pathogenic fungus Rhizoctonia solani. Appl. Soil Ecol. 48:193–200.
Zhang, J. and M.B. Kirkham. 1994. Drought-stress-induced changes in activities of superoxide dismutase, catalase, and peroxidase in wheat species. Plant. Cell. Physiol. 35:785–791.
Zhang, Z. and G.Y. Yuen. 1997. Chitinolytic properties of Stenotrophomonus maltophiliu strain C3, an antagonist of fungal turfgrass pathogens. Phytopathology 87:109.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeon, S.W., Naing, K.W., Lee, Y.S. et al. Promotion of growth and biocontrol of brown patch disease by inoculation of Paenibacillus ehimensis KWN38 in bentgrass. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 56, 263–271 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-015-0109-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-015-0109-y