Abstract
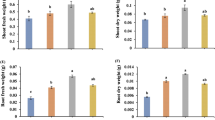
The aim of the present study was to compare the benefit to soybean in terms of phosphate solubilization and host plant growth under salt stress of the endophytic fungi Fusarium verticillioides RK01 and Humicola sp. KNU01. Endophyte F. verticillioides RK01 increased phosphate solubilization significantly more than Humicola sp. KNU01, as confirmed by increasing activities of acid phosphatase (1.0 U−1 g fwt), alkaline phosphatase (2.1 U−1 g fwt ) and fungal biomass (4.6 g), with a concurrent decrease in tri-calcium phosphate concentration in the culture medium. In a plant growth evaluation study, 0.1 M NaCl was added to pots containing soybean plants pre-treated with fungi. The salt-affected plants exhibited stunted growth due to a lower concentration of protein and higher level of lipid peroxidation than their controls. F. verticillioides RK01 and Humicola sp. KNU01 isolates significantly increased shoot length (7.3 % and 2.5 %) and protein content (59.1 % and 65.1 %), while inhibiting the lipid peroxidation level in salt stressed plants. Moreover, carotenoids, the activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase were lower in plants affected by salinity than in non-stressed plants, whereas Humicola sp. KNU01 fungal association significantly mitigated oxidative stress by enhancing carotenoids (24.1 %) and SOD activity (61.2 %). F. verticillioides RK01 also triggered SOD activity to prevent oxidative damage. In addition, salt stress caused an increase of absicsic acid (ABA) in soybean plants, and F. verticillioides RK01 colonization effectively reduced ABA content in stressed plants. Salicylic acid (SA) is another plant hormone that was present in lower amounts in stressed plants, but the endophytic (F. verticillioides RK01 and Humicola sp. KNU01) fungal association increased SA content in salt-affected plants. The results of the present study indicate that the efficient phosphate solubilizing endophytic fungi F. verticillioides RK01 was more favorable to protect soybean plants against oxidative damage than Humicola sp. KNU01.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi H (1983) Catalase. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methods of enzymatic analysis. 3rd edn. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp 273–286
Alonso-Ramirez A, Rodriguez D, Reyes D, Jimenez JA, Nicolas G, Lopez-Climent M, Gomez-Cadenas A, Nicolas C (2009) Evidence for a role of gibberellins in salicylic acid-modulated early plant responses to abiotic stress in Arabidopsis seeds. Plant Physiol 150:1335–1344
Alvarez M, Huygens D, Olivares E, Saavedra I, Alberdi M, Valenzuela E (2009) Ectomycorrhizal fungi enhance nitrogen and phosphorus nutrition of Nothofagus dombeyi under drought conditions by regulating assimilative enzyme activities. Physiol Plant 136(4):426–436
Auge RM (2001) Water relations, drought and vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. Mycorrhiza 11:3–42
Borde M, Dudhane M, Jite P (2011) Growth photosynthetic activity and antioxidant responses of mycorrhizal and non-mycorrhizal bajra (Pennisetum glaucum) crop under salinity stress condition. Crop Prot 30:265–271
Bradford MM (1976) Rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72: 248–254
Dodd IC, Perez-Alfocea F (2012) Microbial amelioration of crop salinity stress. J Exp Bot 63:3415–3428
Enyedi AJ, Yalpani N, Silverman P, Raskin I (1992)Localization, conjugation, and function of salicylic acid in tobacco during the hypersensitive reaction to tobacco mosaic virus.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:2480–2484
Evelin H, Kapoor R, Giri B (2009) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in alleviation of salt stress: a review. Ann Bot 104:1263–1280
Fateh SH, Fagan WF (2002) Fungal endophytes: common host plant symbionts but uncommon mutualists. Integ Comp Biol 42:360–368
Fenice M, Selbman L, Federici F, Vassilev N (2000) Application of encapsulated Penicillium variabile P16 in solubilization of rock phosphate. Bioresour Technol 73:157–162
Ghorbanli M, Ebrahimzadeh H, Sharifi M (2004) Effects of NaCl and mycorrhizal fungi on antioxidative enzymes in soybean. Biol Plant 48:575–581
Gill SS, Tuteja N (2010) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 48:909–930
Giri B, Kapoor R, Mukerji KG (2003) Influence of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and salinity on growth, biomass and mineral nutrition of Acacia auriculiformis. Biol Fertil Soils 38:170–175
Hajiboland R, Aliasgharzadeh N, Laiegh SF, Poschenrieder C (2010) Colonization with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi improves salinity tolerance of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) plants. Plant Soil 331:313–327
Hariprasad P, Niranjana SR (2009) Isolation and characterization of phosphate solubilizing rhizobacteria to improve plant health of tomato. Plant Soil 316:13–24
Ikawa T, Nisizawa K, Miwa T (1964) Specificities of several acid phosphatases from plant sources. Nature 203:939–940
Imlay JA, Linn S (1988) DNA damage and oxygen radical toxicity. Science 240:1302–1309
Jahromi F, Aroca R, Porcel R, Ruiz-Lozano JM (2008) Influence of salinity on the in vitro development of Glomus intraradices and on the in vivo physiological and molecular esponses of mycorrhizal lettuce plants. Microb Ecol 55:45–53
Jha BK, Pragash MG, Cletus J, Raman G, Sakthivel N (2009) Simultaneous phosphate solubilization potential and antifungal activity of new fluorescent pseudomonad strains, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, P. plecoglossicida and P. mosselii. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25:573–581
Jiang M, Zhang J (2001) Effect of abscisic acid on active oxygen species, antioxidative defence system and oxidative damage in leaves of maize seedlings. Plant Cell Pysiol 42:1265–1273
Kang SC, Hat CG, Lee TG, Maheshwari DK (2002) Solubilization of insoluble inorganic phosphates by a soil-inhabiting fungus Fomitopsis sp. PS 102. Curr Sci 82:439–442
Khan AL, Hamayun M, Kim YH, Kang SM, Lee IJ (2011a) Ameliorative symbiosis of endophyte (Penicillium funiculosum LHL06) under salt stress elevated plant growth of Glycine max L. Plant Physiol Biochem 49:852–861
Khan AL, Hamayun M, Ahmad N, Hussain J, Kang SM, Kim YH, Adnan M, Tang DS, Waqas M, Radhakrishnan R, Hwang YH, Lee IJ (2011b) Salinity stress resistance offered by endophytic fungal interaction between Penicillium minioluteum LHL09 and Glycine max L. J Microbiol Biotechnol 21:893–902
Khan AL, Hamayun M, Ahmad N, Waqas M, Kang SM, Kim YH, Lee IJ (2011c) Exophiala sp. LHL08 reprograms Cucumis sativus to higher growth under abiotic stresses. Physiol Plant 143:329–343
Khan AL, Hamayun M, Waqas M, Kang SM, Kim YH, Kim DH, Lee IJ (2012) Exophiala sp.LHL08 association gives heat stress tolerance by avoiding oxidative damage to cucumber plants. Biol Fertil Soils 48:519–529
Khan MS, Zaidi A, Wani PA (2007) Role of phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms in sustainable agriculture—a review. Agron Sustain Dev 27:29–43
King JE (1936) The colorimetric determination of phosphorus. Biochem J 26:292–297
Kohler J, Hernandez JA, Caravaca F, Roldan A (2009) Induction of antioxidant enzymes is involved in the greater effectiveness of a PGPR versus AM fungi with respect to increasing the tolerance of lettuce to severe salt stress. Environ Exp Bot 65:245–252
Marklund S, Marklund G (1974) Involvement of the superoxide anion radical in the autoxidation of pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase. Eur J Biochem 47:469–474
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxidation in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Ann Biochem 95:351–358
Pandey A, Das N, Kumar B, Rinu K, Trivedi P (2008) Phosphate solubilization by Penicillium spp. isolated from soil samples of Indian Himalayan region. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24:97–102
Pradhan N, Sukla LB (2005) Solubilization of inorganic phosphates by fungi isolated from agriculture soil. Afr J Biotechnol 5(10):850–854
Porcel R, Aroca R, Ruiz-Lozano JM (2012) Salinity stress alleviation using arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. A review. Agron Sustain Dev 32:181–200
Poss JA, Pond E, Menge JA, Harrell WM (1985) Effect of salinity on mycorrhizal onion and tomato in soil with and without additional phosphate. Plant Soil 88:307–319
Qi Q, Rose PA, Abrams GD, Taylor DC, Abrams SR, Cutler AJ (1998) (+)-Abscisic acid metabolism, 3-ketoacyl-coenzyme A synthase gene expression, and very long-chain monounstaurated fatty acid biosynthesis in Brassica napus embryos. Plant Physiol 117:979–987
Radhakrishnan R, Leelapriya T, Ranjithakumari BD (2012) Effects of pulsed magnetic field treatment of soybean seeds on calli growth, cell damage, and biochemical changes under salt stress. Bioelectromagnetics 33:670–681
Radhakrishnan R, Lee IJ (2013) Spermine promotes acclimation to osmotic stress by modifying antioxidant, abscisic acid, and jasmonic acid signals in soybean. J Plant Growth Regul 32:22–30
Reyes I, Bernier L, Simard RR, Tanguay P, Antoun H (1999) Characteristics of phosphate solubilization by an isolate of a tropical Penicillium rugulosum and two UV-induced mutants. FEMS Microb Ecol 28:291–295
Richardson AE (2001) Prospects for using soil microorganism to improve the acquisition of phosphate by plant. Aust J Plant Physiol 28:897–906
Seskar M, Shulaev V, Raskin I (1998)Endogenous methyl salicylate in pathogen-inoculated tobacco plants.Plant Physiol 116:387–392
Sharma P, Dubey RS (2005) Drought induces oxidative stress and enhances the activities of antioxidant enzymes in growing rice seedlings. Plant Growth Regul 46:209–221
Sharma YK, Leon J, Raskin I, Davis KR (1996) Ozoneinduced responses in Arabidopsis thaliana: the role of salicylic acid in the accumulation of defense-related transcripts and induced resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:5099–5104
Sheng M, Tang M, Chen H, Yang B, Zhang F, Huang Y (2009) Influence of arbuscular mycorrhizae on the root system of maize plants under salt stress. Can J Microbiol 55:879–886
Siefermann-Harms D (1987) The light-harvesting and protective functions of carotenoids in photosynthetic membranes. Physiol Plant 69:561–568
Sohrabi Y, Heidari G, Weisany W, Ghasemi-Golezani K, Mohammadi K (2012a) Changes of antioxidative enzymes, lipid peroxidation and chlorophyll content in chickpea types colonized by different Glomus species under drought stress. Symbiosis 56:5–18
Sohrabi Y, Heidari G, Weisany W, Ghasemi-Golezani K, Mohammadi K (2012b) Some physiological responses of chickpea cultivars to arbuscular mycorrhiza under drought stress. Russ J Plant Physiol 59:708–716
Vassilev N, Vassileva M, Fenice M, Federici F (2001) Immobilized cell technology applied in solubilization of insoluble inorganic (rock) phosphates and P plant acquisition. Bioresour Technol 79:263–271
Vassilev N, Vassileva M, Nikolaeva I (2006) Simultaneous P-solubilizing and biocontrol activity of microorganisms: potentials and future trends. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 71:137–144
Wu QS, Zon YN, Liu W, Ye XE, Zai HE, Zhao LJ (2010) Alleviation of salt stress in citrus seedlings inoculated with mycorrhiza: changes in leaf antioxidant defense systems. Plant Soil Environ 56:470–475
Wu QS, Zou YN, Huang YM (2013) The arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Diversispora spurca ameliorates effects of waterlogging on growth, root system architecture and antioxidant enzyme activities of citrus seedlings. Fungal Ecol 6:37–43
Yates IE, Widstrom NW, Bacon CW, Glenn A, Hinton DM, Sparks D, Jaworski AJ (2005) Field performance of maize grown from Fusarium verticillioides-inoculated seed. Mycopathologia 159:65–73
Zhang J, Jia W, Yang J, Ismail AM (2006) Role of ABA in integrating plant responses to drought and salt stresses. Field Crop Res 97:111–119
Acknowledgment
This research work was supported financially by the Eco-Innovation Project, Korea Ministry of the Environment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Radhakrishnan, R., Khan, A.L., Kang, S.M. et al. A comparative study of phosphate solubilization and the host plant growth promotion ability of Fusarium verticillioides RK01 and Humicola sp. KNU01 under salt stress. Ann Microbiol 65, 585–593 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-014-0894-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-014-0894-z