Abstract
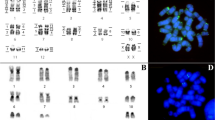
The presnt study provides illustated characterization of the chromosomal rearrangement of the male dusky langur (Trachypithecus obscurus Ried, 1837; TOB) using Chromosome Painting technique. Ear tissues specimen collection was kindly provided by Songkla Zoo, Songkla province, Thailand. The fibroblast cells were cultured and cryopreserved after that all 24 Human chromosome-specific probes (22 autosomes, X and Y) were hybridized in situ to the TOB mitotic cells and captured and analyzed by GENUS software. The results showed that the TOB chromosomes were highly rearranged compared to the 30 conserved regions of human chromosomes of different sizes. Majority, TOB chromosomes, such as TOB chromosomes 1, 2, 3, 4, 9, 11, 12, 13, 15, 17, 18, 20, 21, X and Y which were homologous to only one human chromosome, are conserved.. Some of those were constituted of regions being two TOB chromosomes that composed one of HSA homologous regions or one TOB chromosomes homologous to two human chromosomes. This is the first report of molecular cytogenetics on TOB using all 24 human chromosome-specific probes. The chromosome mappingis useful for a comparisonof Langur either in the same or other genus that had been reported to elucidate and clarify evolutionary relationship of primates shared by the same common ancestor.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bigoni F, Houck ML, Ryder OA, Wienberg J, Stanyon R. Chromosome painting shows that Pygathrix nemaeus has the most basal karyotype among Asian Colobinae. Int J Primatol. 2004;25(3):679–88.
Bigoni F, Koehler U, Stanyon R, Ishida T, Wienberg J. Fluorescence in situ hybridization establishes homology between human and silvered leaf monkey chromosomes, reveals reciprocal translocations between chromosomes homologous to human Y/5, 1/9, and 6/16, and delineates an X1X2Y1Y2/X1X1X2X2 sex-chromosome system. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1997;102(3):315–27.
Bigoni F, Stanyon R, Koehler U, Morescalchi AM, Wienberg J. Mapping homology between human and black and white colobine monkey chromosomes by fluorescent in situ hybridization. Am J Primatol. 1997;42(4):289–98.
Bigoni F, Stanyon R, Wimmer R, Schempp W. Chromosome painting shows that the proboscis monkey (Nasalis larvatus) has a derived karyotype and is phylogenetically nested within Asian Colobines. Am J Primatol. 2003;60(3):85–93.
Bigoni F. Omologia cromosomica e filogenesi nei primati: analisi molecolare e citogenetica. Genoa: University of Genoa; 1995.
Boonratana R, Traeholt CBW, HtunS. Trachypithecus obscurus. IUCN Red List Threat Species eT2203 9A9349397, 2008.
Brandon-Jones D, Eudey AA, Geissmann T, Groves CP, Melnick DJ, Morales JC, Shekelle M, Stewart CB. Asian primate classification. Int J Primatol. 2004;25(1):97–164.
Chen Y, Luo L, Shan X, Cao X. No TitlePrimates chromosome in China. Beijing: Science Publishing House; 1981.
Chiarelli B. Comparative morphometric analysis of primate chromosomes. III. The chromosomes of the genera Hylobates Colobus and Presbytis. Caryologia. 1963;16(3):637–48.
Dutrillaux B, Webb G, Muleris M, Couturier J, Butler R. Chromosome study of Presbytis cristatus: presence of a complex Y-autosome rearrangement in the male. InAnnales de genetique. 1984;27(1):148–53.
Groves CP. Primate taxonomy. Washington, DC: Smithsonian Institution; 2001.
Groves CP. The forgotten leaf-eaters, and phylogeny of the colobinae. Old World Monkeys, 1970.
Jauch A, Wienberg J, Stanyon R, Arnold N, Tofanelli S, Ishida T, Cremer T. Reconstruction of genomic rearrangements in great apes and gibbons by chromosome painting. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 1992;89(18):8611–5.
Kampiranont A. Cytogenetics. Department of Genetics, Faculty of Science, Kasetsart University, Bangkok, Thailand.; 2003
Koehler U, Arnold N, Wienberg J, Tofanelli S, Stanyon R. Genomic reorganization and disrupted chromosomal synteny in the siamang (Hylobates syndactylus) revealed by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1995;97(1):37–47.
Koehler U, Bigoni F, Wienberg J, Stanyon R. Genomic reorganization in the concolor gibbon (Hylobates concolor) revealed by chromosome painting. Genomics. 1995;30(2):287–92.
Krishna-Murthy DS. Giemsa banding pattern in the langur monkey Presbytis entellus entellus (Dufresne). Curr Sci. 1979;48:180–1.
Napier JR, Napier PH, Napier JR. The natural history of the primates. Cambridge: MIT Press; 1985.
Napier JR, Napier PH. Handbook of living primates. New York: Academic Press; 1967.
Nie W, Liu R, Chen Y, Wang J, Yang F. Mapping chromosomal homologies between humans and two langurs (Semnopithecus francoisi and S phayrei) by chromosome painting. Chromosome Res: Int J Mol Supramol Evol Aspects Chromosome Biol. 1998;6(6):447–53.
Oates JF, Davies AG. Colobine monkeys: their ecology, behaviour, and evolution. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 1994.
Oates JF. The diversity of living colobines. Colobine Monkeys Their Ecol Behav Evol. 1994;45:45–73.
Ponsa M, De Boer LE, Egozcue J. Banding patterns of the chromosomes of Presbytis cristatus pyrrhus and P. obscurus. Am J Primatol. 1983;4(2):165–9.
Rooney DE, Czepulkowski B. Human cytogenetics: constitutional analysis: a practical approach, vol. 1. New York: Oxford University Press; 2001.
Sangpakdee W, Tanomtong A, Monthatong M, Pinthong K, Gomontean B, Nie W. The homology and relationship of human (Homo sapiens) chromosomes 1, 19 and dusky langur (Trachypithacus obscurus) chromosomes 6, 8 demonstrated with chromosome painting. Cytologia. 2008;73(4):349–55.
Sharma GP, Sobti RC, Gupta CM. An analysis of chromosomes in three primates from India. J Hum Evol. 1973;2(4):283–7.
Stanyon R, Wienberg J, Romagno D, Bigoni F, Jauch A, Cremer T. Molecular and classical cytogenetic analyses demonstrate an apomorphic reciprocal chromosomal translocation in Gorilla gorilla. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1992;88(2):245–50.
Ushijima RN, Shininger FS, Grand TI. Chromosome complements of two species of primates: Cynopithecus niger and Presbytis entellus. Science. 1964;146(3640):78–9.
Vogel C, Winkler P. NoLangurs and Colobi. In Grzimek’s encyclopedia of mammals title. vol. 2. McGraw-Hill, London; 1990.
Wang XP, Yu L, Roos C, Ting N, Chen CP, Wang J, Zhang YP. Phylogenetic relationships among the colobine monkeys revisited: new insights from analyses of complete mt genomes and 44 nuclear non-coding markers. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(4):e36274.
Wienberg J, Jauch A, Stanyon R, Cremer T. Molecular cytotaxonomy of primates by chromosomal in situ suppression hybridization. Genomics. 1990;8(2):347–50.
Wienberg J, Stanyon R, Jauch A, Cremer T. Homologies in human and Macasa fuscata chromosomes revealed by in situ suppression hybridization with human chromosome specific DNA libraries. Chromosoma. 1992;101(5–6):265–70.
Yu D, Yang F, Liu R. A comparative chromosome map between human and Hylobates hoolock built by chromosome painting. Yi chuan xue bao = Acta genetica Sinica. 1997;24(5):417–23.
Acknowledgements
The financial support from Toxic Substances in Livestock and Aquatic Animals Research Group, Khon Kaen University is gratefully acknowledged.
Funding
Research Fund for Toxic Substances in Livestock and Aquatic Animals Research Group, Khon Kaen University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
Under the permission of animal for scientific purposes code U1-05662-2559.
Consent to participate
Yes.
Consent for publication
Yes.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Corresponding Editor: Rabondra Nath Chatterjee.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thongnetr, W., Sangpakdee, W., Tanomtong, A. et al. The chromosomal homology between dusky langur (Trachypithecus obscurus Ried, 1837) and human (Homo sapiens) revealed by chromosome painting. Nucleus 65, 233–237 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13237-021-00381-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13237-021-00381-0