Abstract
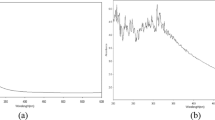
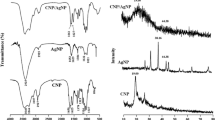
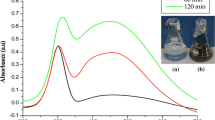
The present study deals with the use of cell-free supernatant of bacteria Morganella morganii for synthesizing copper nanoparticles and analysing its larvicidal activity on mosquito larvae. A colour change from blue to pickle green specifies the synthesis production of CuNPs. The nanoparticles were characterized using ultraviolet–visible spectrophotometry, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). XRD pattern shows the major peaks, viz. (111), (200) and (220). SEM analysis shows that nanoparticles are in a spherical shape with a small percentage of elongated particles and size of about 13.5 ± 0.6 nm. A UV–Vis absorption peak was observed at 540 nm. FTIR analysis of nanoparticles exhibits functional groups such as aromatics, alkanes, ethers and alkyl halides. In EDaX (energy-dispersive X-ray) analysis, the peak signal confirms the presence of copper atoms that bound to the synthesized nanoparticles. The synthesized copper nanoparticles were tested for larvicidal efficacy at different time intervals. The above result shows that the copper nanoparticles produce increased toxicity in a time- and dose-dependent manner. An antibacterial and antifungal activity was tested against clinical pathogens, and the highest zone of inhibition was found to be in E. coli, B. subtilis, A. niger, M. anisopliae and Verticillium sp. This study shows that CuNPs possess a good antimicrobial and insecticidal activity which can be explored for commercial purpose.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali, M.A.; Rehman, I.; Iqbal, A.; Din, S.; Rao, A.Q.; Latif, A.; Husnain, T.: Nanotechnology, a new frontier in Agriculture. Adv. Life Sci. 1(3), 129–138 (2014)
Bhushan, B. (ed.): Springer Handbook of Nanotechnology. Springer, Berlin (2017)
Saeed, K.; Khan, I.; Khan, I.: Nanoparticles: Properties, applications and toxicities. Arab. J. Chem. 18 (2017).
Singh, P.; Kim, Y.J.; Zhang, D.; Yang, D.C.: Biological synthesis of nanoparticles from plants and microorganisms. Trends Biotechnol. 34(7), 588–599 (2016)
Li, Q.; Mahendra, S.; Lyon, D.Y.; Brunet, L.; Liga, M.V.; Li, D.; Alvarez, P.J.: Antimicrobial nanomaterials for water disinfection and microbial control: potential applications and implications. Water Res. 42(18), 4591–4602 (2008)
Dizaj, S.M.; Lotfipour, F.; Barzegar-Jalali, M.; Zarrintan, M.H.; Adibkia, K.: Antimicrobial activity of the metals and metal oxide nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 44, 278–284 (2014)
Besinis, A.; De Peralta, T.; Handy, R.D.: The antibacterial effects of silver, titanium dioxide and silica dioxide nanoparticles compared to the dental disinfectant chlorhexidine on Streptococcus mutans using a suite of bioassays. Nanotoxicology 8(1), 1–16 (2014)
Shafie, A.; Roslan, M.A.; Ngui, R.; Lim, Y.A.L.; Sulaiman, W.Y.W.: Mosquito biology and mosquito-borne disease awareness among island communities in Malaysia. J. Am. Mosq. Contr. A. 32(4), 273–282 (2016)
Soni, N.; Prakash, S.: Synthesis of gold nanoparticles by the fungus Aspergillus niger and its efficacy against mosquito larvae. Rep. Parasitol. 2, 1–7 (2012)
Hazra, D.K.; Samanta, A.; Karmakar, R.; Sen, K.; Bakshi, P.: Mosquito vector management knowledge, attitude, practices and future of user and environment friendly new generation botanical mosquitocide formulations: a review. Int. J. Chem. Sci. 5(3), 32–37 (2017)
Hemingway, J.; Beaty, B.J.; Rowland, M.; Scott, T.W.; Sharp, B.L.: The Innovative Vector Control Consortium: improved control of mosquito-borne diseases. Trends Parasitol. 22(7), 308–312 (2006)
Benelli, G.: Plant-mediated synthesis of nanoparticles: a newer and safer tool against mosquito-borne diseases? Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 6(4), 353–354 (2016)
Stadler, T.; Buteler, M.; Weaver, D.K.: Novel use of nanostructured alumina as an insecticide. Pest Manag. Sci 66(6), 577–579 (2010)
Gawande, M.B.; Goswami, A.; Felpin, F.X.; Asefa, T.; Huang, X.; Silva, R.; Varma, R.S.: Cu and Cu-based nanoparticles: synthesis and applications in catalysis. Chem. Rev. 116(6), 3722–3811 (2016)
Kruk, T.; Szczepanowicz, K.; Stefarska, J.; Socha, R.P.; Warszynski, P.: Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of monodisperse copper nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B 128, 17–22 (2015)
Emelianoff, V.; Le Brun, N.; Pagès, S.; Stock, S.P.; Tailliez, P.; Moulia, C.; Sicard, M.: Isolation and identification of entomopathogenic nematodes and their symbiotic bacteria from Herault and Gard (Southern France). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 98(2), 211–217 (2008)
Glaeser, S.P.; Tobias, N.J.; Thanwisai, A.; Chantratita, N.; Bode, H.B.; Kampfer, P.: Photorhabdus luminescens subsp. namnaonensis subsp. nov., isolated from Heterorhabditis baujardi nematodes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 67(4), 1046–1051 (2017)
Eski, A.; Cakici, F.O.; Gullu, M.; Muratoglu, H.; Demirbag, Z.; Demir, I.: Identification and pathogenicity of bacteria in the Mediterranean corn borer Sesamia nonagrioides Lefebvre (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Turk. J. Biol. 39(1), 31–48 (2015)
Vyas, R.V.; Patel, B.; Maghodia, A.; Patel, D.J.: Significance of metabolites of native Xenorhabdus, a bacterial symbiont of Steinernema, for suppression of collar rot and root knot diseases of groundnut. Indian J. Biotechnol. 7, 371–377 (2008)
Nishiwaki, H.; Ito, K.; Shimomura, M.; Nakashima, K.; Matsuda, K.: Insecticidal bacteria isolated from predatory larvae of the antlion species Myrmeleon bore (Neuroptera: Myrmeleontidae). j. Inverte. Pathol. 96(1), 80–88 (2007)
Webster, J.; Chen, G.; Hu, K.: Bacterial metabolites. Entomopathog. Nematol. 99–114
Condorelli, G.G.; Costanzo, I.L.; Fragala, I.L.; Giuffrida, S.; Ventimiglia, G.: A single photochemical route for the formation of both copper nanoparticles and patterned nanostructured films. J. Mater. Chem. 13(10), 2409–2411 (2003)
Boemare, N.; Givaudan, A.; Brehelin, M.; Laumond, C.: Symbiosis and pathogenicity of nematode-bacterium complexes. Symbiosis (1997)
Prabhu, R.; Thenmozhi, R.; Thajuddin, N.; Suganthy, N.: In vitro assessment of antimicrobial, antibiofilm and larvicidal activities of bioactive nickel metal organic framework. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 56, 101560 (2020)
Arjunan, N.K.; Murugan, K.; Rejeeth, C.; Madhiyazhagan, P.; Barnard, D.R.: Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles for the control of mosquito vectors of malaria, filariasis, and dengue. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 12(3), 262–268 (2012)
Abbott, W.S.: Method of computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. J. Econ. Entomol. 18, 265–266 (1925)
Magaldi, S.; Mata-Essayag, S.; De Capriles, C.H.; Perez, C.; Colella, M.T.; Olaizola, C.; Ontiveros, Y.: Well diffusion for antifungal susceptibility testing. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 8(1), 39–45 (2004)
Manjusha, R.; Kora, A.J.; Arunachalam, J.: Superior bactericidal activity of SDS capped silver nanoparticles: synthesis and characterization. Mater. Sci. Eng., C 29(7), 2104–2109 (2009)
Aktar, W.; Sengupta, D.; Chowdhury, A.: Impact of pesticides use in agriculture: their benefits and hazards. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2(1), 1–12 (2009)
Sharma, P.; Mohan, L.; Srivastava, C.N.: Larvicidal potential of Neriumindicum and Thujaoriertelis extracts against malaria and Japanese encephalitis vector. J. Environ. Biol. 26(4), 657–660 (2005)
Lees, R.S.; Knols, B.; Bellini, R.; Benedict, M.Q.; Bheecarry, A.; Bossin, H.C.: Review: improving our knowledge of male mosquito biology in relation to genetic control programmes. Acta Trop. 132S, S2–S11 (2014)
Martinez, H.; Toledo, J.; Liedo, P.; Mateo, M.: Survey of heritable endosymbionts in Southern Mexico populations of the fruit fly species Anastrepha striata and A. ludens. Curr. Micro. Boil. 65, 711–718 (2012)
Cox, C.R.; Gilmore, M.S.: Native microbial colonization of Drosophila melanogaster and its use as a model of Enterococcus faecalis pathogenesis. Infect. Immun. 75, 1565–1576 (2007)
Eivazian Kary, N.; Mohammadi, D.; Girling, R.: New reports on dixenic associations between the symbionts of entomopathogenic nematodes, Photorhabdus and Xenorhabdus, and non-symbiotic bacteria. J. Crop Prot. 6(4), 497–511 (2017)
Borkow, G.; Gabbay, J.: Copper as a biocidal tool. Curr. Med. Chem. 12(18), 2163–2175 (2005)
Krithiga, N.; Jayachitra, A.; Rajalakshmi, A.: Synthesis, characterization and analysis of the effect of copper oxide nanoparticles in biological systems. An Indian J. Nano. Sci. 1(1), 6–15 (2013)
SubhankariIpsaNayak, P.L.: Antimicrobial activity of copper nanoparticles synthesised by ginger (Zingiber officinale) extract. World J. Nano Sci. Technol. 2(1), 10–13 (2013)
Yoon, K.; Byeon, J.H.; Park, J.; Hwang, J.: Susceptibility constants of E. coli and Bacillus subtilis to Ag and Cu nanoparticles. Sci. Total Environ. 373, 572–575 (2007)
Das, D.; Nath, B.C.; Phukon, P.; Dolui, S.K.: Synthesis and evaluation of antioxidant and antibacterial behavior of CuO nanoparticles. Colloid Surf. B. 101, 430–433 (2013)
Nabila, M.I.; Kannabiran, K.: Biosynthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of copper oxide nanoparticles (CuO NPs) from actinomycetes. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 15, 56–62 (2018)
Jayaseelan, C.; Rahuman, A.A.; Kirthi, A.V.; Marimuthu, S.; Santhoshkumar, T.; Bagavan, A.; Rao, K.B.: Novel microbial route to synthesize ZnO nanoparticles using Aeromonas hydrophila and their activity against pathogenic bacteria and fungi. Spectrochim Acta A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 90, 78–84 (2012)
Ramaswamy, S.V.P.; Narendhran, S.; Sivaraj, R.: Potentiating effect of ecofriendly synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using brown alga: antimicrobial and anticancer activities. Bull. Mater. Sci. 39(2), 361–364 (2016)
Saad, E.L.; Salem, S.S.; Fouda, A.; Awad, M.A.; El-Gamal, M.S.; Abdo, A.M.: New approach for antimicrobial activity and bio-control of various pathogens by biosynthesized copper nanoparticles using endophytic actinomycetes. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 11(3), 262–270 (2018)
El-Sadawy, H.A.; El Namaky, A.H.; Hafez, E.E.; Baiome, B.A.; Ahmed, A.M.; Ashry, H.M.; Ayaad, T.H.: Silver nanoparticles enhance the larvicidal toxicity of Photorhabdus and Xenorhabdus bacterial toxins: an approach to control the filarial vector, Culex pipiens. Trop. Biomed. 35(2), 392–407 (2018)
Ghorbani, H.R.; Mehr, F.P.; Poor, A.K.: Extracellular synthesis of copper nanoparticles using culture supernatants of Salmonella typhimurium. Orient. J. Chem. 31(1), 527–529 (2015)
Jang, G.G.; Jacobs, C.B.; Gresback, R.G.; Ivanov, I.N.; Meyer, H.M.; Kidder, M.: Size tunable elemental copper nanoparticles: extracellular synthesis by thermoanaerobic bacteria and capping molecules. J. Mater. Chem. C. 3, 644–650 (2015)
Rahman, A.; Ismail, A.; Jumbianti, D.; Magdalena, S.; Sudrajat, H.: Synthesis of copper oxide nano particles by using Phormidium cyanobacterium. Indones. J. Chem. 9(3), 355–360 (2009)
Parikh, R.Y.; Singh, S.; Prasad, B.L.V.; Patole, M.S.; Sastry, M.; Shouche, Y.S.: Extracellular synthesis of crystalline silver nanoparticles and molecular evidence of silver resistance from Morganella sp. towards understanding biochemical synthesis mechanism. Chem. Bio. Chem. 9(9), 1415–1422 (2008)
Selvan, S.M.; Anand, K.V.; Govindaraju, K.; Tamilselvan, S.; Kumar, V.G.; Subramanian, K.S.; Raja, K.: Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles and mosquito larvicidal activity against dengue, zika and chikungunya causing vector Aedes aegypti. IET Nanobiotechnol. 12(8), 1042–1046 (2018)
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the Department of Biotechnology, Periyar University, Salem, Tamil Nadu, India, for providing the infrastructural facility for carrying out this research work. We would also acknowledge the instrument support from DST-FIST (SR/FIST/LSI-673/2016), Department of Biotechnology, Periyar University, Salem.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lalitha, K., Kalaimurgan, D., Nithya, K. et al. Antibacterial, Antifungal and Mosquitocidal Efficacy of Copper Nanoparticles Synthesized from Entomopathogenic Nematode: Insect–Host Relationship of Bacteria in Secondary Metabolites of Morganella morganii sp. (PMA1). Arab J Sci Eng 45, 4489–4501 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04487-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04487-6